La hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus es una infección del hígado causada por el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus ( HCV HCV Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). Hepatitis C virus is an RNA virus and a member of the genus Hepacivirus and the family Flaviviridae. The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C Virus, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés). El virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus es un virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de ácido ribonucleico (ARN) que pertenece al AL Amyloidosis género Hepacivirus Hepacivirus A genus of flaviviridae causing parenterally-transmitted hepatitis C which is associated with transfusions and drug abuse. Hepatitis c virus is the type species. Hepatitis C Virus y a la familia Flaviviridae Flaviviridae A family of RNA viruses, many of which cause disease in humans and domestic animals. There are three genera flavivirus; pestivirus; and hepacivirus, as well as several unassigned species. Hepatitis C Virus. La infección puede transmitirse a través de sangre o fluidos corporales infecciosos y puede transmitirse durante el parto o a través del uso de drogas intravenosas o las relaciones sexuales. El virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus puede causar tanto hepatitis aguda como crónica, desde una enfermedad leve hasta una grave, de por vida, incluyendo cirrosis hepática y carcinoma hepatocelular. La infección por hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus se diagnostica mediante pruebas para detectar la presencia de anticuerpos y ARN del HCV HCV Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). Hepatitis C virus is an RNA virus and a member of the genus Hepacivirus and the family Flaviviridae. The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C Virus. El tratamiento es de soporte, pero incluye agentes antivirales directos si la infección no se resuelve espontáneamente.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025

Diagrama de flujo de los virus de ARN
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0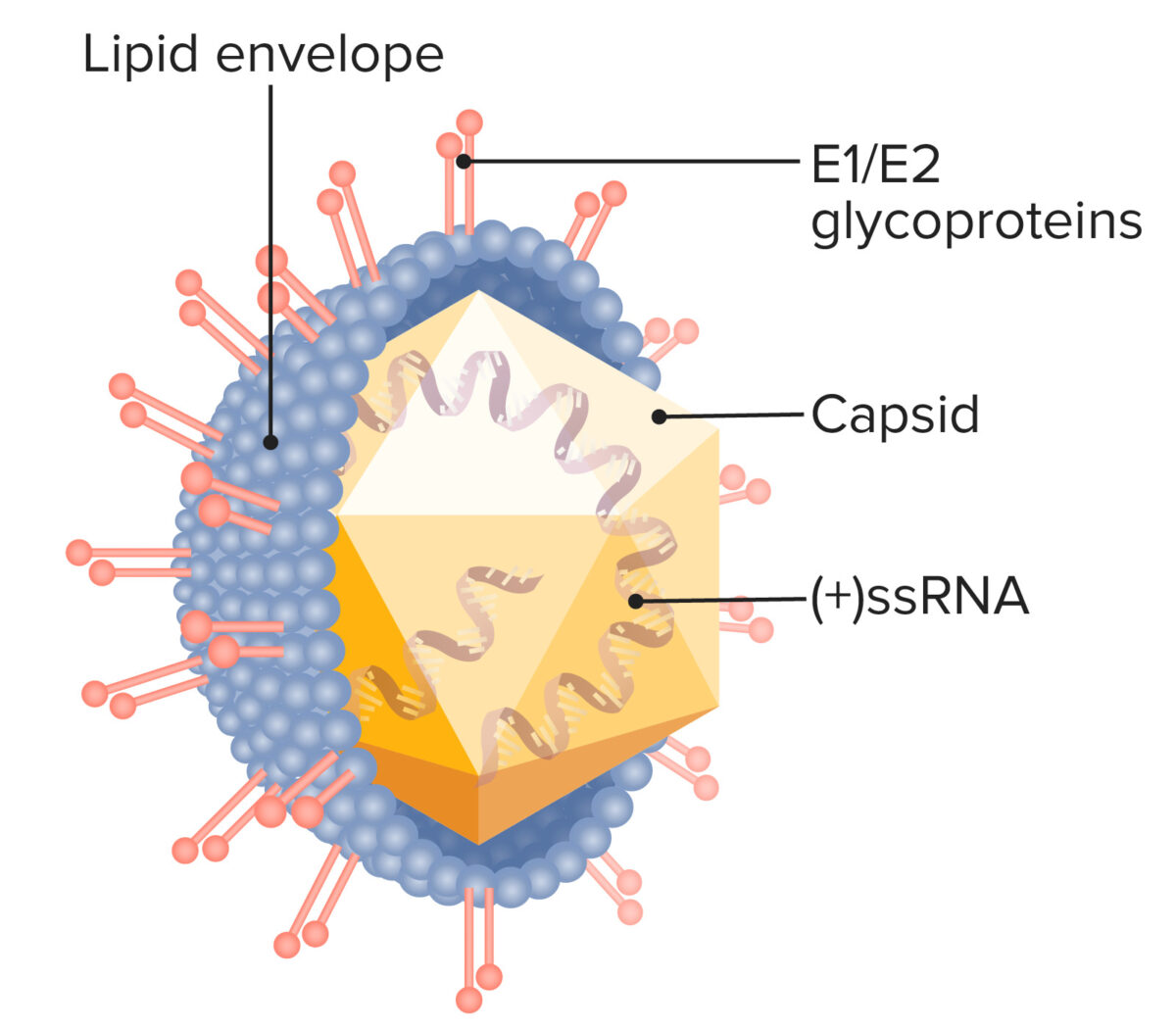
Estructura del virus de la hepatitis C:
Obsérvese el ARN de cadena simple y sentido positivo y las glicoproteínas incrustadas en la envoltura lipídica del virus, que median la entrada en la célula.
Los LOS Neisseria humanos son el único reservorio del virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology. Los LOS Neisseria modos de transmisión incluyen:
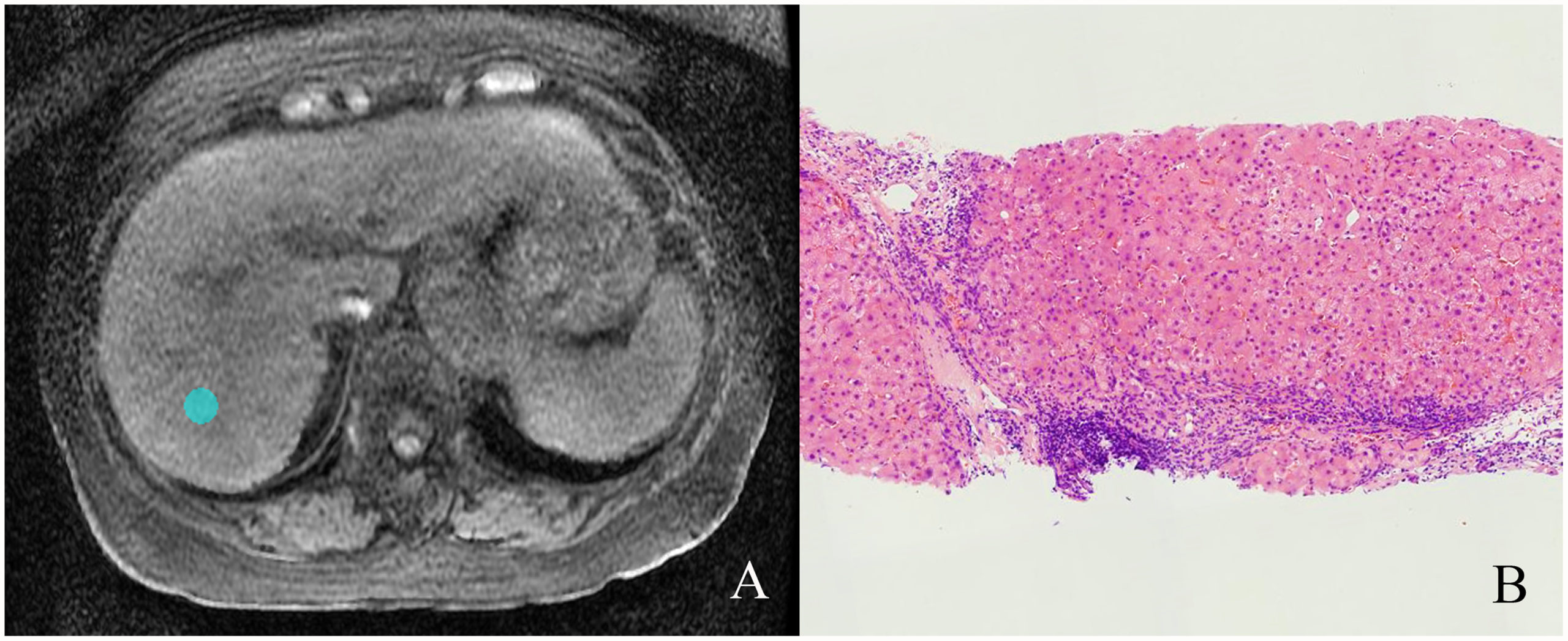
Un individuo con una infección crónica de hepatitis C:
A) RM que muestra fibrosis hepática
B) Biopsia hepática que muestra fibrosis hepática en estadio 4 y actividad necroinflamatoria de grado 2
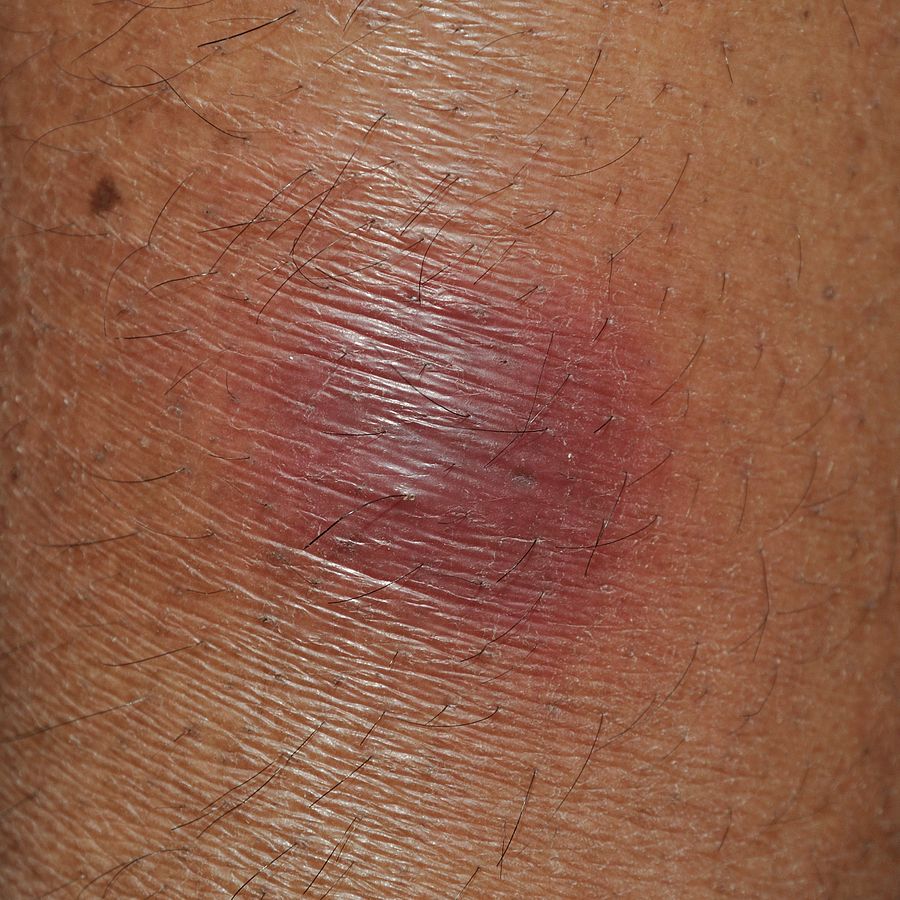
Un individuo con eritema nodoso debido a una infección crónica de hepatitis C
Imagen: “Erythema nodosum – Kolkata 2012-01-03 7753” por Biswarup Ganguly. Licencia: CC BY 3.0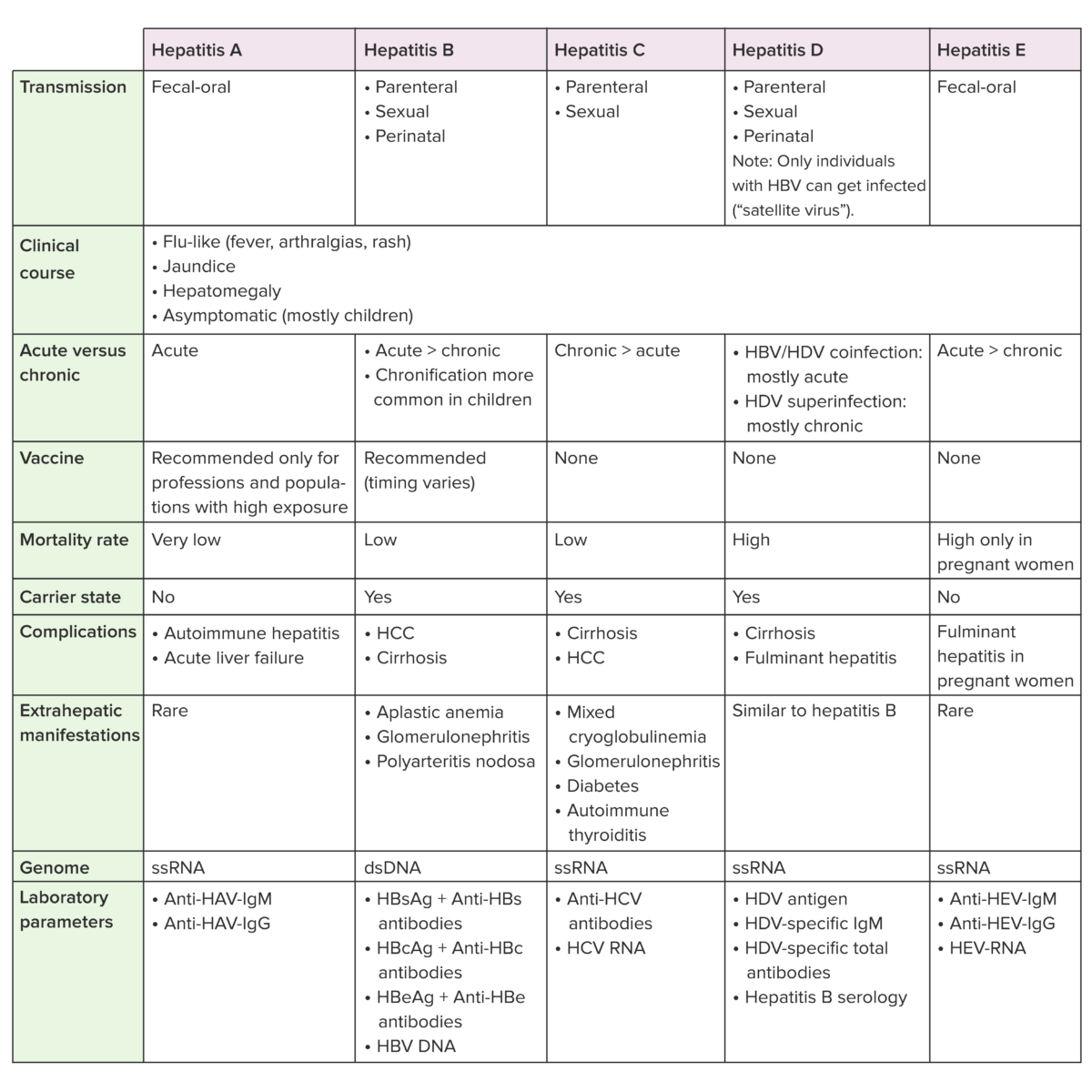
Anti-HBc: anticuerpo del núcleo de la hepatitis B
Anti-HBs: anticuerpo de superficie de la hepatitis B
HBcAg: antígeno del núcleo de la hepatitis B
HBsAg: antígeno de superficie de la hepatitis B
HBV: virus de la hepatitis B
HCC: carcinoma hepatocelular
HCV: virus de la hepatitis C
HDV: virus de la hepatitis D