El ultrasonido es una técnica de imagenología que se utiliza en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum medicina para obtener imágenes de las estructuras corporales subcutáneas, los LOS Neisseria vasos sanguíneos, las articulaciones y los LOS Neisseria órganos internos para excluir patologías estructurales. Esta técnica se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la utilización de ultrasonido (u ondas sonoras inaudibles de alta frecuencia). En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la imagenología médica, las ondas sonoras tienen una frecuencia de 2–18 megahertz (MHz). El equipo utiliza un transductor que actúa como emisor y receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors de ondas sonoras, y un ordenador central procesa las señales eléctricas para generar la imagen. Las ventajas generales de este tipo de imagenología son su bajo costo, su disponibilidad y su seguridad. Algunas de las especialidades que dependen en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum gran medida del ultrasonido son cardiología, nefrología, cirugía general, gastroenterología, medicina de emergencias y obstetricia.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
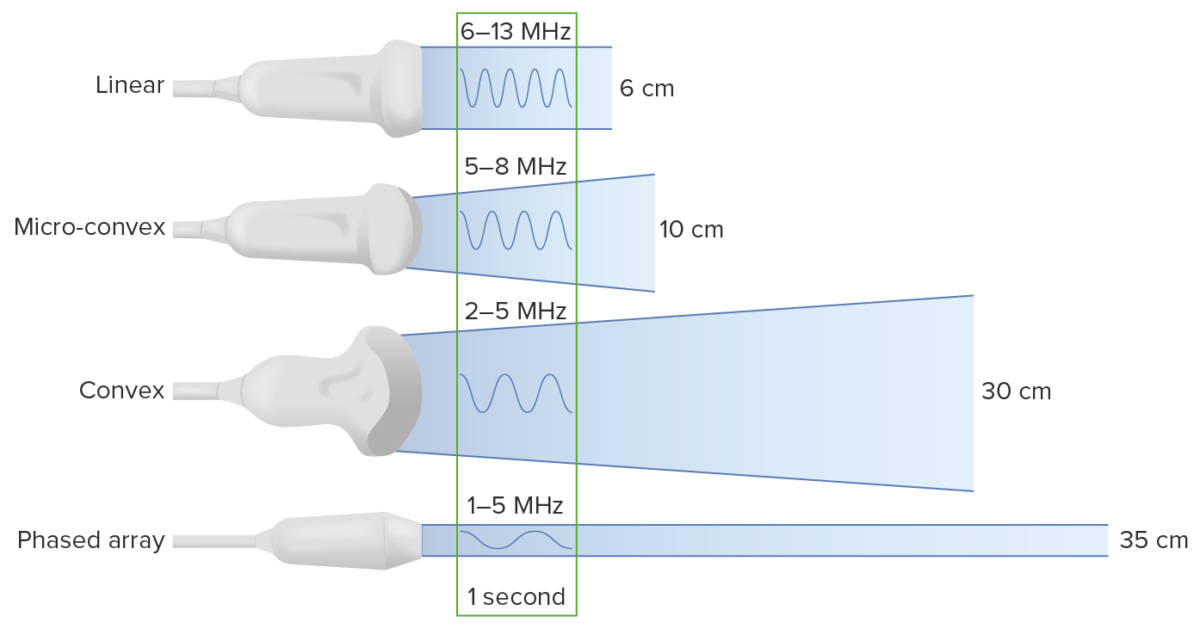
Tipos de transductores:
Obsérvese que al disminuir la frecuencia aumenta la profundidad a la que viaja la onda de ultrasonido. Sin embargo, esto se produce a costa de la resolución de la imagen.
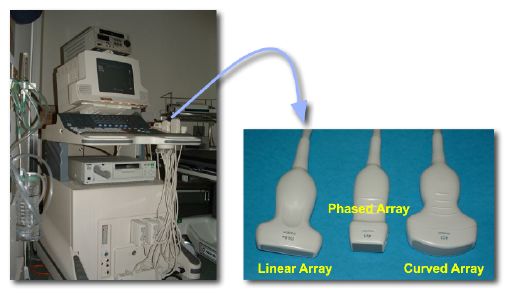
Un equipo de ultrasonido y diferentes transductores
Imagen: “Photos of a sonography system and typical transducers.” por Kieran Maher. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoEl principio fundamental del ultrasonido es la transmisión y reflexión de las ondas sonoras a través de los LOS Neisseria tejidos.
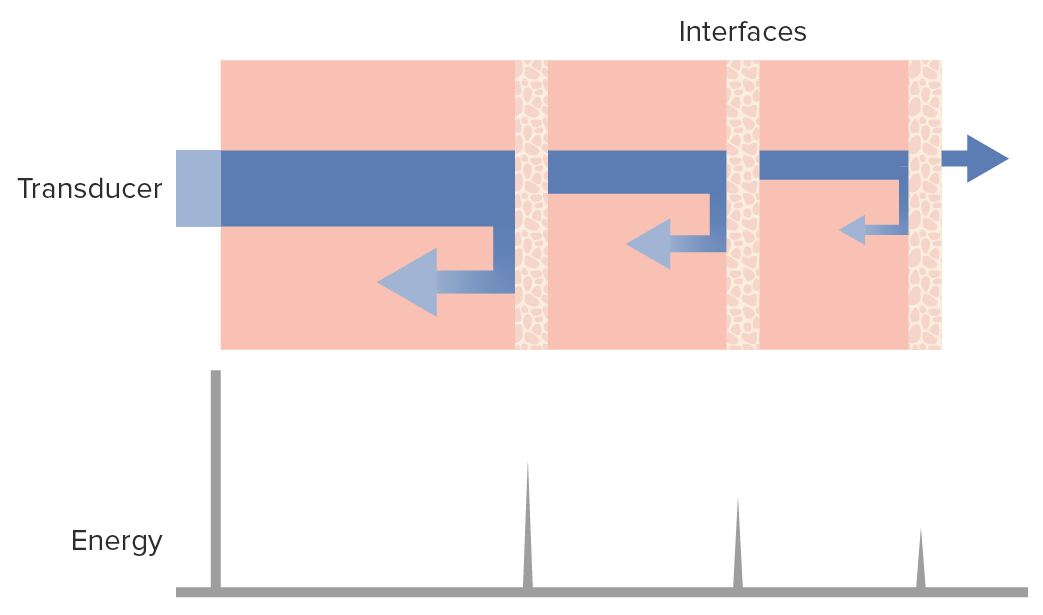
Las ondas de ultrasonido y los tejidos:
El diagrama muestra que, a medida que el haz de ondas de ultrasonido (barra horizontal azul) penetra en los tejidos, un porcentaje se refleja de vuelta (flechas a la izquierda) hacia el transductor, mientras que otro continúa adentrándose en los tejidos (flecha a la derecha), perdiendo algo de energía en el parénquima a su paso.
Planos imagenológicos:
Tipos de imágenes:
La definición o nitidez de la imagen generada puede caracterizarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum términos de:
La definición de la imagen también viene determinada por la proximidad de los objetos al transductor; según sus frecuencias, los transductores tienen un campo de “visión” cercano y otro lejano:
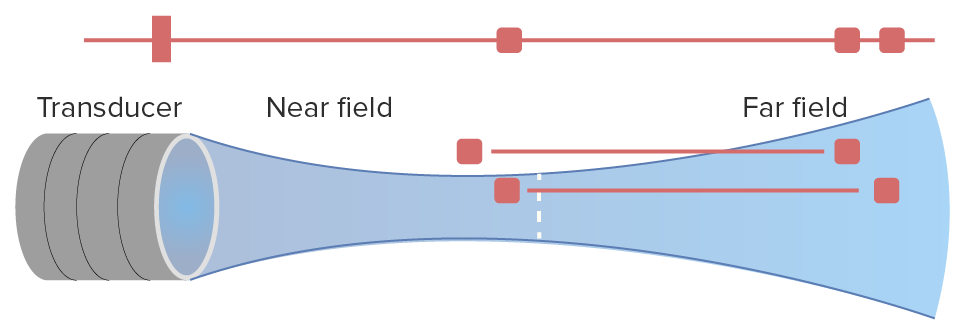
Campos cercano y lejano de un transductor en el ultrasonido:
Obsérvese cómo, en el campo cercano, el transductor tiene una adecuada definición lateral, siendo capaz de distinguir entre 2 puntos. Por otro lado, en el campo lejano, el aumento de la definición axial (profundidad) sacrifica la definición lateral.
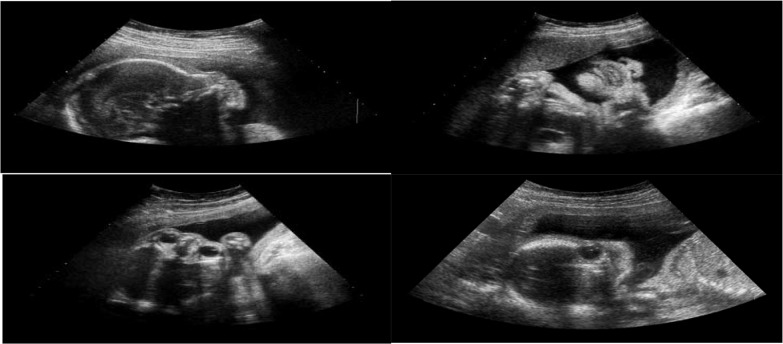
Diferentes planos del ultrasonido fetal:
Arriba a la izquierda: Plano sagital
Arriba a la derecha: Plano coronal
Abajo a la izquierda: Plano axial
Abajo a la derecha: Plano estándar facial no fetal
El ultrasonido Doppler (o simplemente “Doppler”) es un método de ultrasonido muy utilizado que se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el principio de la compresión y dilatación de las ondas sonoras con respecto al AL Amyloidosis receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors. El ultrasonido Doppler Doppler Ultrasonography applying the doppler effect, with frequency-shifted ultrasound reflections produced by moving targets (usually red blood cells) in the bloodstream along the ultrasound axis in direct proportion to the velocity of movement of the targets, to determine both direction and velocity of blood flow. Ultrasound (Sonography) es el más utilizado para visualizar el flujo sanguíneo.
La interpretación de las imágenes de ultrasonido se realiza en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum tiempo real, mientras se realiza el examen.
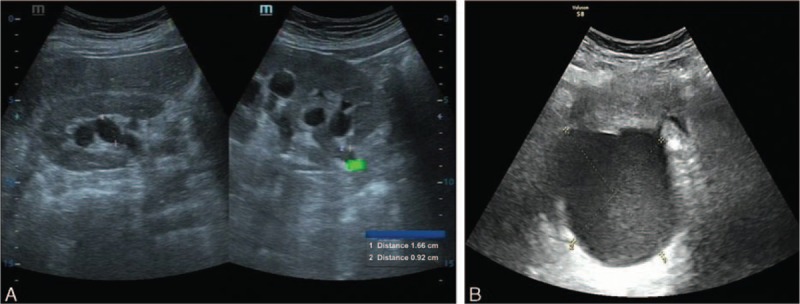
A: Ultrasonido urinario que muestra hidronefrosis del lado derecho y la sección superior irregular del uréter derecho
B: Ultrasonido ginecológico que muestra una masa quística (8,8 X 7,5 X 8,6 cm) en la parte posterior derecha del útero
Obsérvese que ambos hallazgos son de hipoecoicos a anecoicos debido a su contenido líquido
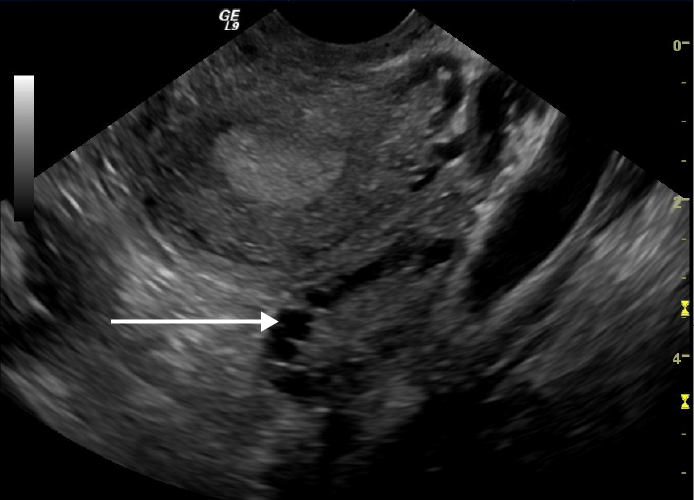
Ultrasonido transvaginal que muestra un ovario poliquístico:
Nótese los múltiples quistes en la periferia del ovario (flecha blanca)
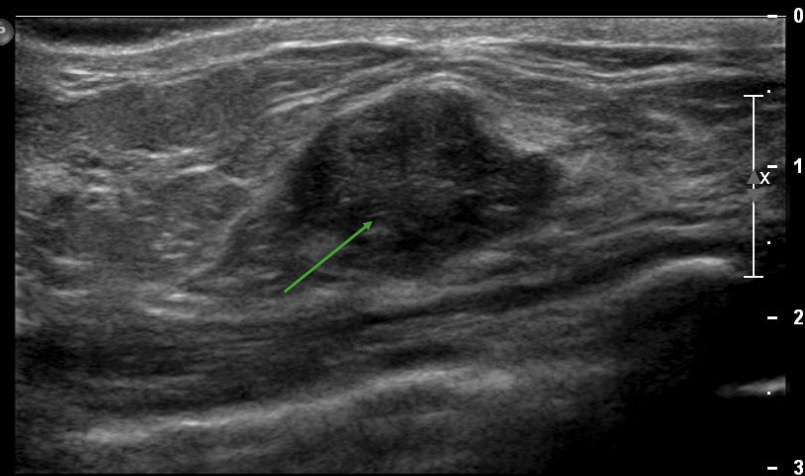
Ejemplo de una estructura hipoecoica inespecífica en un ultrasonido de mama derecha, que podría representar una neoplasia maligna, un absceso o un tumor benigno, según el escenario clínico
Imagen por Hetal Verma.
Ejemplo de un nódulo tiroideo que contiene calcificaciones internas, representadas como focos hiperecoicos en un ultrasonido de la glándula tiroides
Imagen por Hetal Verma.Por convención, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el Doppler Doppler Ultrasonography applying the doppler effect, with frequency-shifted ultrasound reflections produced by moving targets (usually red blood cells) in the bloodstream along the ultrasound axis in direct proportion to the velocity of movement of the targets, to determine both direction and velocity of blood flow. Ultrasound (Sonography) color:
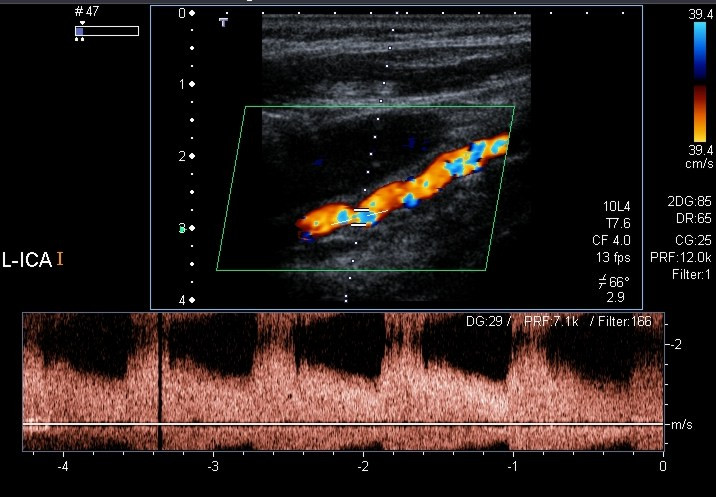
Evaluación con Doppler color y Doppler espectral de la arteria carótida interna izquierda que revela estenosis de aproximadamente el 70%
Imagen: “Color Doppler and spectral Doppler examination of the left ICA” por Christian Arning et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0
Ultrasonido Doppler de las arterias carótidas que muestra una estenosis carotídea:
Se puede observar una placa que obstruye < 40% del lumen y focos hiperecoicos dentro de la pared del vaso, probablemente debido a calcificación
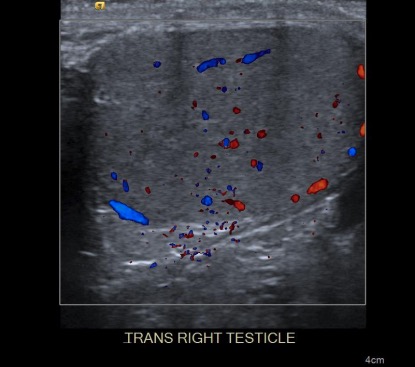
Ultrasonido Doppler del testículo derecho:
Observe la diferencia de color entre el flujo que viene hacia el transductor (rojo) y el que se aleja del transductor (azul).
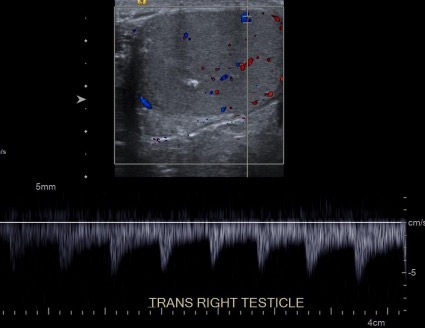
Ultrasonido Doppler espectral del testículo derecho:
En la parte inferior de la imagen aparece un gráfico del flujo.
Los LOS Neisseria artefactos son objetos artificiales producidos por la mala interpretación que hace HACE Altitude Sickness el equipo de los LOS Neisseria datos de las ondas sonoras procedentes de los LOS Neisseria tejidos y que no representan estructuras reales.
Algunos ejemplos de artefactos son:
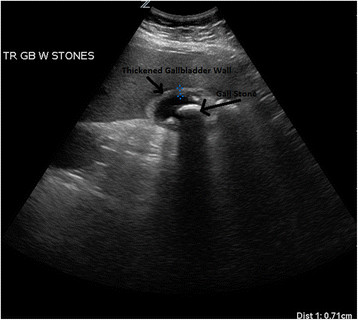
Ultrasonido de un paciente con colecistitis aguda:
Se visualizan múltiples cálculos biliares dentro de la luz de la vesícula biliar con engrosamiento de la pared de la vesícula y líquido pericolecístico. Se puede ver una sombra detrás del cálculo biliar.
| Ventajas | Desventajas |
|---|---|
|
|
Indicaciones:
No hay contraindicaciones para el ultrasonido.
| Radiografía | TC | Ultrasonido | RM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mecanismo de adquisición | Radiación ionizante | Radiación ionizante | Energía acústica | Pulsos ferromagnéticos |
| Costo relativo | Bajo costo | Costoso | Bajo costo | Muy costoso |
| Portátil | Sí | No | Sí | No |
| Duración del examen | Segundos | < 1 minuto | Segundos | Aproximadamente 1 hora |
| Contraste | No | Puede ser necesario | Puede ser necesario | Puede ser necesario |