El virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la rabia es un virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de ácido ribonucleico (ARN) monocatenario de sentido negativo. Este virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum forma de bala pertenece a la familia Rhabdoviridae Rhabdoviridae A family of bullet-shaped viruses of the order mononegavirales, infecting vertebrates, arthropods, protozoa, and plants. Genera include vesiculovirus; lyssavirus; ephemerovirus; novirhabdovirus; cytorhabdovirus; and nucleorhabdovirus. Rabies Virus y al AL Amyloidosis género Lyssavirus Lyssavirus A genus of the family rhabdoviridae that includes rabies virus and other rabies-like viruses. Rabies Virus. La rabia es una enfermedad prevenible que con mayor frecuencia se transmite a los LOS Neisseria humanos a través de la mordedura de un animal infectado (e.g., murciélagos, mapaches, zorrillos y zorros). Esta enfermedad potencialmente mortal afecta el sistema nervioso central (SNC) y produce manifestaciones neurológicas graves. Hay 5 etapas de la enfermedad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria seres humanos: incubación, pródromo, período neurológico agudo, coma Coma Coma is defined as a deep state of unarousable unresponsiveness, characterized by a score of 3 points on the GCS. A comatose state can be caused by a multitude of conditions, making the precise epidemiology and prognosis of coma difficult to determine. Coma y muerte. El diagnóstico se realiza mediante la detección de anticuerpos, antígenos o ARN viral en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum biopsia de tejido, suero, líquido cefalorraquídeo (LCR) y saliva Saliva The clear, viscous fluid secreted by the salivary glands and mucous glands of the mouth. It contains mucins, water, organic salts, and ptyalin. Salivary Glands: Anatomy. No existe un tratamiento eficaz para la enfermedad sintomática, por lo que la prevención con inmunoglobulina antirrábica humana y la vacunación son el pilar del tratamiento.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025

Identificación de virus de ARN:
Los virus se pueden clasificar de muchas formas. La mayoría de los virus, sin embargo, tendrán un genoma formado por ácido desoxirribonucleico (ADN) o ARN. Los virus del genoma de ARN pueden caracterizarse además por ARN monocatenario o bicatenario. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular (generalmente extraída de la célula huésped). Si la envoltura está ausente, los virus se denominan virus “desnudos”. Los virus con genomas monocatenarios son virus de “sentido positivo” si el genoma se emplea directamente como ARN mensajero (ARNm), que se traduce en proteínas. Los virus monocatenarios de “sentido negativo” emplean la ARN polimerasa dependiente de ARN, una enzima viral, para transcribir su genoma en ARN mensajero.
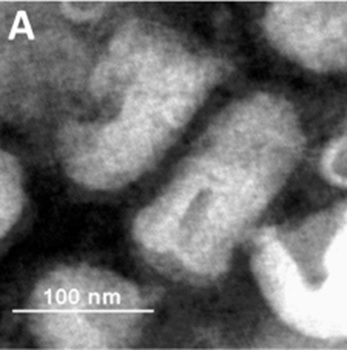
Rabdovirus teñido negativamente
Imagen: “Biological characterization of purified SRV9” por Xu H et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0, recortado por Lecturio.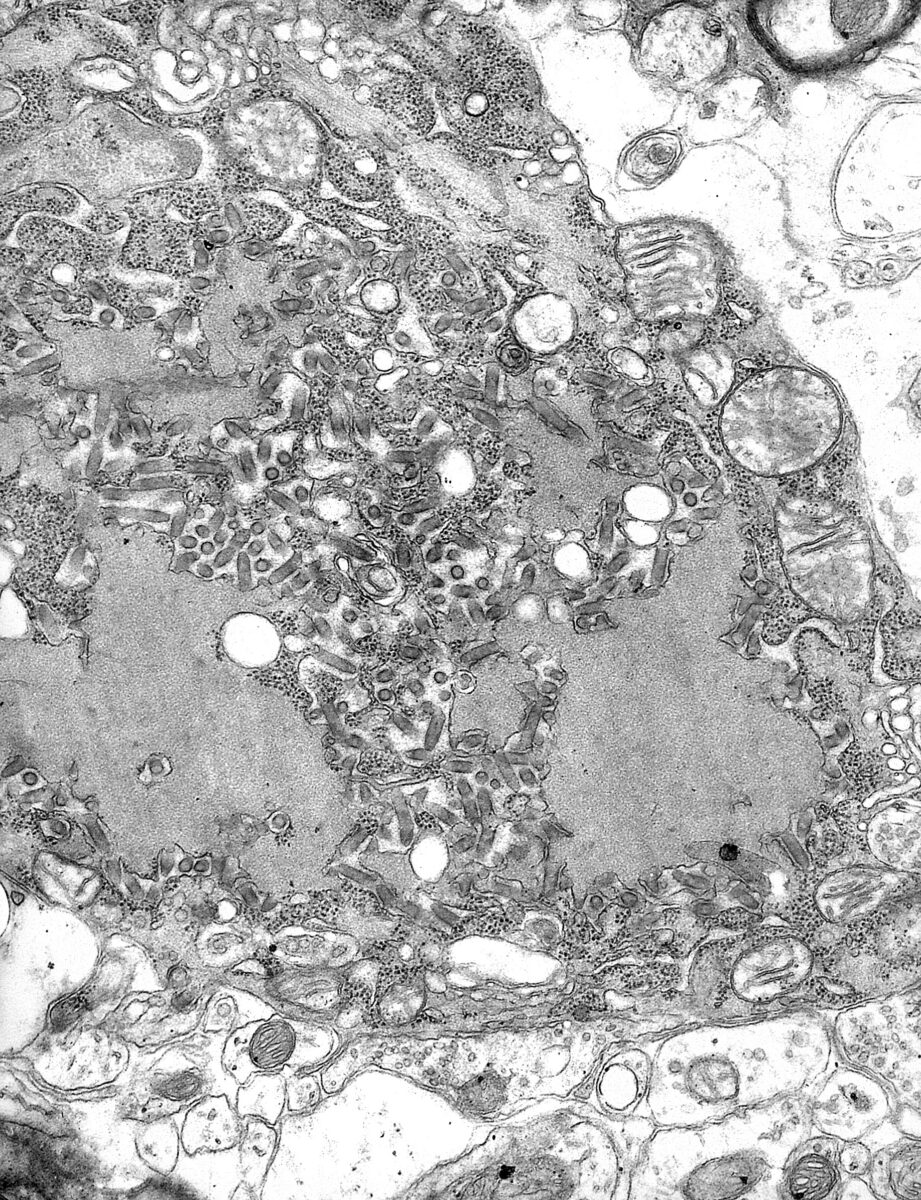
Micrografía electrónica de transmisión con numerosos viriones de la rabia (partículas pequeñas, de color gris oscuro, con forma de varilla o de bala)
Imagen: “TEM micrograph with numerous rabies virions” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público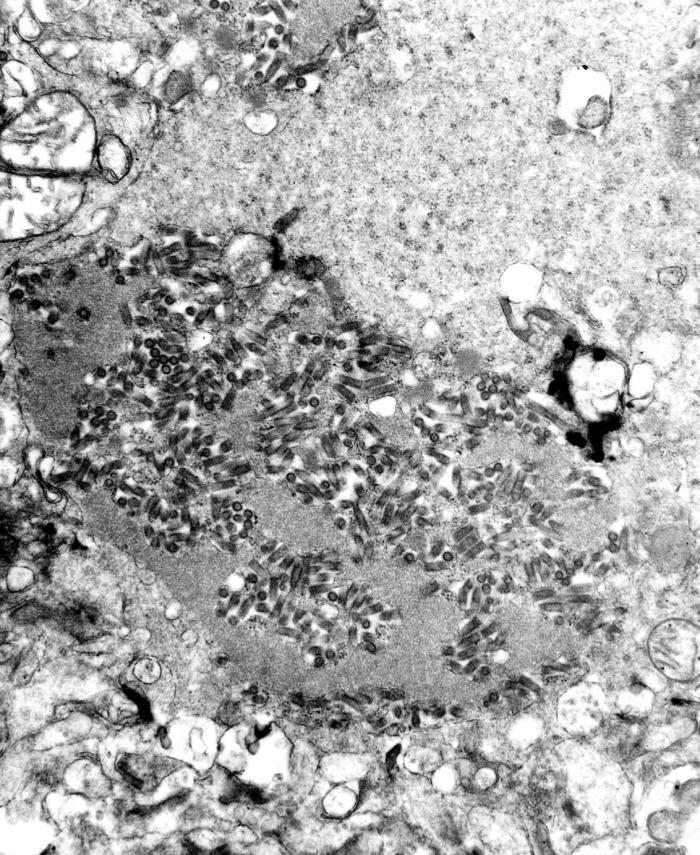
Imagen de microscopio electrónico de transmisión que muestra numerosos viriones de rabia oscuros, con forma de bala, dentro de una muestra de tejido infectado
Imagen: “TEM image revealed the presence of numerous dark, bullet-shaped, rabies virions within an infected tissue sample” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoEl virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la rabia causa la enfermedad de la rabia.
Especies de mamíferos sirven como huéspedes. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum Estados Unidos, estos pueden incluir:
La infección de humanos casi siempre se debe a la mordedura de un mamífero infectado.
La susceptibilidad a infecciones letales está relacionada con:
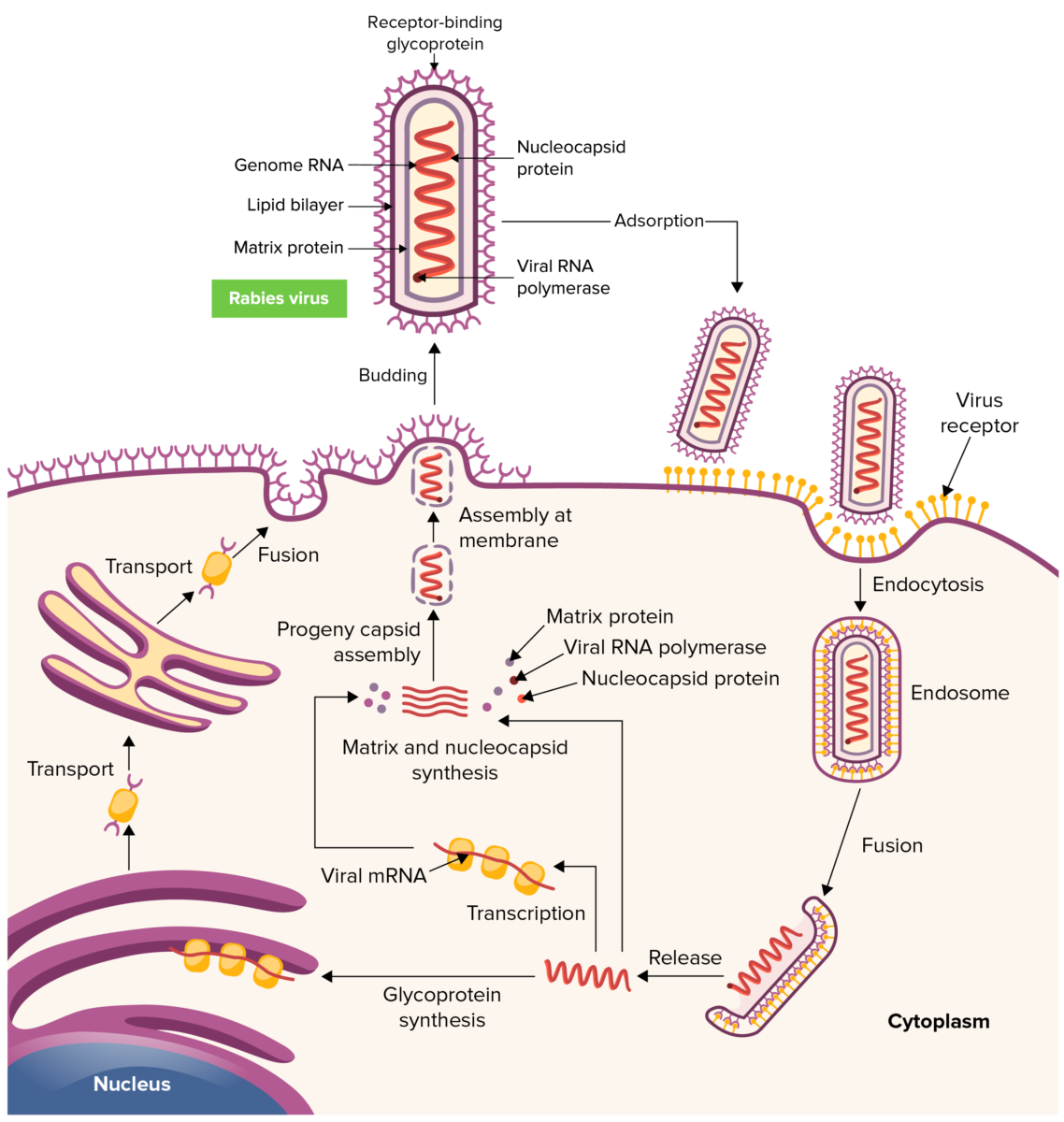
Ciclo de replicación del virus de la rabia
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Se reconocen 5 estadios generales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum humanos: incubación → pródromo → período neurológico agudo → coma Coma Coma is defined as a deep state of unarousable unresponsiveness, characterized by a score of 3 points on the GCS. A comatose state can be caused by a multitude of conditions, making the precise epidemiology and prognosis of coma difficult to determine. Coma → muerte
El período neurológico agudo dura de 2–7 días.
Forma encefalítica (más común):
Forma paralítica:
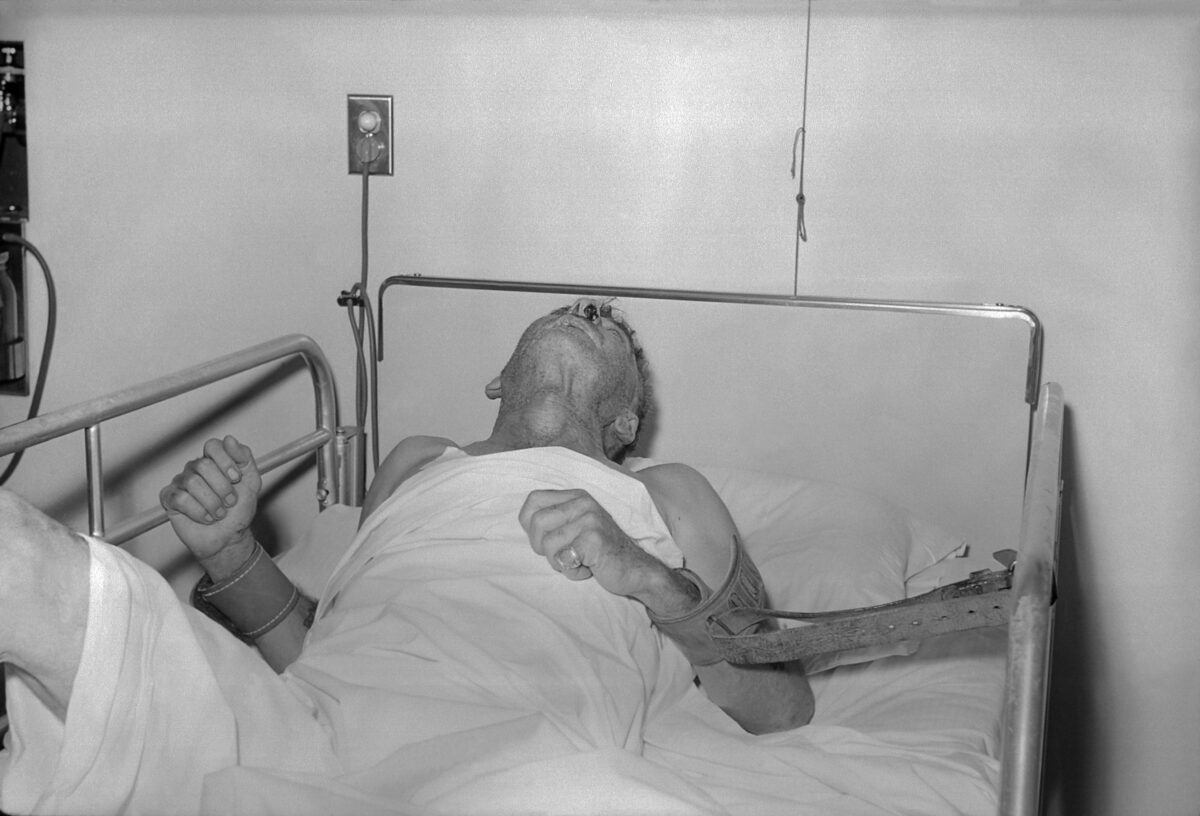
Un hombre con rabia en 1959.
Imagen: “Rabies patient” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoEl diagnóstico debe sospecharse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casos de encefalitis viral inexplicable con antecedentes de mordedura de animal.
Métodos de diagnóstico:
Muestras que se pueden analizar:
No existe un tratamiento eficaz para la rabia sintomática y pocos pacientes sobreviven.
La prevención es el pilar de la atención.