A cetoacidose diabética (CAD) e o estado de hiperglicemia hiperosmolar ( HH HH Hereditary hemochromatosis (HH) is an autosomal recessive disorder most often associated with hfe gene mutations. Patients have increased iron intestinal absorption and iron deposition in several organs, such as the liver, heart, skin, and pancreas. The clinical presentation includes the triad of cirrhosis, diabetes, and skin bronzing. Hereditary Hemochromatosis) são complicações graves e agudas da diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus. A cetoacidose diabética é caracterizada por hiperglicemia e cetoacidose devido a uma deficiência absoluta de insulina. O estado hiperglicémico hiperosmolar ocorre devido a uma deficiência relativa de insulina ou resistência à insulina, levando a hiperglicemia grave e a uma osmolalidade sérica elevada. Fatores desencadeantes incluem insulinoterapia inadequada, infeção subjacente, doença médica concomitante ou efeitos colaterais de medicamentos. Os pacientes com cetoacidose diabética tendem a ser mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome jovens, com diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus tipo 1, apresentando sintomas agudos, incluindo dor abdominal, náuseas e vómitos. Por outro lado, os pacientes com HH HH Hereditary hemochromatosis (HH) is an autosomal recessive disorder most often associated with hfe gene mutations. Patients have increased iron intestinal absorption and iron deposition in several organs, such as the liver, heart, skin, and pancreas. The clinical presentation includes the triad of cirrhosis, diabetes, and skin bronzing. Hereditary Hemochromatosis são geralmente mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome velhos, com diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus tipo 2 e com início gradual dos sintomas, incluindo alteração do estado mental e alterações neurológicas. Os dois conjuntos de pacientes terão poliúria, polidipsia e evidência de desidratação grave. O diagnóstico é baseado em valores laboratoriais que demonstram hiperglicemia com cetoacidose ou hiperosmolalidade. O tratamento envolve re-hidratação agressiva de líquidos, terapia de insulina e correção de distúrbios eletrolíticos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
A cetoacidose diabética (CAD) e o estado de hiperglicemia hiperosmolar ( HH HH Hereditary hemochromatosis (HH) is an autosomal recessive disorder most often associated with hfe gene mutations. Patients have increased iron intestinal absorption and iron deposition in several organs, such as the liver, heart, skin, and pancreas. The clinical presentation includes the triad of cirrhosis, diabetes, and skin bronzing. Hereditary Hemochromatosis) são complicações graves e agudas da diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus.
A resposta normal ao aumento da glicose sérica envolve a libertação de insulina pelas células beta pancreáticas. Isto leva a..:
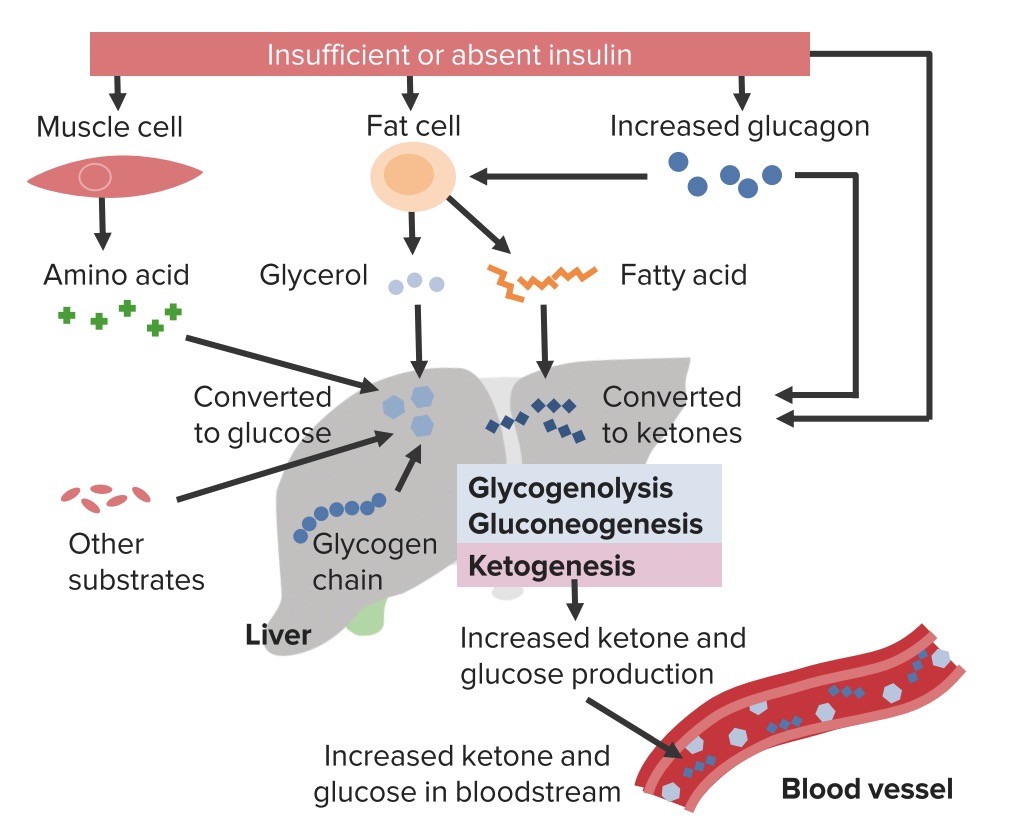
Fisiopatologia da cetoacidose diabética
Imagem de Lecturio.| Teste de laboratório | Cetoacidose diabética | Estado hiperglicémico hiperosmolar |
|---|---|---|
| Glucose Glucose A primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. It is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. Lactose Intolerance sérica | > 250 mg/dL | > 600 mg/dL |
| Bicarbonato sérico | ↓↓ | > 18 mEq/L |
| Anion gap Anion gap Metabolic Acidosis | ↑ | Geralmente normal |
| Osmolalidade do soro | Variável | > 320 mOsm/L |
| Cetonas séricas (beta-hidroxibutirato, acetona) | Positivo | Minimamente positivo ou negativo |
| Cetonas urinárias | Positivo | Minimamente positivo ou negativo |
| Gasimetria arterial |
|
pH pH The quantitative measurement of the acidity or basicity of a solution. Acid-Base Balance: > 7.3 |
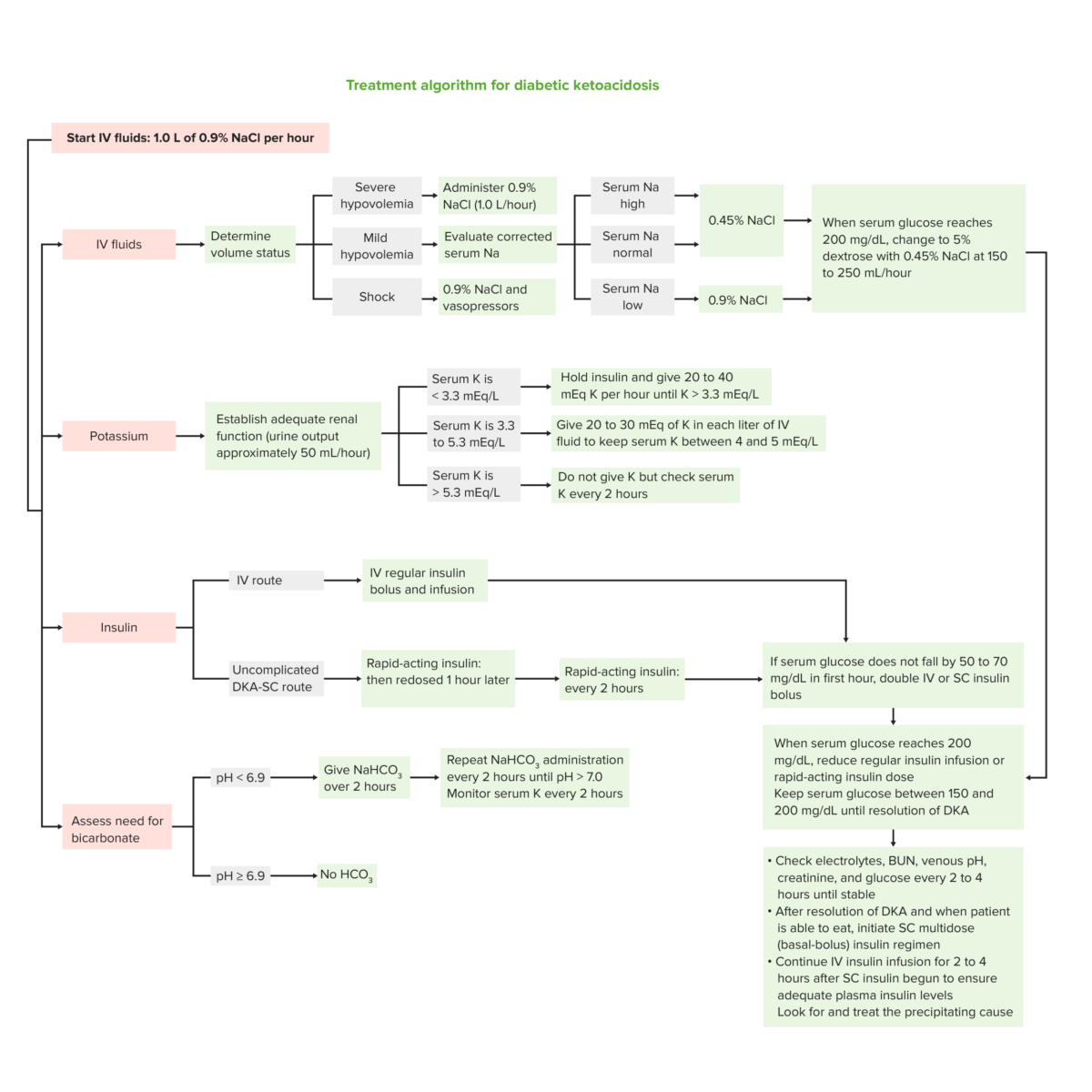
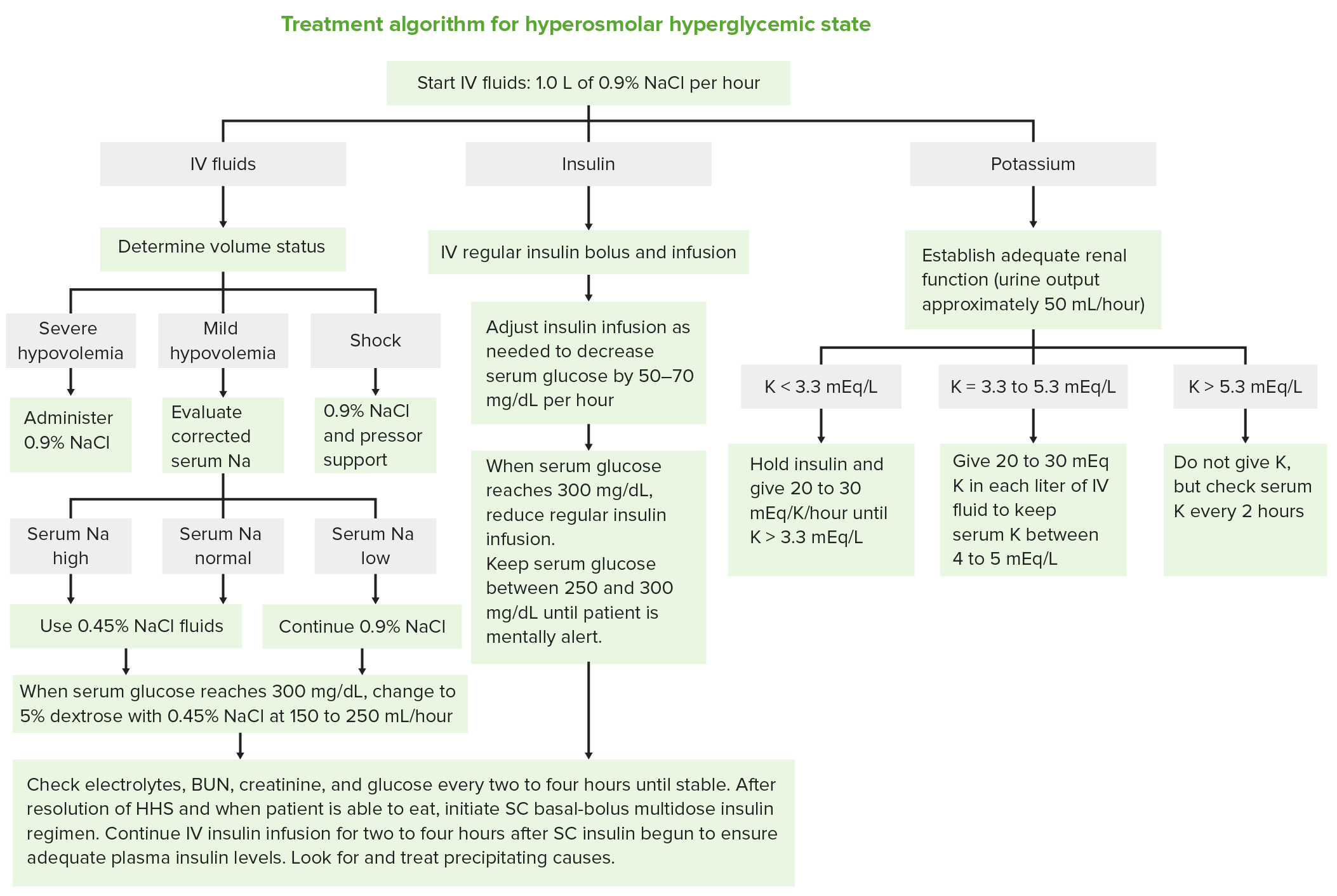
Algoritmo de tratamento do estado hiperglicémico hiperosmolar
Imagem de Lecturio.