Os antiestrogénios são fármacos que diminuem os efeitos estrogénicos no corpo. Os antiestrogénios incluem moduladores seletivos do recetor de estrogénio ( SERMs SERMs A structurally diverse group of compounds distinguished from estrogens by their ability to bind and activate estrogen receptors but act as either an agonist or antagonist depending on the tissue type and hormonal milieu. They are classified as either first generation because they demonstrate estrogen agonist properties in the endometrium or second generation based on their patterns of tissue specificity. Antiestrogens, pela sigla em inglês), reguladores negativos seletivos do recetor de estrogénio ( SERDs SERDs Antiestrogens, pela sigla em inglês), inibidores da aromatase Aromatase An enzyme that catalyzes the desaturation (aromatization) of the ring a of C19 androgens and converts them to C18 estrogens. In this process, the 19-methyl is removed. This enzyme is membrane-bound, located in the endoplasmic reticulum of estrogen-producing cells of ovaries, placenta, testes, adipose, and brain tissues. Aromatase is encoded by the cyp19 gene, and functions in complex with NADPH-ferrihemoprotein reductase in the cytochrome p450 system. Adipose Tissue: Histology e vários outros, que incluem fármacos que suprimem as gonadotrofinas ou neutralizam os efeitos do estrogénio. Os antiestrogénios são mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome frequentemente usados no tratamento do cancro de mama, mas também tratam a puberdade precoce, a ginecomastia, a infertilidade anovulatória e várias queixas ginecológicas. Os efeitos adversos incluem ondas de calor Calor Inflammation, eventos tromboembólicos venosos, perda de densidade mineral óssea e eventos cardiovasculares isquémicos. Os antiestrogénios estão contraindicados em indivíduos com reações de hipersensibilidade conhecidas e gravidez.
Last updated: May 19, 2022
Devem ser consideradas várias classes principais de antiestrogénios. Os fármacos protótipos em cada classe estão assinalados com um asterisco (*).
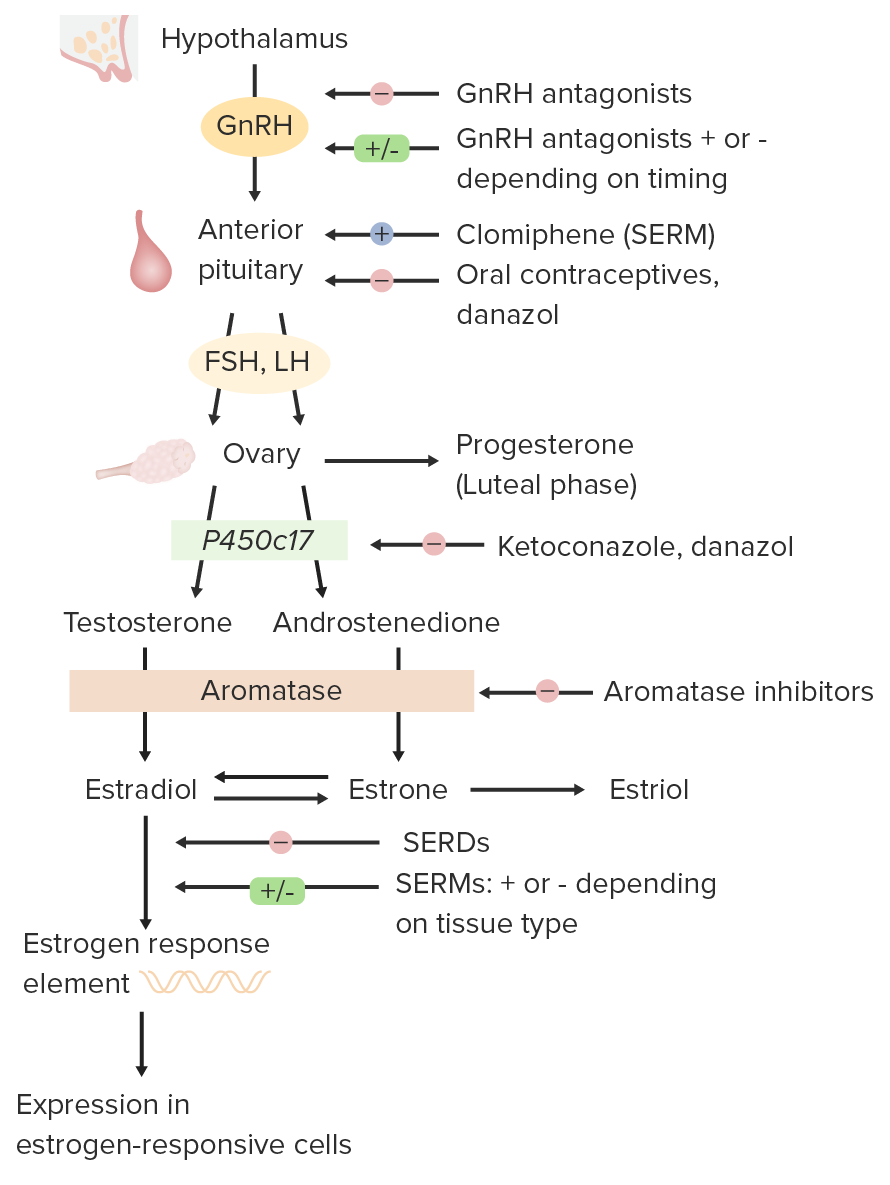
Visão geral dos antiestrogénios e das suas ações associadas
GnRH: hormona libertadora de gonadotrofinas
SERM: moduladores seletivos do recetor de estrogénio
FSH: hormona folículo estimulante
LH: hormona luteinizante
SERD: reguladores negativos seletivos do recetor de estrogénios
Tamoxifeno, raloxifeno, ospemifeno, bazedoxifeno e citrato de clomifeno:
Fulvestranto:
Os SERMs SERMs A structurally diverse group of compounds distinguished from estrogens by their ability to bind and activate estrogen receptors but act as either an agonist or antagonist depending on the tissue type and hormonal milieu. They are classified as either first generation because they demonstrate estrogen agonist properties in the endometrium or second generation based on their patterns of tissue specificity. Antiestrogens atuam como agonistas do estrogénio em alguns tecidos e antagonistas do estrogénio noutros.
| Tecido | Efeitos normais do estrogénio | Efeitos dos SERMs SERMs A structurally diverse group of compounds distinguished from estrogens by their ability to bind and activate estrogen receptors but act as either an agonist or antagonist depending on the tissue type and hormonal milieu. They are classified as either first generation because they demonstrate estrogen agonist properties in the endometrium or second generation based on their patterns of tissue specificity. Antiestrogens |
|---|---|---|
| Mama |
|
Efeitos antagonistas :
|
| Hipotálamo e hipófise | Inibe a libertação de GnRH e das gonadotrofinas (ou seja, FSH FSH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates gametogenesis and the supporting cells such as the ovarian granulosa cells, the testicular sertoli cells, and leydig cells. Fsh consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle, LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle) | Efeitos antagonistas : ↓ inibição de FSH FSH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates gametogenesis and the supporting cells such as the ovarian granulosa cells, the testicular sertoli cells, and leydig cells. Fsh consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle/ LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle → ↑ libertação de FSH FSH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates gametogenesis and the supporting cells such as the ovarian granulosa cells, the testicular sertoli cells, and leydig cells. Fsh consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle/ LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle → ↑ desenvolvimento folicular e ovulação |
| Osso | ↑ DMO | Efeitos agonistas : protege contra a perda de DMO no estado hipoestrogénico da menopausa |
| Útero |
|
|
| Fígado |
|
Efeitos agonistas :
|
Efeitos fisiológicos dos SERDs SERDs Antiestrogens:
O fulvestrant Fulvestrant An estradiol derivative and estrogen receptor antagonist that is used for the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive, locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer. Antiestrogens possui efeitos puramente antiestrogénicos nos tecidos. Os principais efeitos fisiológicos incluem:
As indicações primárias para cada medicamento são indicadas com um asterisco (*):
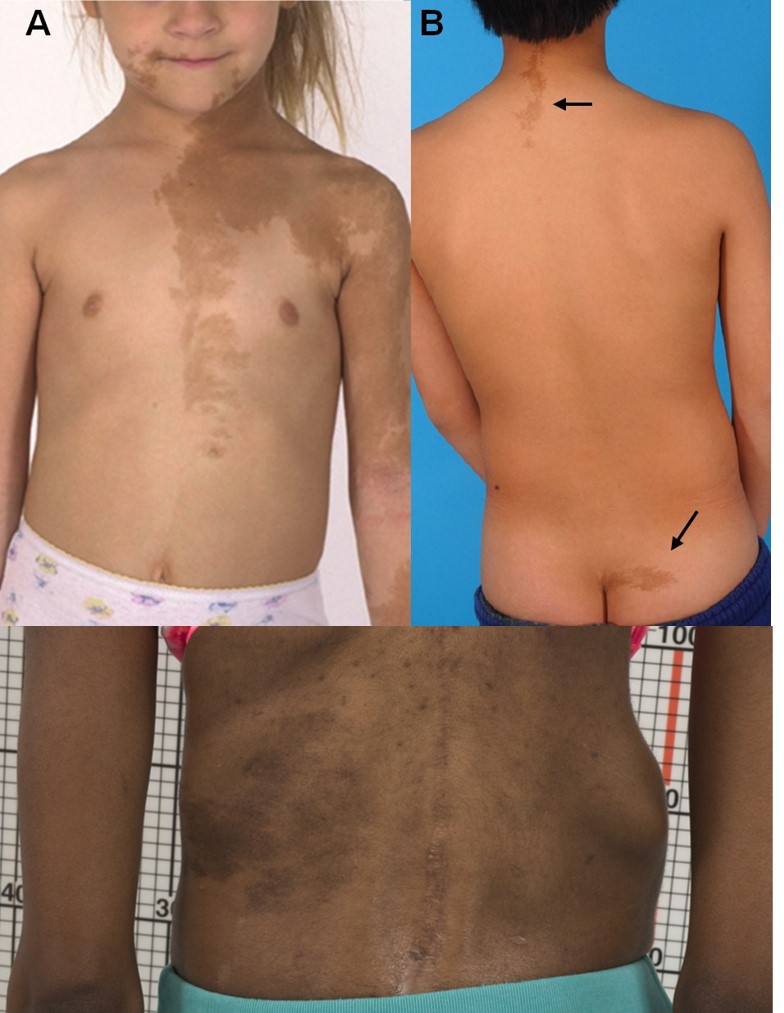
Síndrome de McCune-Albright:
A síndrome de McCune-Albright apresenta uma tríade clássica. A tríade inclui puberdade precoce periférica, displasia fibrosa do osso e hiperpigmentação da pele com manchas café com leite, que é frequentemente encontrada na nuca e na pregas das nádegas.
Os inibidores de aromatase Aromatase An enzyme that catalyzes the desaturation (aromatization) of the ring a of C19 androgens and converts them to C18 estrogens. In this process, the 19-methyl is removed. This enzyme is membrane-bound, located in the endoplasmic reticulum of estrogen-producing cells of ovaries, placenta, testes, adipose, and brain tissues. Aromatase is encoded by the cyp19 gene, and functions in complex with NADPH-ferrihemoprotein reductase in the cytochrome p450 system. Adipose Tissue: Histology impedem a conversão de testosterona em estrogénio, que é um processo conhecido como aromatização. Os fármacos da classe incluem o anastrozol, o letrozol e o exemestano. Estes fármacos são mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome frequentemente usados no tratamento do cancro da mama na pós-menopausa.
Anastrozol, Letrozol:
Exemestano:
Leuprolida:
Ganirelix Ganirelix Antiestrogens, Elagolix Elagolix Antiestrogens:
| Fármaco | Classe do fármaco | Mecanismo de ação | Indicações | Notas |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moduladores seletivos de recetores de estrogénio ( SERMs SERMs A structurally diverse group of compounds distinguished from estrogens by their ability to bind and activate estrogen receptors but act as either an agonist or antagonist depending on the tissue type and hormonal milieu. They are classified as either first generation because they demonstrate estrogen agonist properties in the endometrium or second generation based on their patterns of tissue specificity. Antiestrogens) | Tamoxifeno |
|
Tratamento do cancro da mama positivo para receptores hormonais em mulheres na pré-menopausa | Aumenta o risco de cancro do endométrio |
| Raloxifeno |
|
Sem efeito significativo no crescimento endometrial | ||
| Reguladores negativos seletivos do recetor de estrogénio ( SERDs SERDs Antiestrogens) | Fulvestrant Fulvestrant An estradiol derivative and estrogen receptor antagonist that is used for the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive, locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer. Antiestrogens | Antagonista competitivo “puro” do estrogénio nos recetores de estrogénio | Cancro da mama |
|
| Inibidores da aromatase Aromatase An enzyme that catalyzes the desaturation (aromatization) of the ring a of C19 androgens and converts them to C18 estrogens. In this process, the 19-methyl is removed. This enzyme is membrane-bound, located in the endoplasmic reticulum of estrogen-producing cells of ovaries, placenta, testes, adipose, and brain tissues. Aromatase is encoded by the cyp19 gene, and functions in complex with NADPH-ferrihemoprotein reductase in the cytochrome p450 system. Adipose Tissue: Histology | Anastrozol | Inibidor da aromatase Aromatase An enzyme that catalyzes the desaturation (aromatization) of the ring a of C19 androgens and converts them to C18 estrogens. In this process, the 19-methyl is removed. This enzyme is membrane-bound, located in the endoplasmic reticulum of estrogen-producing cells of ovaries, placenta, testes, adipose, and brain tissues. Aromatase is encoded by the cyp19 gene, and functions in complex with NADPH-ferrihemoprotein reductase in the cytochrome p450 system. Adipose Tissue: Histology competitivo não esteroide | Cancro da mama em mulheres na pós-menopausa | Os efeitos adversos incluem:
|
| Exemestano | Inibidor irreversível da aromatase Aromatase An enzyme that catalyzes the desaturation (aromatization) of the ring a of C19 androgens and converts them to C18 estrogens. In this process, the 19-methyl is removed. This enzyme is membrane-bound, located in the endoplasmic reticulum of estrogen-producing cells of ovaries, placenta, testes, adipose, and brain tissues. Aromatase is encoded by the cyp19 gene, and functions in complex with NADPH-ferrihemoprotein reductase in the cytochrome p450 system. Adipose Tissue: Histology | |||
| Análogos da hormona libertadora de gonadotrofinas (GnRH) | Leuprolida | Agonista da GnRH → administração contínua suprime a hormona folículo-estimulante ( FSH FSH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates gametogenesis and the supporting cells such as the ovarian granulosa cells, the testicular sertoli cells, and leydig cells. Fsh consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle) e a horomona luteinizante ( LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle) |
|
|
| Elagolix Elagolix Antiestrogens | Antagonista direto da GnRH → suprime FSH FSH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates gametogenesis and the supporting cells such as the ovarian granulosa cells, the testicular sertoli cells, and leydig cells. Fsh consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle/ LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle |
|
As doses são menores → os efeitos colaterais da menopausa são menores do que com leuprolida |