La pupila es el espacio dentro del ojo que permite que la luz se proyecte sobre la retina Retina The ten-layered nervous tissue membrane of the eye. It is continuous with the optic nerve and receives images of external objects and transmits visual impulses to the brain. Its outer surface is in contact with the choroid and the inner surface with the vitreous body. The outermost layer is pigmented, whereas the inner nine layers are transparent. Eye: Anatomy. Situada anatómicamente delante del cristalino, el tamaño de la pupila está controlado por el iris que la rodea. La pupila proporciona información sobre la función de los LOS Neisseria sistemas nerviosos central y autónomo. La vía aferente para la función visual parte de la retina Retina The ten-layered nervous tissue membrane of the eye. It is continuous with the optic nerve and receives images of external objects and transmits visual impulses to the brain. Its outer surface is in contact with the choroid and the inner surface with the vitreous body. The outermost layer is pigmented, whereas the inner nine layers are transparent. Eye: Anatomy y se desplaza por los LOS Neisseria tractos ópticos y los LOS Neisseria núcleos geniculados laterales, para terminar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la corteza visual. El estímulo luminoso es conducido por el sistema parasimpático al AL Amyloidosis mesencéfalo, mientras que la reacción psicosensorial es procesada por el sistema simpático. Las vías eferentes producen la respuesta pertinente: miosis Miosis Pupil: Physiology and Abnormalities y midriasis Midriasis Pupil: Physiology and Abnormalities a partir de las inervaciones parasimpática y simpática, respectivamente. Los LOS Neisseria trastornos pupilares son el resultado de defectos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum áreas de las vías ópticas aferentes y eferentes. La presentación varía según el tamaño de la pupila en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum conjunto con la respuesta a la luz y a los LOS Neisseria medicamentos.
Last updated: Dec 25, 2022
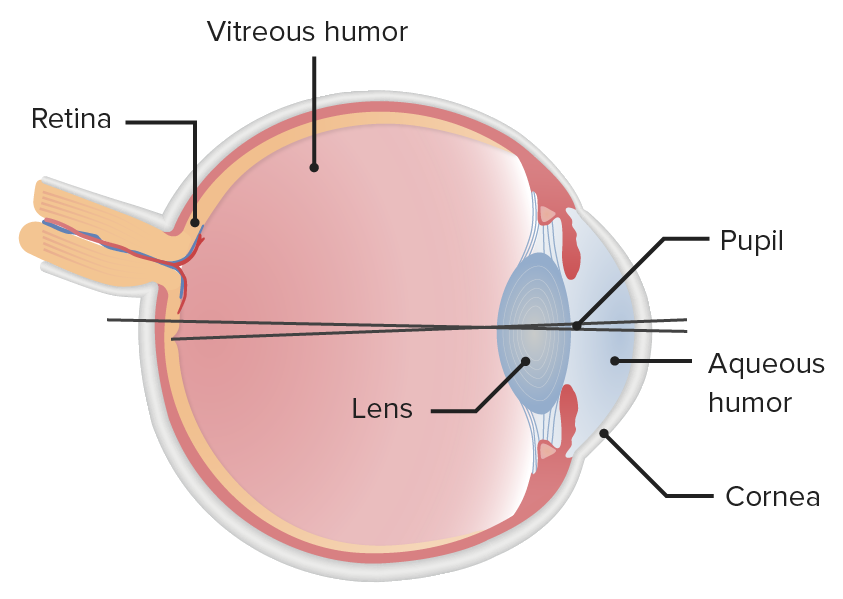
Ilustración de la estructura del globo ocular, destacando la ubicación espacial que define la pupila
Imagen por Lecturio.De los LOS Neisseria estímulos a la corteza visual primaria:
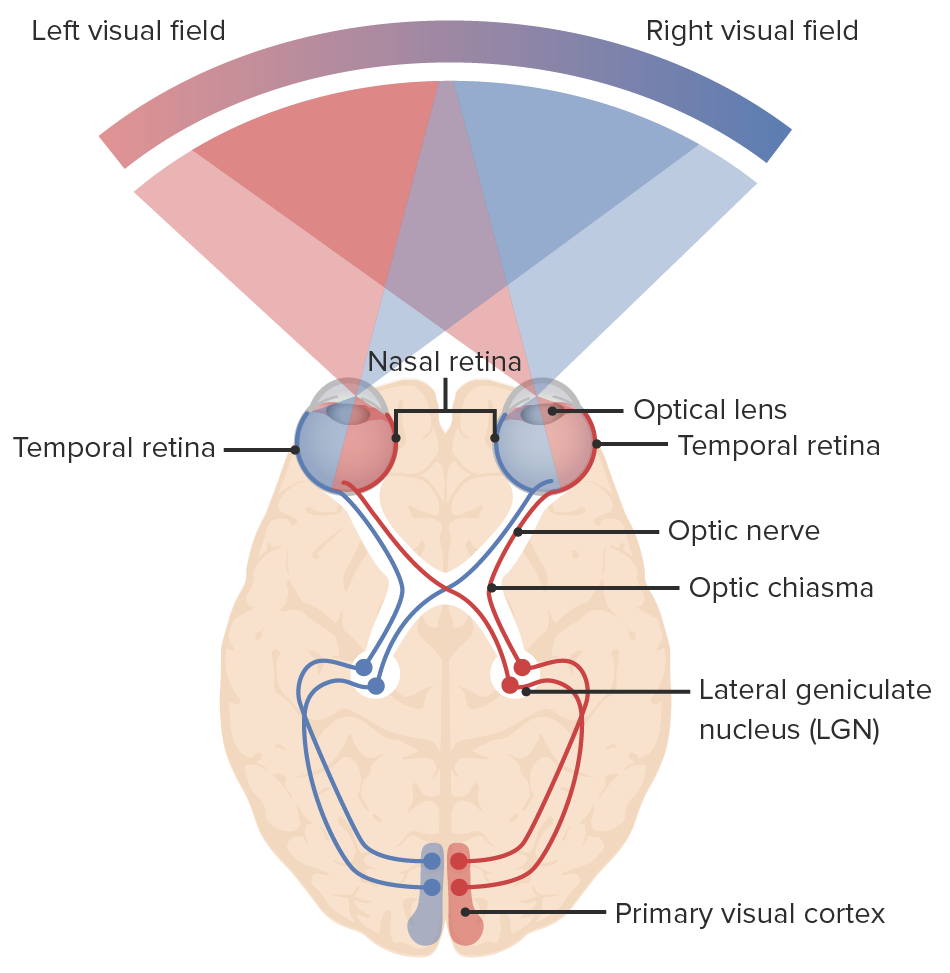
Diagrama de la vía óptica y de los campos visuales: la luz entra en el ojo, enviando señales a la retina y a través del nervio óptico. Las fibras nasales de cada ojo se decusan en el quiasma óptico, continuando hacia el tracto óptico con las fibras temporales: las fibras nasales derechas se unen a las fibras temporales izquierdas (líneas azules) y las fibras nasales izquierdas se unen a las fibras temporales derechas (líneas rojas). Las neuronas hacen sinapsis en el núcleo geniculado lateral. Las radiaciones ópticas conectan el núcleo geniculado lateral con la corteza visual primaria del lóbulo occipital, donde se procesa la información visual.
Imagen por Lecturio.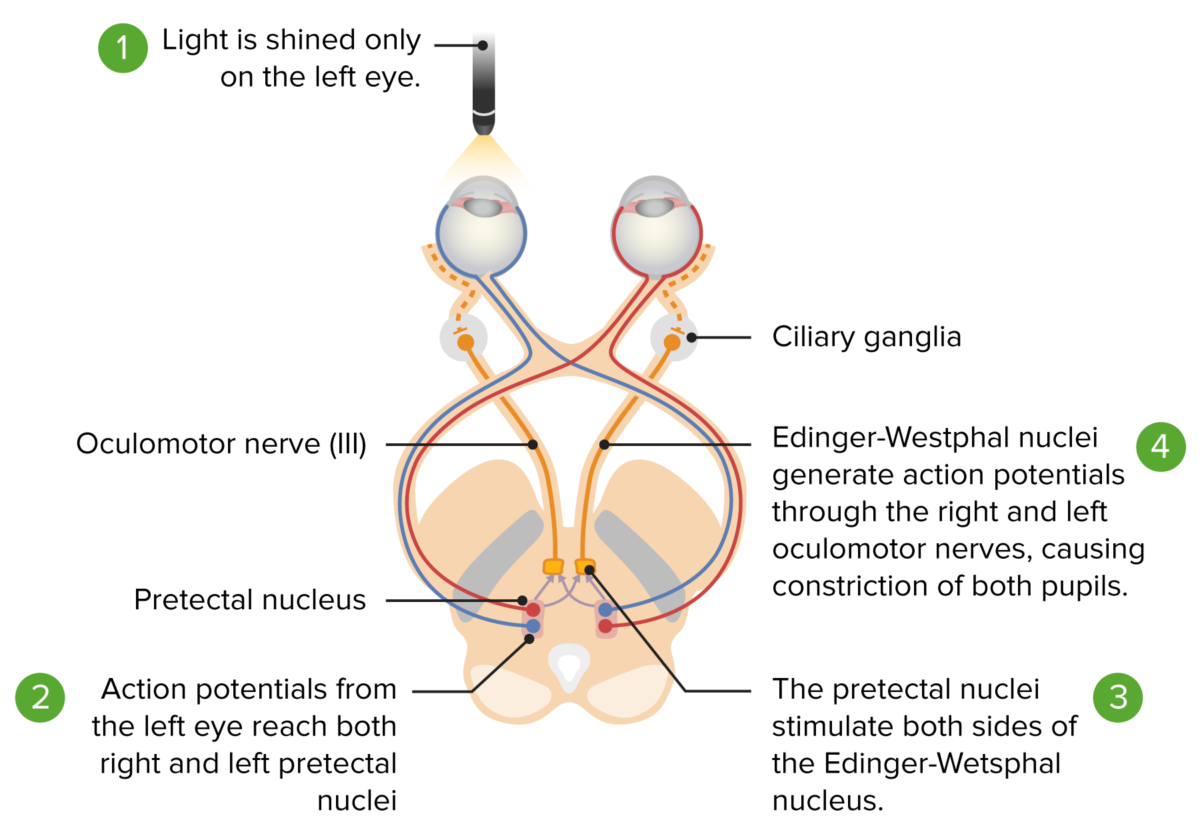
Vía del reflejo fotomotor: de la estimulación lumínica de la retina al mesencéfalo. Vía aferente (líneas roja y azul): El estímulo luminoso izquierdo va de la retina izquierda al quiasma óptico y al tracto óptico, terminando en el núcleo pretectal ipsilateral. El núcleo pretectal inerva a los núcleos de Edinger-Westphal izquierdo y derecho. Las líneas amarillas muestran el impulso de ambos núcleos que llega a los dos ganglios ciliares y da lugar a la miosis bilateral.
Imagen por Lecturio.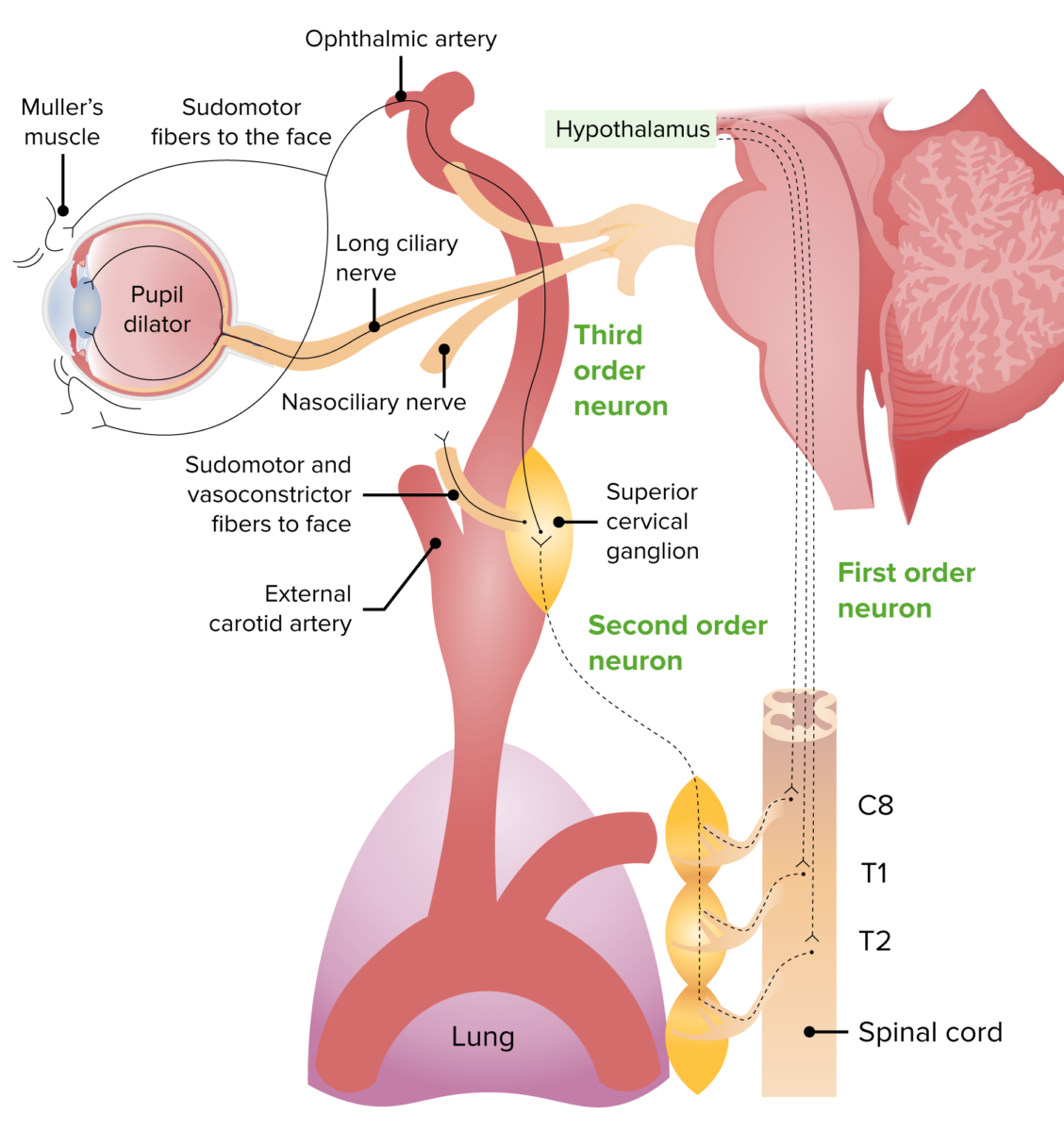
Imagen de la vía de inervación simpática:
Neurona de 1er orden: parte del hipotálamo hacia el centro de Budge (médula espinal C8–T2)
Neurona de 2do orden: sale de la médula espinal dirigiéndose hacia el ganglio cervical superior
Neurona de 3er orden: se une al nervio trigémino y a las fibras oculosimpáticas, hace sinapsis en el músculo dilatador de la pupila y en el músculo de Müller, provocando midriasis y apertura de los párpados.
Consta de 3 respuestas:
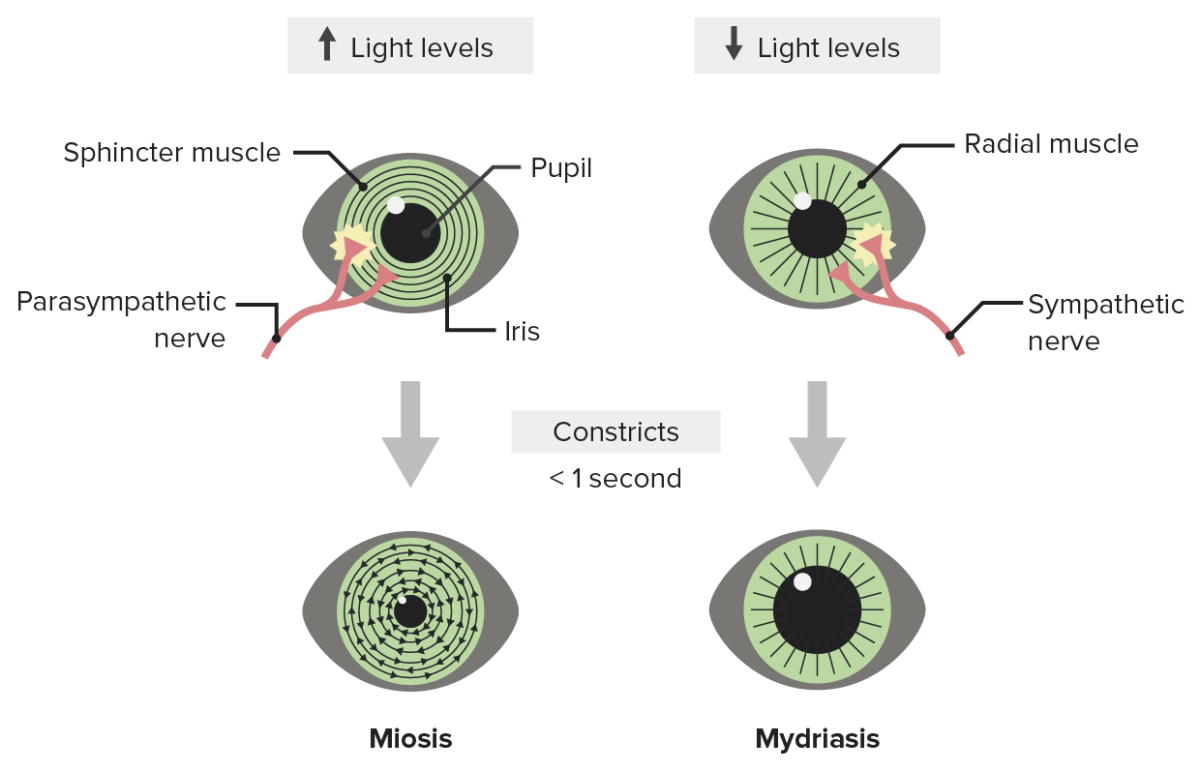
Ilustración de la respuesta pupilar a la luz: Los niveles de luz brillantes provocan miosis y los niveles de luz bajos estimulan la actividad simpática, lo que provoca midriasis.
Imagen por Lecturio.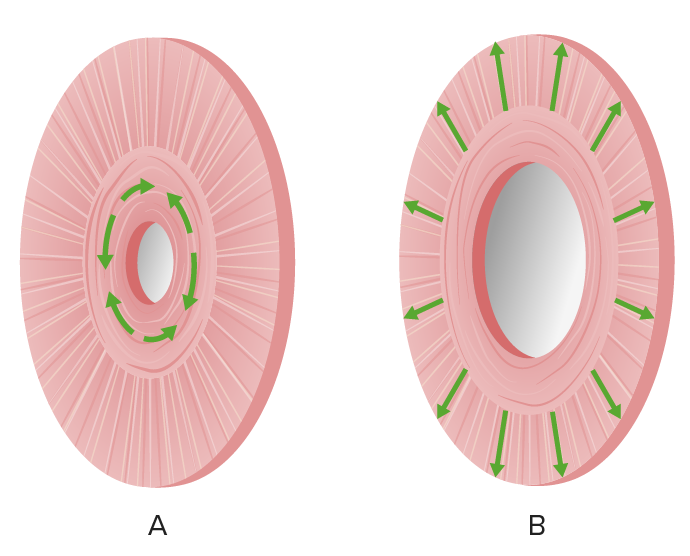
Ilustración de las acciones del músculo del iris:
(a) miosis por el músculo esfínter de la pupila.
(b) midriasis por el músculo dilatador de la pupila (músculos radiales)
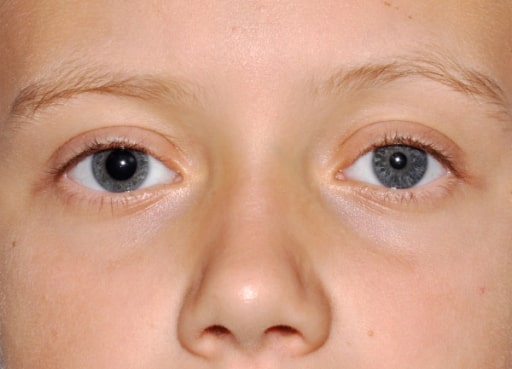
Anisocoria con midriasis derecha
Imagen: “Evident right mydriasis” por U,O,C Pediatria Generale Dipartimento di Medicina Pediatrica, Ospedale Pediatrico Bambino Gesù, Piazza Sant’Onofrio 4, 00165 Roma, Italy. Licencia: CC BY 2.0
Pupila derecha tónica: no responde a la estimulación lumínica
Imagen: “Holmes-Adie’s Syndrome” por US National Library of Medicine. Licencia: CC BY 4.0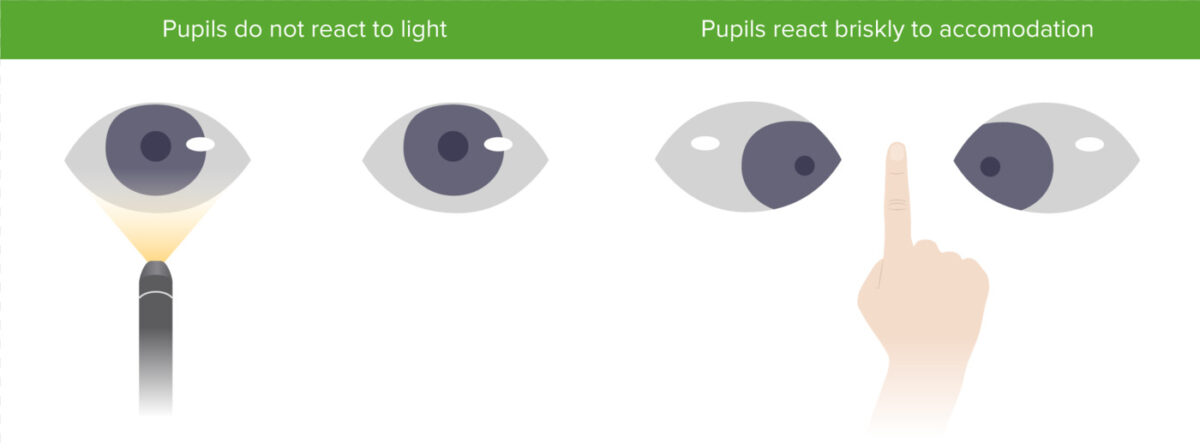
Pupila de Argyll Robertson con miosis bilateral que no se contrae a la luz, pero sí a la acomodación
Imagen por Lecturio.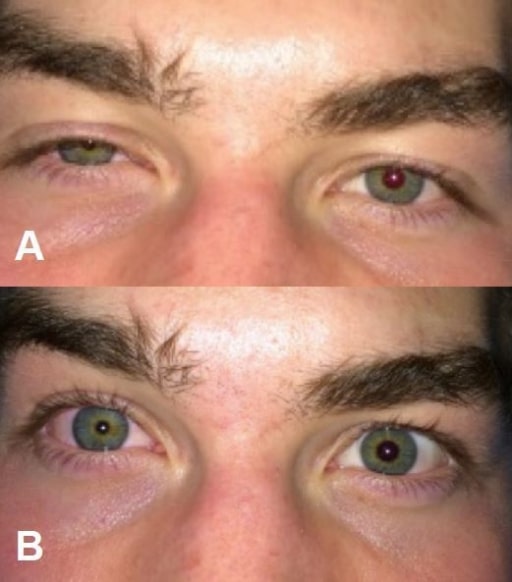
Síndrome de Horner después de bloquear el plexo cervical superficial (anestesia regional para una fractura clavicular). A: ptosis derecha; B: miosis derecha.
Imagen: “Horner’s syndrome” por Highland Hospital-Alameda Health System, Department of Emergency Medicine, Oakland, California. Licencia: CC BY 4.0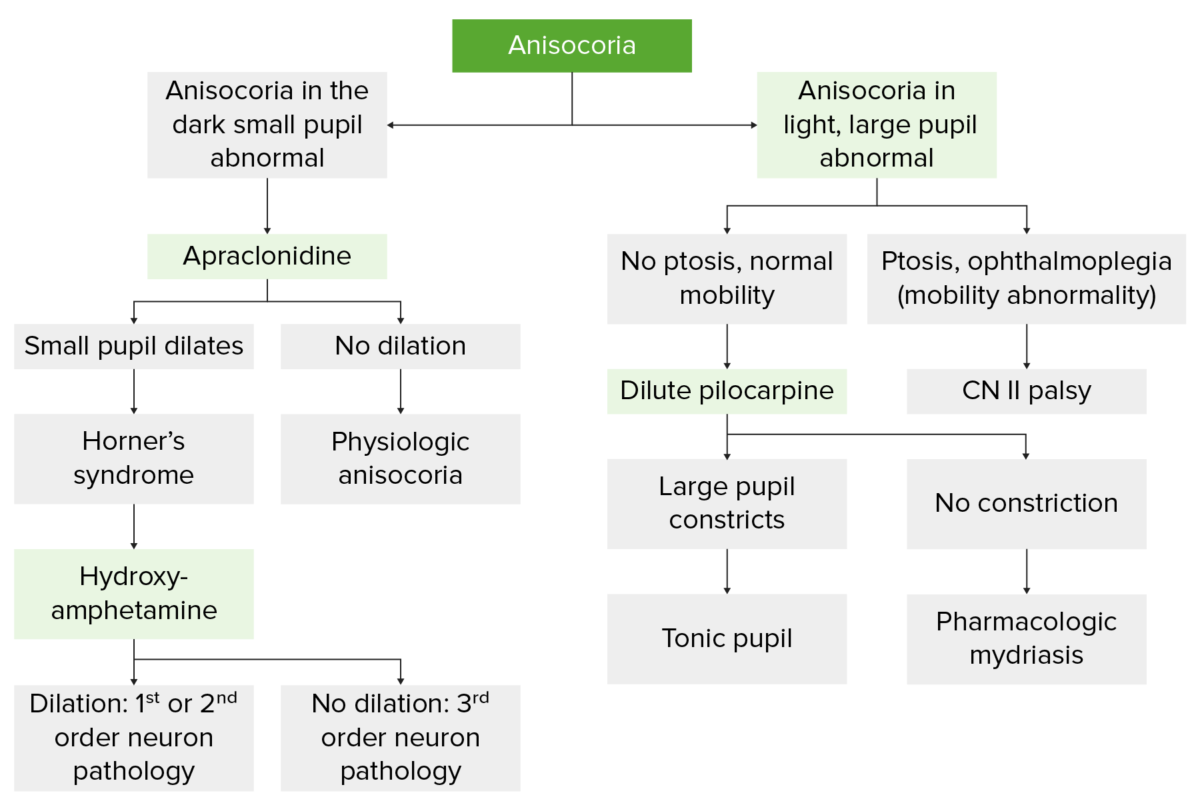
Diagrama de flujo que ilustra la evaluación de la anisocoria
Imagen por Lecturio.| Medicamento | Midriasis Midriasis Pupil: Physiology and Abnormalities | Miosis Miosis Pupil: Physiology and Abnormalities |
|---|---|---|
| Medicamentos oftálmicos |
|
|
| Drogas ilícitas |
|
Heroína |
| Otros medicamentos |
|
Opioides
|
| Hierbas | Estramonio (con propiedades anticolinérgicas) |