El sistema linfático consta de los LOS Neisseria órganos linfoides que contienen las células del sistema inmunitario y los LOS Neisseria vasos linfáticos, que transportan el líquido intersticial (como linfa) de regreso a la circulación venosa. Los LOS Neisseria vasos linfáticos se distribuyen ampliamente por todo el cuerpo, drenando y filtrando la linfa, facilitando la homeostasis Homeostasis The processes whereby the internal environment of an organism tends to remain balanced and stable. Cell Injury and Death y ayudando en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la defensa contra los LOS Neisseria patógenos circulantes. El flujo de líquido es unidireccional, habilitado por válvulas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria vasos linfáticos colectores. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria vasos sin válvulas, la contracción muscular de los LOS Neisseria órganos y los LOS Neisseria vasos sanguíneos adyacentes ayudan al AL Amyloidosis movimiento del fluido. Para regresar a la circulación venosa, la linfa es recolectada por los LOS Neisseria principales conductos linfáticos: conducto linfático derecho (recolecta del lado derecho de la cabeza y el cuello, el lado derecho del tórax y la extremidad superior derecha) y el conducto torácico (recolecta del resto del cuerpo). Las afecciones patológicas que involucran el sistema linfático están asociadas con infecciones, daño linfático o lesiones y tumores malignos.
Last updated: Apr 2, 2025
El sistema linfático (vasos linfáticos, líquido linfático y órganos linfoides) es parte del sistema inmunológico del cuerpo.
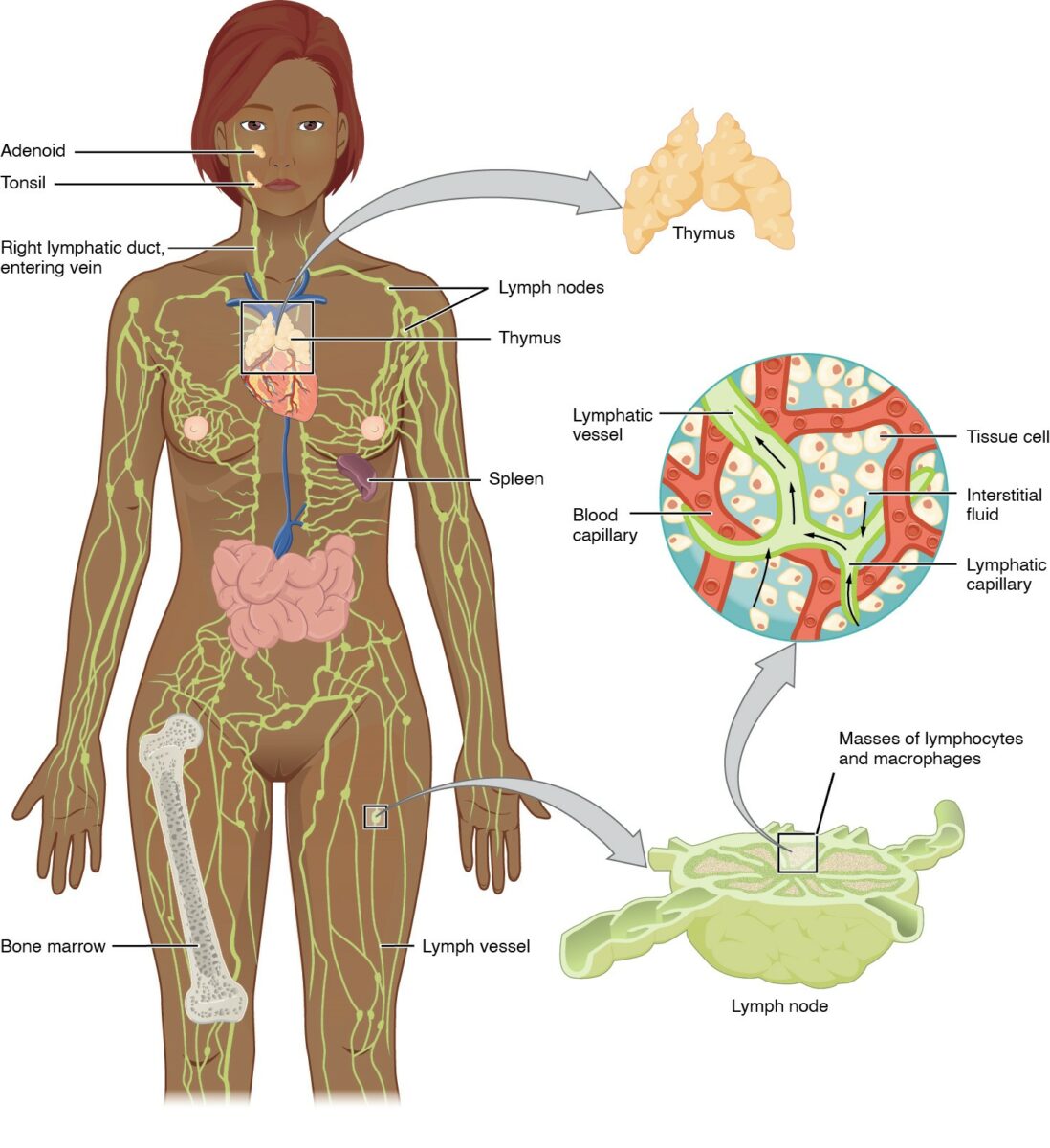
Anatomía del sistema linfático: incluye los órganos linfoides primarios (médula ósea, timo) y secundarios (bazo, ganglios linfáticos y tejido linfoide asociado a mucosa).
Los vasos linfáticos transportan linfa a los vasos linfáticos más grandes del torso, transportando líquido de vuelta a la circulación venosa.
El sistema glinfático es una red especializada de canales perivasculares en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el SNC, responsable del intercambio entre el líquido cefalorraquídeo (LCR) y el líquido intersticial (LSI) dentro del cerebro.
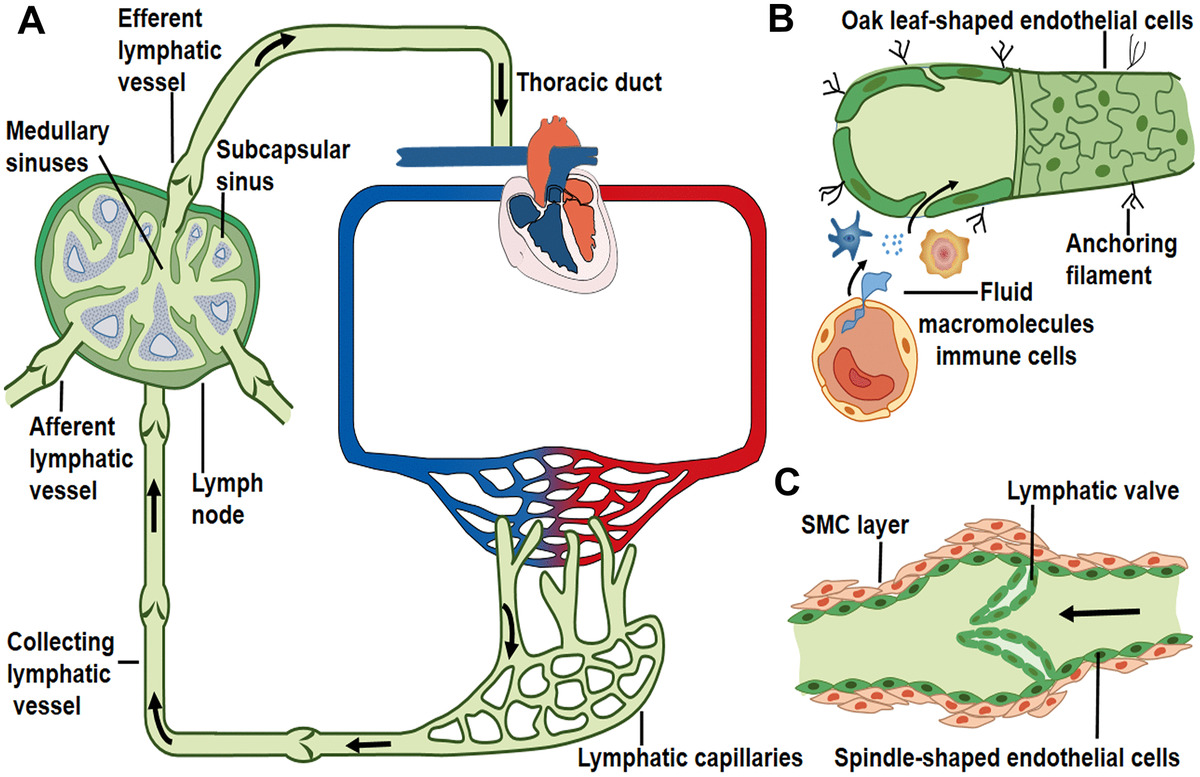
Transporte linfático a lo largo de los vasos linfáticos:
A: Ruta de flujo linfático unidireccional: los capilares linfáticos recolectan líquido tisular periférico y convergen en vasos colectores más grandes, y luego la linfa drena en los vasos linfáticos aferentes del ganglio linfático y sale del vaso linfático eferente. Posteriormente, el líquido linfático fluye a través del conducto torácico y el conducto/tronco linfático derecho, y eventualmente ingresa a la circulación venosa. Las flechas indican la dirección del flujo linfático.
B: los capilares linfáticos recogen el líquido intersticial, las macromoléculas y las células inmunitarias que se extravasan de los vasos sanguíneos. Los linfáticos iniciales carecen de capas musculares y están compuestos por una capa de células endoteliales en forma de hoja de roble, a través de las cuales ingresan líquido (y componentes).
C: los vasos linfáticos colectores contienen una válvula intraluminal y capas de células musculares lisas que permiten el flujo linfático unidireccional.
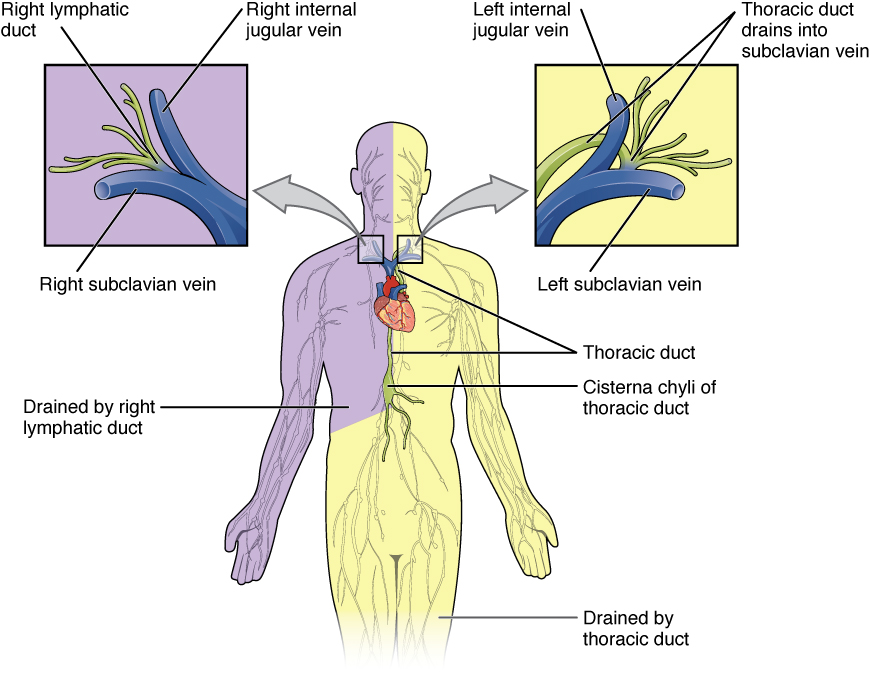
Conductos linfáticos:
El conducto linfático derecho drena desde el lado derecho del cuerpo (púrpura) por encima del diafragma (el lado derecho de la cabeza y el cuello, el lado derecho del tórax y la extremidad superior derecha).
El conducto torácico drena del resto del cuerpo (amarillo), particularmente de ambos miembros inferiores, el miembro superior izquierdo y la mitad izquierda de la cabeza y el cuello.
Estos conductos linfáticos llevan linfa al sistema venoso en la unión de las venas yugular y subclavia en el cuello (conducto linfático derecho a la derecha y conducto torácico a la izquierda).
La linfadenopatía es causada por varias etiologías, y un enfoque para determinar la etiología se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la(s) ubicación(es) y las áreas drenadas por el( los LOS Neisseria) ganglio(s) linfático(s).
| Grupo de ganglios linfáticos | Áreas drenadas | Enfermedades asociadas |
|---|---|---|
| Ganglios linfáticos cervicales | Cabeza y cuello |
|
| Ganglios linfáticos preauriculares |
|
Infecciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum áreas drenadas |
| Ganglios linfáticos postauriculares | Cuero cabelludo parietotemporal | Infecciones (común en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la rubéola) |
| Ganglios linfáticos supraclaviculares |
|
|
| Ganglios linfáticos axilares |
|
|
| Ganglios linfáticos epitrocleares | Lado medial del brazo por debajo del codo |
|
| Ganglios linfáticos mediastínicos |
|
|
| Ganglios linfáticos hiliares | Pulmones | |
| Ganglios linfáticos celíacos |
|
|
| Ganglios linfáticos mesentéricos superiores |
|
|
| Ganglios linfáticos mesentéricos inferiores | Colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy desde la flexura esplénica hasta el recto superior | |
| Ganglios linfáticos paraaórticos (lumbares) |
|
|
| Ganglios linfáticos ilíacos (externos e internos) |
|
|
| Ganglios linfáticos inguinales |
|
|
| Ganglios linfáticos poplíteos | Parte inferior de la pierna | Infección (celulitis) |
Regiones de ganglios linfáticos que indican los grupos de ganglios linfáticos
Imagen: “Lymph node regions” por Fred the Oyster y Mikael Häggström. Licencia: Dominio Público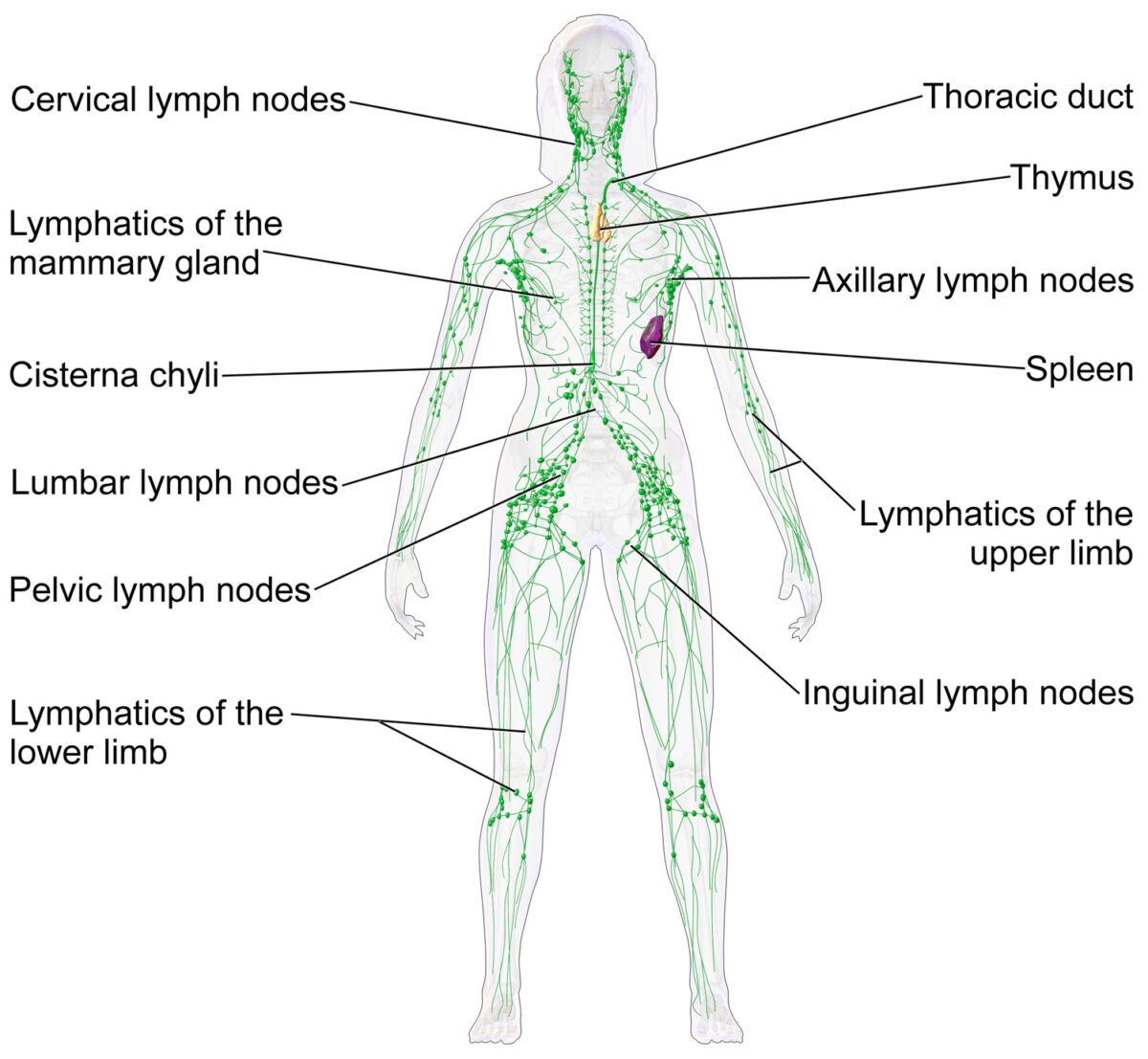
Los ganglios linfáticos y el sistema linfático
Imagen: “Blausen 0623 LymphaticSystem Female” por Blausen. Licencia: CC BY 3.0