La rotura esplénica es una emergencia médica que conlleva un riesgo importante de shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock hipovolémico y muerte. La lesión del bazo representa casi la mitad de todas las lesiones de los LOS Neisseria órganos intraabdominales. La razón más común para una ruptura del bazo es un traumatismo abdominal cerrado, específicamente, los LOS Neisseria accidentes automovilísticos. Sin embargo, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el caso de las personas con esplenomegalia, incluso un traumatismo mínimo puede provocar una lesión o rotura esplénica. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes suelen presentar dolor Dolor Inflammation en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuadrante superior izquierdo del abdomen; sin embargo, el dolor Dolor Inflammation puede irradiarse al AL Amyloidosis hombro izquierdo. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes corren el riesgo de sufrir inestabilidad hemodinámica debido a la pérdida de sangre. El diagnóstico se hace HACE Altitude Sickness generalmente con imagenología de TC; y el tratamiento, que va VA Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing desde la observación hasta la esplenectomía, depende de la estabilidad hemodinámica del paciente.
Last updated: Jan 15, 2026
La rotura esplénica suele estar asociada a un traumatismo (e.g., un accidente de tráfico) que provoca una laceración del órgano.
La rotura esplénica puede tener graves consecuencias debido a la función fisiológica del bazo.
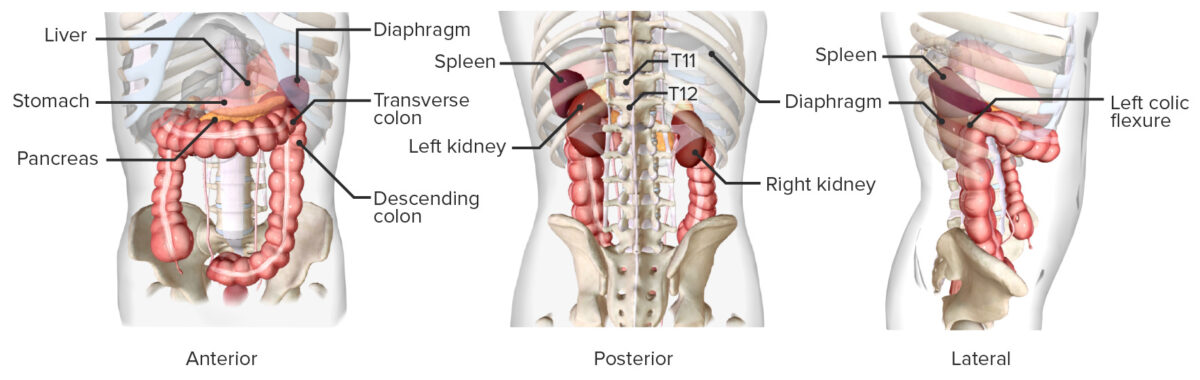
Localización del bazo
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por LecturioLa exploración física y la toma de antecedentes pueden ser útiles, pero no todos los LOS Neisseria pacientes con rotura esplénica presentan hallazgos clínicamente significativos.
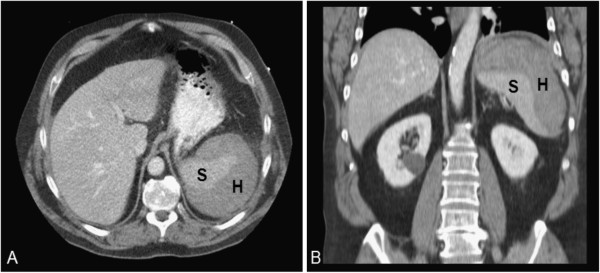
TC de abdomen de un paciente con rotura esplénica:
La rotura esplénica tiene múltiples etiologías posibles. El examen clínico y los antecedentes suelen ser insuficientes para el diagnóstico. Una TC de abdomen puede revelar áreas de hematoma (H) o sangre libre.
S: bazo
El tratamiento de la rotura esplénica depende del estado hemodinámico del paciente:
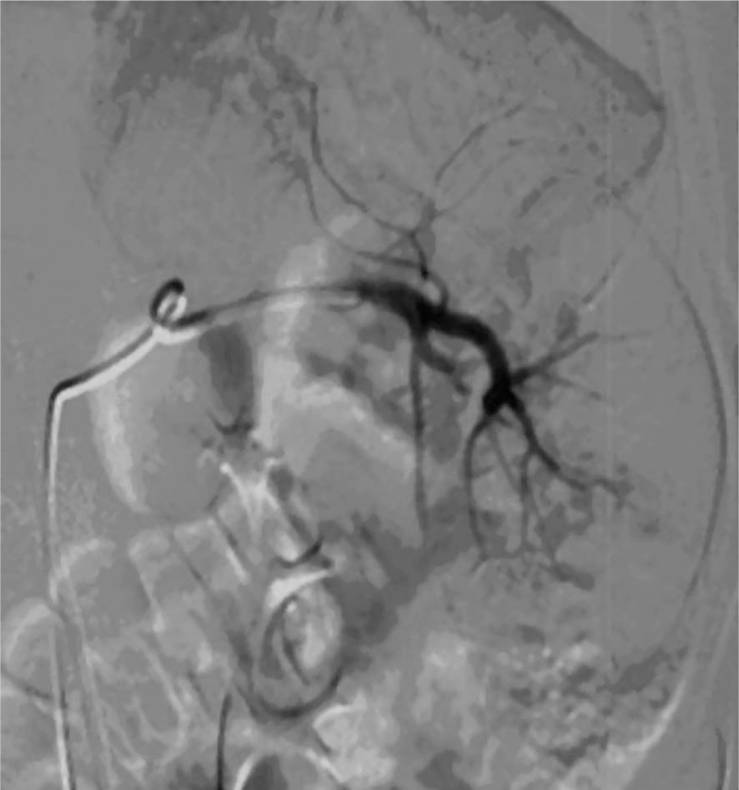
Embolización de la arteria esplénica:
Esta imagen muestra la embolización angiográfica en el marco de una lesión esplénica. El tratamiento no quirúrgico ha conseguido grandes mejoras en los resultados de los pacientes hemodinámicamente estables.
Post-esplenectomía:
Los LOS Neisseria pacientes asplénicos requieren vacunación contra bacterias encapsuladas: