El síndrome IPEX (inmunodesregulación, poliendocrinopatía, enteropatía, ligada al AL Amyloidosis cromosoma X) es una deficiencia congénita poco común de células T asociada a la disfunción del factor de transcripción FOXP3. Este factor regula el desarrollo de una línea de células T reguladoras y las disfunciones suelen resultar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum autoinmunidad. La enfermedad se manifiesta como enteropatía autoinmune, dermatitis Dermatitis Any inflammation of the skin. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) eczematosa, distrofia ungueal, endocrinopatías autoinmunes y afecciones cutáneas autoinmunes. La única forma de tratamiento del IPEX es el trasplante de médula ósea.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Epidemiología
Etiología
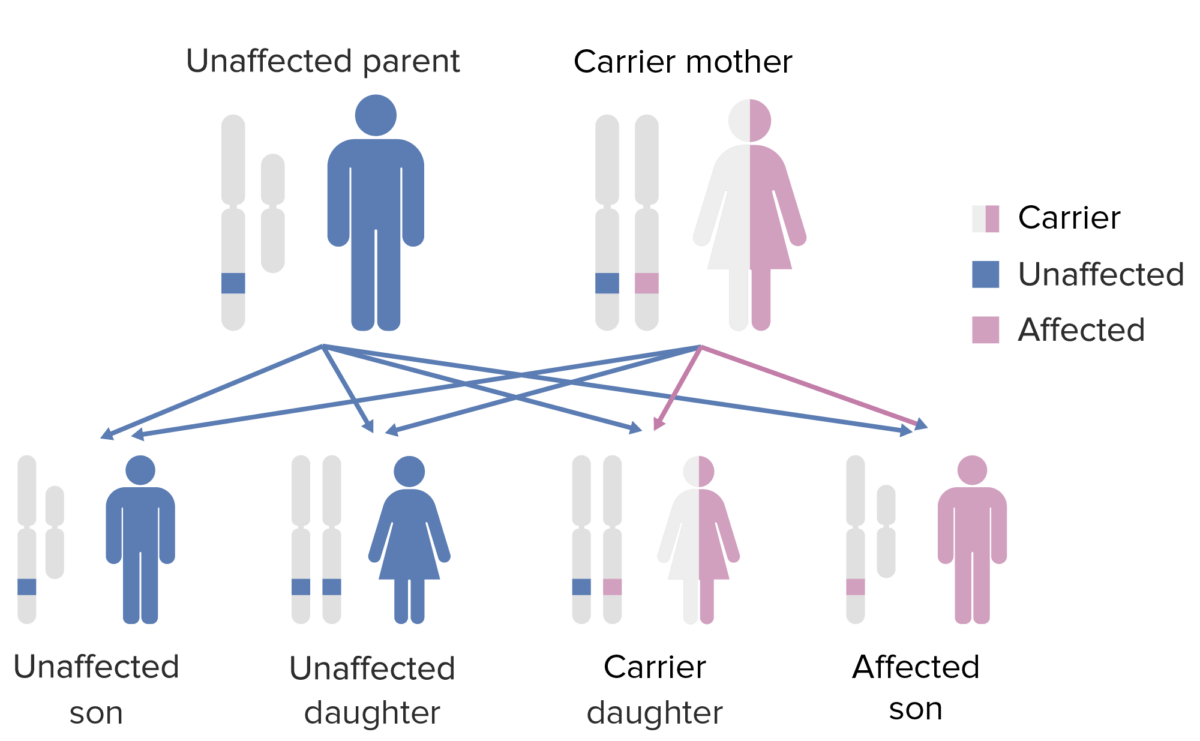
El patrón de herencia de la agammaglobulinemia ligada al cromosoma X. Obsérvese que la madre debe aportar el gen X defectuoso al hijo varón para que éste exprese este fenotipo. Imagen por Lecturio.
Los LOS Neisseria signos de autoinmunidad sistémica comienzan a presentarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el 1er año de vida.

Paciente que presenta una linfadenopatía cervical
Imagen: “Ixodholfem8” de Hudson, Bernard. Licencia: CC BY 3.0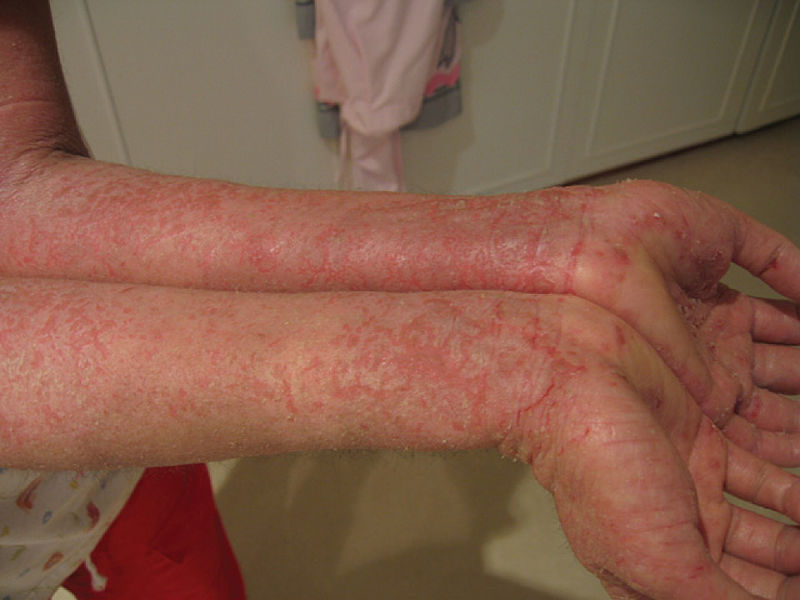
Eczema severo presentado por un paciente con síndrome IPEX
Imagen: “Eczema” por OpenStax College. Licencia: CC BY 3.0Las pruebas diagnósticas del síndrome IPEX siguen criterios sistemáticos coherentes con:
Se utilizan numerosos medicamentos y su administración depende de las manifestaciones de cada paciente:
Las siguientes condiciones son diagnósticos diferenciales para el síndrome IPEX: