El síndrome de Cowden, también conocido como síndrome de hamartoma Hamartoma A focal malformation resembling a neoplasm, composed of an overgrowth of mature cells and tissues that normally occur in the affected area. Colorectal Cancer múltiple, es una condición hereditaria autosómica dominante que se presenta con múltiples crecimientos no cancerosos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum varias partes del cuerpo. El síndrome se clasifica como un síndrome de tumor Tumor Inflammation hamartoma Hamartoma A focal malformation resembling a neoplasm, composed of an overgrowth of mature cells and tissues that normally occur in the affected area. Colorectal Cancer homólogo de la fosfatasa y tensina (PTEN, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) causado por mutaciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el gen PTEN. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes suelen tener macrocefalia, triquilemomas (tumores del folículo piloso) y pápulas papilomatosas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la boca. El síndrome de Cowden se asocia con un mayor riesgo de desarrollar cáncer de mama, tiroides, colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy y endometrio. El tratamiento incluye vigilancia de tumores asociados y cirugías profilácticas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El síndrome de Cowden es una genodermatosis autosómica dominante causada por una mutación en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el gen PTEN y se caracteriza por múltiples hamartomas benignos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cualquier localización del cuerpo, lesiones mucocutáneas y macrocefalia.
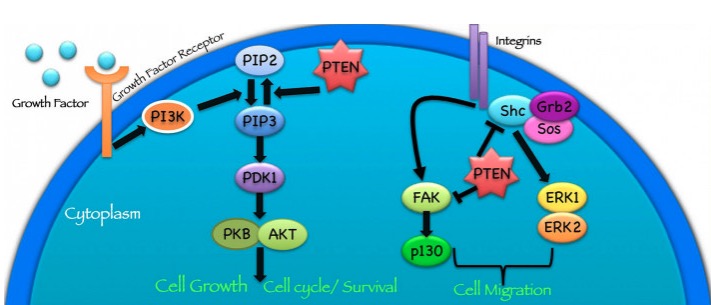
Función de la proteína PTEN:
La proteína PTEN funciona de diferentes maneras para suprimir la formación y propagación de tumores.
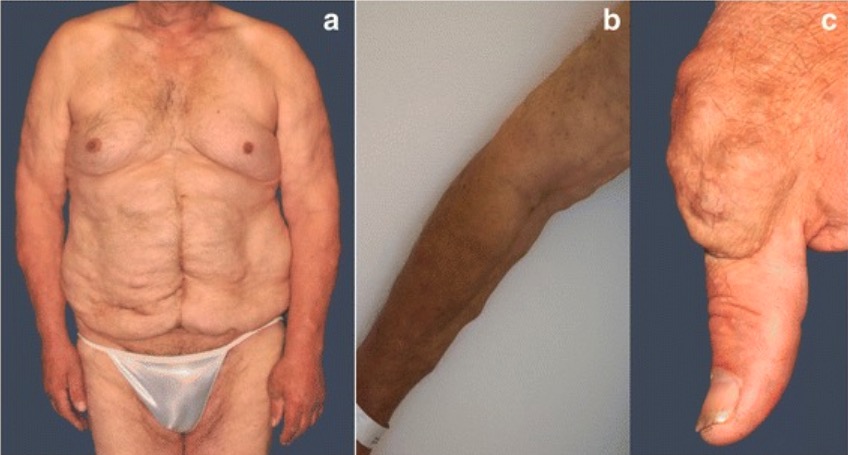
Múltiples tumores de tejidos blandos en (a) el torso, (b) extremidades, y (c) la articulación de la base del pulgar izquierdo
Imagen: “Fig. 2” por Steffen Pistorius et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0
Macrocefalia y tiroides difusamente agrandada en un paciente pediátrico con síndrome de Cowden
Imagen: “Diffusely enlarged thyroid gland” por Cláudia Patraquim et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0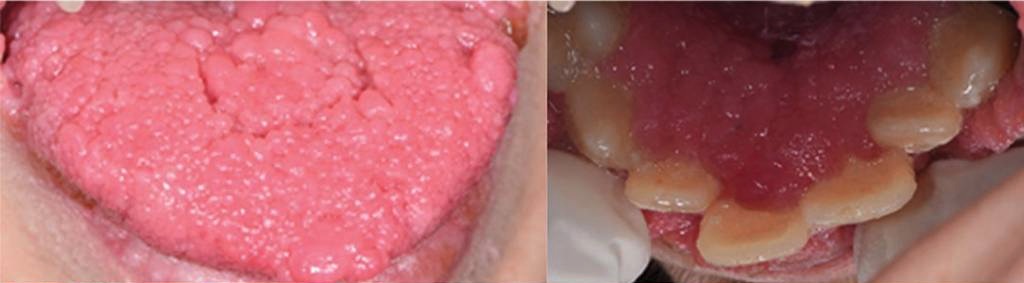
Izquierda: múltiples lesiones papilomatosas en la lengua
Derecha: múltiples lesiones papilomatosas coalescentes que cubren el área cervical de los dientes
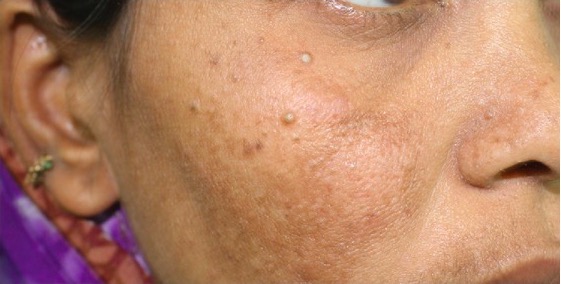
Triquilemomas en el hueso malar derecho de un paciente con enfermedad de hamartoma múltiple
Imagen: “Trichilemmomas on the right malar bone” por Prashanthi Chippagiri et al. Licencia: CC BY 3.0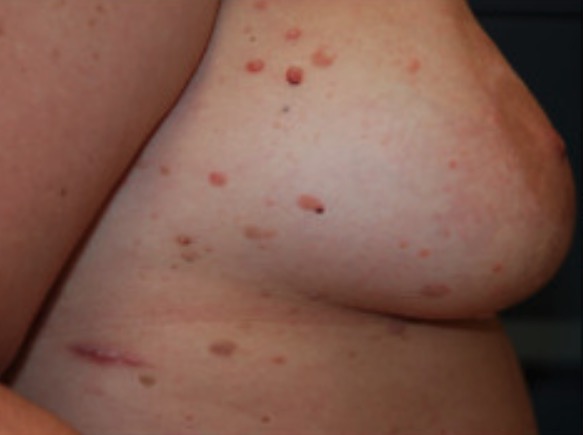
Múltiples queratosis seborreicas en una paciente con cáncer de mama bilateral de inicio precoz
Imagen: “Cutaneous findings of our case” por Laura Maria Pradella et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0, recortada por Lecturio.Las pruebas de laboratorio están dirigidas por la presentación clínica, y el síndrome de Cowden puede presentarse con anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types (por pérdidas gastrointestinales), enfermedad renal, enfermedad tiroidea y lesiones cutáneas.
Basado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el motivo de consulta, los LOS Neisseria estudios de imagen pueden incluir:
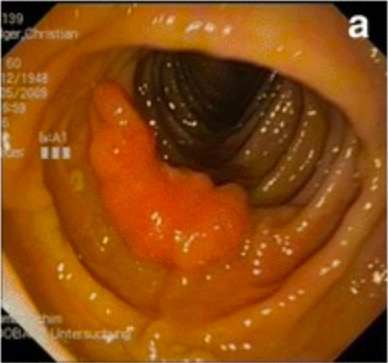
Hamartoma de colon descendente en paciente con síndrome de Cowden
Imagen: “Preoperative colonoscopic views” por Pistorius et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0, recortada por Lecturio.Tratamiento