La urticaria Urticaria Urticaria is raised, well-circumscribed areas (wheals) of edema (swelling) and erythema (redness) involving the dermis and epidermis with associated pruritus (itch). Urticaria is not a single disease but rather is a reaction pattern representing cutaneous mast cell degranulation. Urticaria (Hives) consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum áreas elevadas y bien circunscritas (habones) de edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema (inflamación) y eritema (enrojecimiento) que afectan a la dermis Dermis A layer of vascularized connective tissue underneath the epidermis. The surface of the dermis contains innervated papillae. Embedded in or beneath the dermis are sweat glands; hair follicles; and sebaceous glands. Skin: Structure and Functions y la epidermis Epidermis The external, nonvascular layer of the skin. It is made up, from within outward, of five layers of epithelium: (1) basal layer (stratum basale epidermidis); (2) spinous layer (stratum spinosum epidermidis); (3) granular layer (stratum granulosum epidermidis); (4) clear layer (stratum lucidum epidermidis); and (5) horny layer (stratum corneum epidermidis). Skin: Structure and Functions con prurito (picor) asociado. La urticaria Urticaria Urticaria is raised, well-circumscribed areas (wheals) of edema (swelling) and erythema (redness) involving the dermis and epidermis with associated pruritus (itch). Urticaria is not a single disease but rather is a reaction pattern representing cutaneous mast cell degranulation. Urticaria (Hives) no es una enfermedad única, sino que es un patrón de reacción que representa la degranulación de los LOS Neisseria mastocitos cutáneos, dando lugar a la liberación de histamina y otras sustancias vasoactivas por parte de los LOS Neisseria mastocitos y basófilos de la dermis Dermis A layer of vascularized connective tissue underneath the epidermis. The surface of the dermis contains innervated papillae. Embedded in or beneath the dermis are sweat glands; hair follicles; and sebaceous glands. Skin: Structure and Functions, lo que provoca extravasación de plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la dermis Dermis A layer of vascularized connective tissue underneath the epidermis. The surface of the dermis contains innervated papillae. Embedded in or beneath the dermis are sweat glands; hair follicles; and sebaceous glands. Skin: Structure and Functions. La urticaria Urticaria Urticaria is raised, well-circumscribed areas (wheals) of edema (swelling) and erythema (redness) involving the dermis and epidermis with associated pruritus (itch). Urticaria is not a single disease but rather is a reaction pattern representing cutaneous mast cell degranulation. Urticaria (Hives) puede estar causada por un sinfín de acontecimientos, como por ejemplo, reacciones alérgicas, infecciones, exposición y muchos otros. El diagnóstico se realiza clínicamente. Los LOS Neisseria antagonistas H1 se utilizan como tratamiento de 1ra línea.
Last updated: Apr 19, 2022
La urticaria Urticaria Urticaria is raised, well-circumscribed areas (wheals) of edema (swelling) and erythema (redness) involving the dermis and epidermis with associated pruritus (itch). Urticaria is not a single disease but rather is a reaction pattern representing cutaneous mast cell degranulation. Urticaria (Hives) es una reacción vascular de la piel que se manifiesta con la aparición transitoria de manchas ligeramente elevadas (ronchas) más rojas o pálidas que la piel adyacente, que suelen estar acompañadas de un importante picor.
Las urticarias mediadas por IgE IgE An immunoglobulin associated with mast cells. Overexpression has been associated with allergic hypersensitivity. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions (hipersensibilidad de tipo I, liberación de histamina de los LOS Neisseria mastocitos) suelen deberse a la exposición a ciertos alérgenos:
Urticaria Urticaria Urticaria is raised, well-circumscribed areas (wheals) of edema (swelling) and erythema (redness) involving the dermis and epidermis with associated pruritus (itch). Urticaria is not a single disease but rather is a reaction pattern representing cutaneous mast cell degranulation. Urticaria (Hives) no mediada por IgE IgE An immunoglobulin associated with mast cells. Overexpression has been associated with allergic hypersensitivity. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions (liberación de histamina secundaria):
Urticarias físicas:
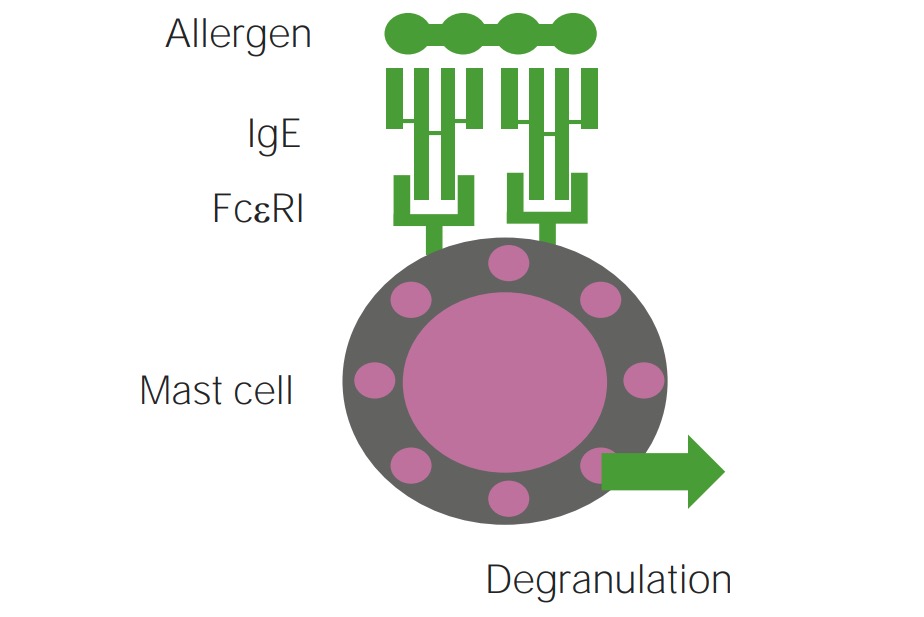
Mecanismo de la reacción de hipersensibilidad de tipo 1 implicada en las urticarias mediadas por IgE (degranulación de mastocitos mediada por IgE)
Imagen por Lecturio.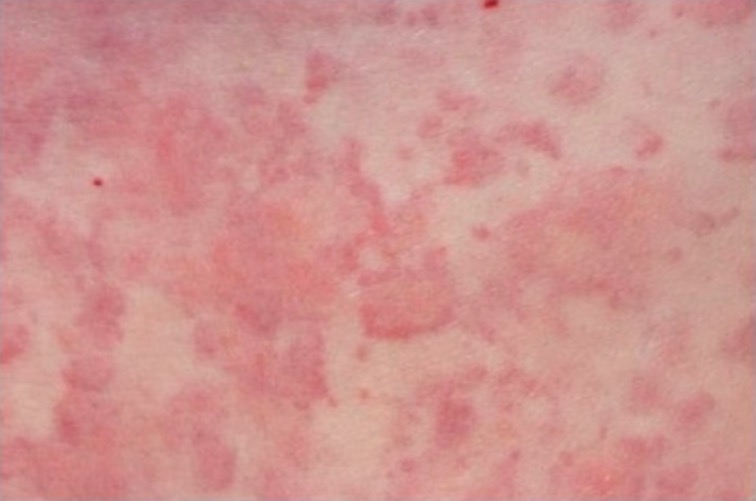
Erupción tipo urticaria
Imagen: “Urticarial rash at presentation” por Regional Immunology Service, Royal Hospitals, The Belfast Trust, Grosvenor Road, Belfast BT12 6BN. Licencia: CC BY 2.0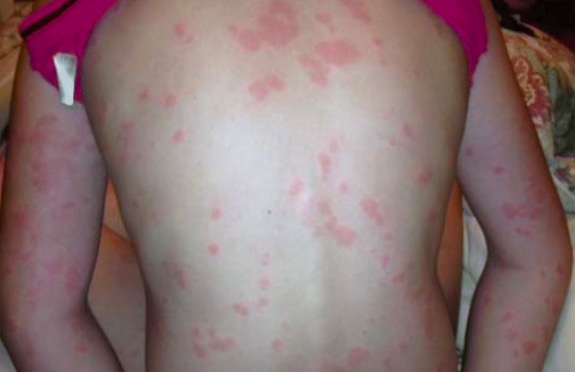
Erupción tipo urticaria
Imagen: “Chronic spontaneous urticaria” por University of Toronto, Medicine, Toronto, ON Canada. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Las pruebas de estimulación pueden utilizarse para inducir síntomas de urticaria Urticaria Urticaria is raised, well-circumscribed areas (wheals) of edema (swelling) and erythema (redness) involving the dermis and epidermis with associated pruritus (itch). Urticaria is not a single disease but rather is a reaction pattern representing cutaneous mast cell degranulation. Urticaria (Hives) física.
Si se asocia con anafilaxia: