Yersinia Yersinia Yersinia is a genus of bacteria characterized as gram-negative bacilli that are facultative anaerobic with bipolar staining. There are 2 enteropathogenic species that cause yersiniosis, Y. enterocolitica and Y. pseudotuberculosis. Infections are manifested as pseudoappendicitis or mesenteric lymphadenitis, and enterocolitis. Yersinia spp./Yersiniosis es un género de bacterias caracterizadas como bacilos gramnegativos que son anaeróbicos facultativos con tinción bipolar Bipolar Nervous System: Histology. Hay 2 especies enteropatógenas que causan yersiniosis Yersiniosis Yersinia is a genus of bacteria characterized as gram-negative bacilli that are facultative anaerobic with bipolar staining. There are 2 enteropathogenic species that cause yersiniosis, Y. enterocolitica and Y. pseudotuberculosis. Infections are manifested as pseudoappendicitis or mesenteric lymphadenitis, and enterocolitis. Yersinia spp./Yersiniosis, Y. enterocolitica Y. enterocolitica A species of the genus yersinia, isolated from both man and animal. It is a frequent cause of bacterial gastroenteritis in children. Yersinia spp./Yersiniosis y Y. pseudotuberculosis. Las infecciones se manifiestan como pseudoapendicitis o linfadenitis mesentérica y enterocolitis Enterocolitis Inflammation of the mucosa of both the small intestine and the large intestine. Etiology includes ischemia, infections, allergic, and immune responses. Yersinia spp./Yersiniosis. La bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology se transmite a través del consumo de alimentos o agua contaminados. Las manifestaciones incluyen fiebre, dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal y/o diarrea. La enfermedad gastrointestinal suele ser autolimitada. Los LOS Neisseria antibióticos se administran para infecciones graves y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes inmunocomprometidos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
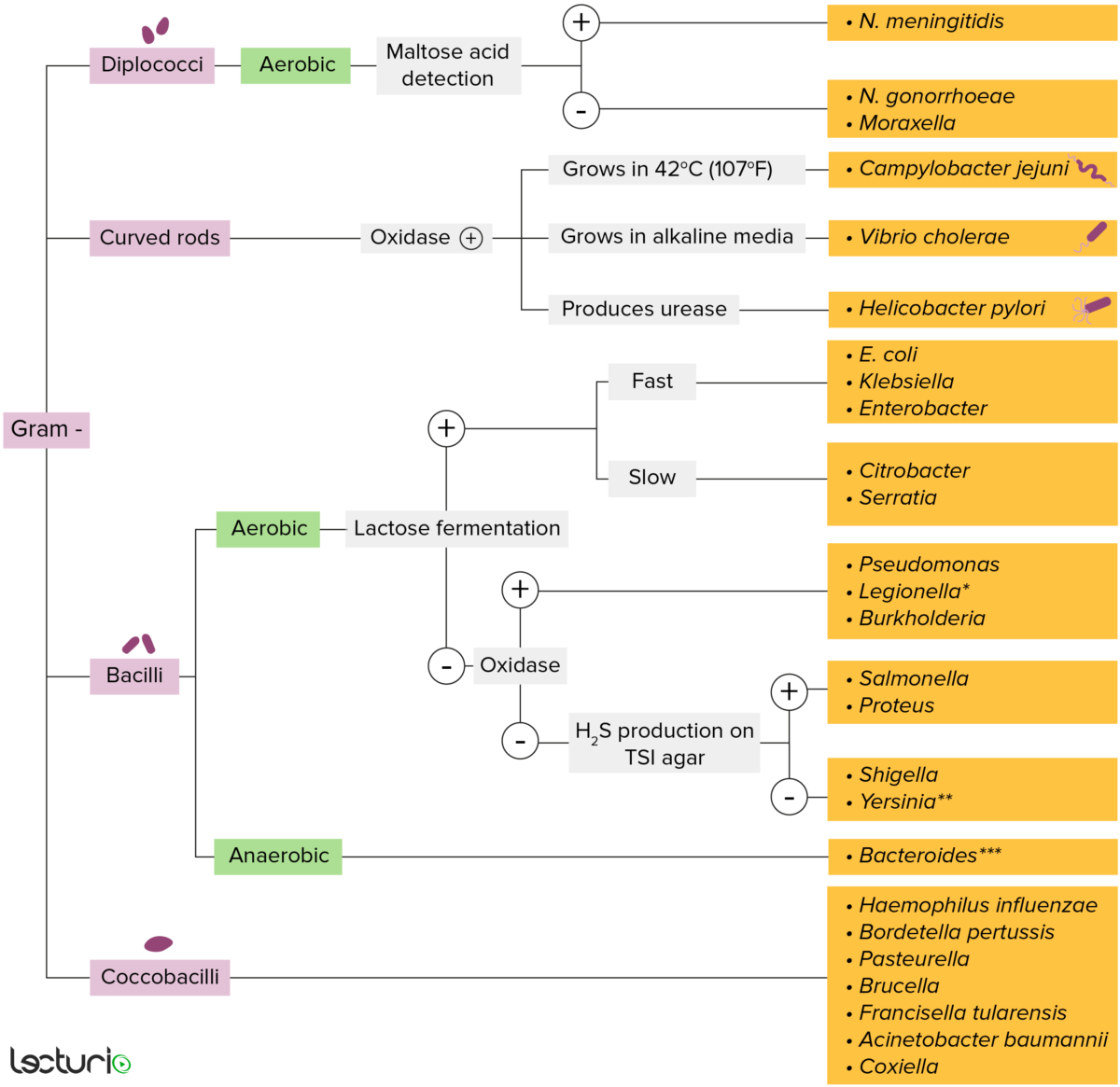
Bacterias gram-negativas:
La mayoría de las bacterias se pueden clasificar de acuerdo con un procedimiento de laboratorio llamado tinción de Gram.
Las bacterias con paredes celulares que tienen una capa delgada de peptidoglicano no retienen la tinción de cristal violeta utilizada en la tinción de Gram. Sin embargo, estas bacterias retienen la contratinción de safranina y, por lo tanto, aparecen de pintadas de color rojo rosado, lo que las convierte en gram negativas. Estas bacterias pueden clasificarse además según su morfología (diplococos, bastoncillos curvos, bacilos y cocobacilos) y su capacidad para crecer en presencia de oxígeno (aeróbicos frente a anaeróbicos). Las bacterias se pueden identificar de manera más estrecha cultivándolas en medios específicos (agar triple azúcar en hierro (TSI, por sus siglas en inglés)) donde se pueden identificar sus enzimas (ureasa, oxidasa) y se puede probar su capacidad para fermentar lactosa.
* Se tiñe mal en la tinción de Gram
** Baston pleomórfico/cocobacilo
*** Requiere medios de transporte especiales
Yersinia Yersinia Yersinia is a genus of bacteria characterized as gram-negative bacilli that are facultative anaerobic with bipolar staining. There are 2 enteropathogenic species that cause yersiniosis, Y. enterocolitica and Y. pseudotuberculosis. Infections are manifested as pseudoappendicitis or mesenteric lymphadenitis, and enterocolitis. Yersinia spp./Yersiniosis causa enfermedad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum animales; los LOS Neisseria seres humanos suelen ser huéspedes incidentales. Tres especies son patógenas para los LOS Neisseria humanos:
Imagen tridimensional (3D) generada por computadora de Y. enterocolitica de forma oblonga
Imagen: “3D computer generated image of Yersinia enterocolita” por Jennifer Oosthuizen. Licencia: Dominio Público.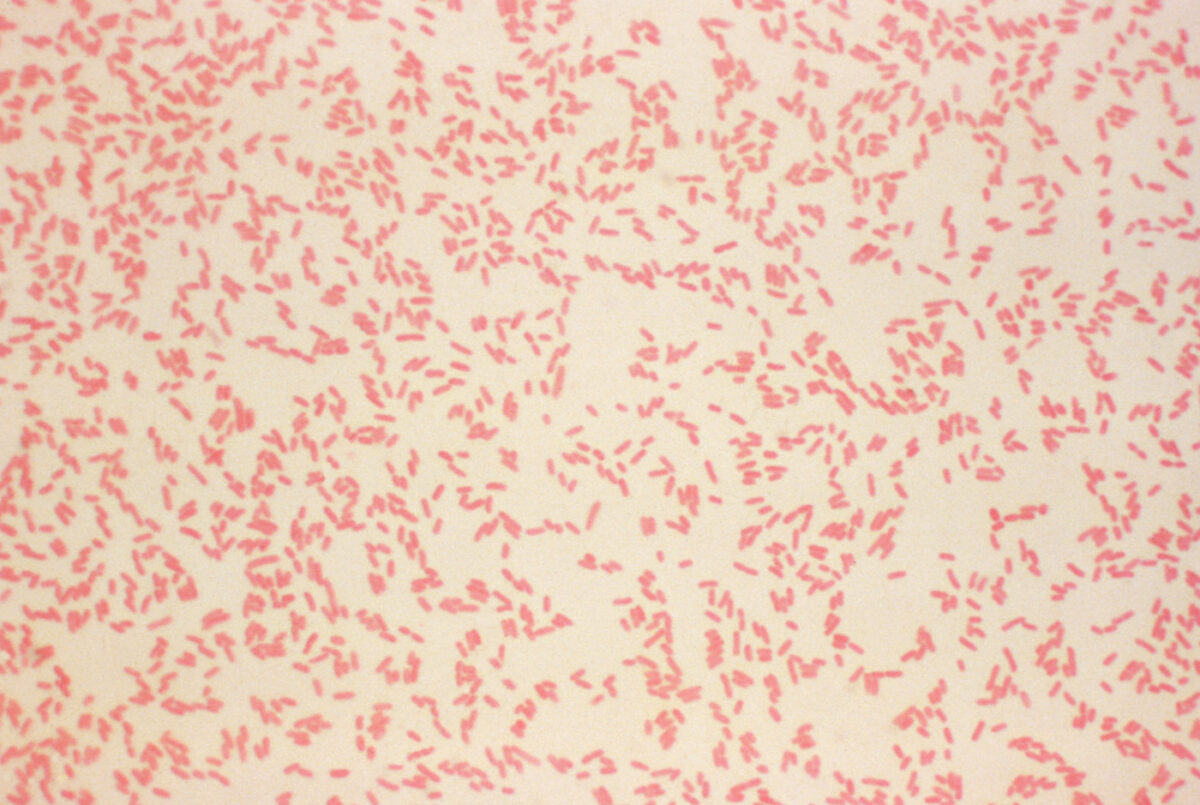
Yersinia enterocolitica: microfotografía de un cultivo teñido con Gram que revela la presencia de numerosas bacterias gramnegativas Y. enterocolitica
Imagen: “Yersinia enterocolitica gram” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público.