El eritroparvovirus 1 de primates (generalmente denominado parvovirus B19, virus B19 o, a veces, eritrovirus B19) se encuentra entre los virus de ADN más pequeños. El parvovirus B19 pertenece a la familia Parvoviridae y al género Erythroparvovirus. En los seres humanos inmunocompetentes, el parvovirus B19 provoca clásicamente el eritema infeccioso (5ta enfermedad) o "síndrome de mejilla abofeteada". Otras manifestaciones varían con el estado inmunológico y hematológico del huésped debido al AL Amyloidosis tropismo viral por los LOS Neisseria precursores eritrocitarios. El diagnóstico es principalmente clínico y el tratamiento es generalmente de soporte.
Last updated: Dec 29, 2025
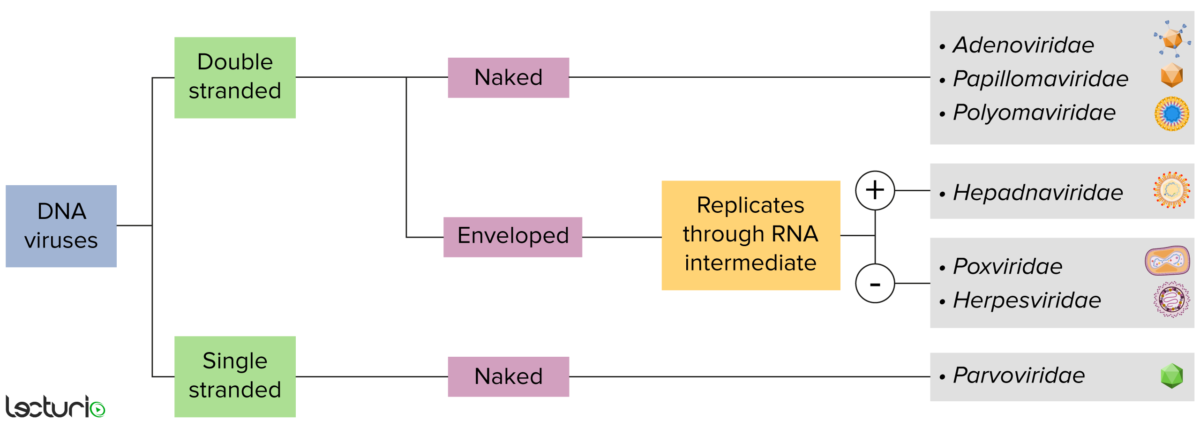
Identificación de virus de ADN:
Los virus pueden clasificarse de muchas maneras. Sin embargo, la mayoría de los virus tienen un genoma formado por ADN o ARN. Los virus con un genoma de ADN pueden caracterizarse además como monocatenario o bicatenario. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular, que generalmente es tomado de la célula huésped. Sin embargo, si la capa está ausente, los virus se denominan “desnudos”. Algunos virus con envoltura traducen el ADN en ARN antes de incorporarse al genoma de la célula huésped.
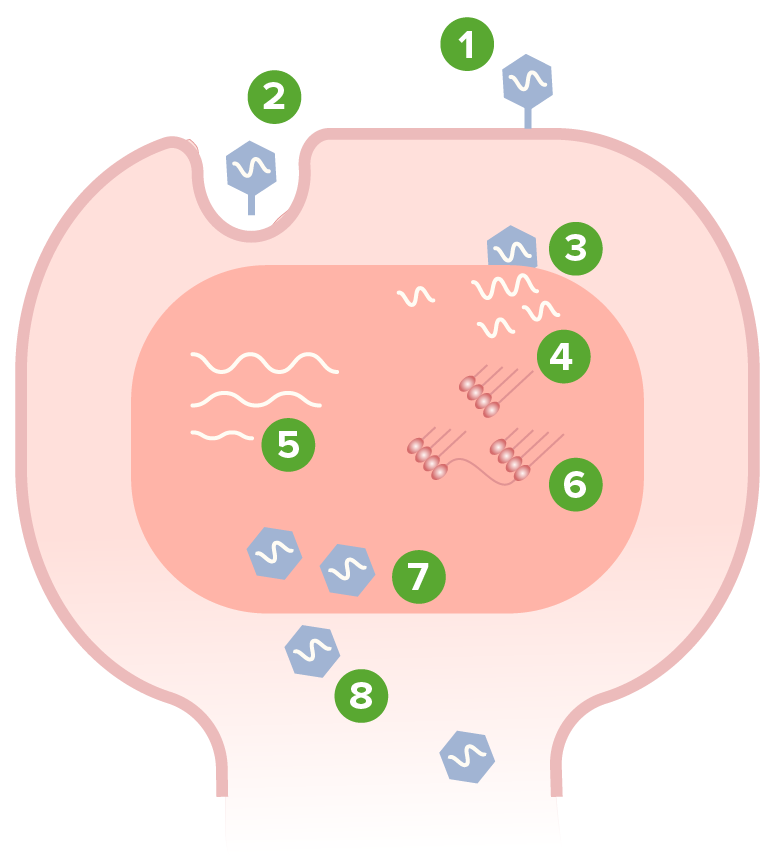
Patogénesis del parvovirus humano B19 (ciclo de replicación):
1. El virus se une a la célula huésped.
2. Penetración/endocitosis
3. Desprendimiento de la cápside viral
4. Replicación del ADN
5. Transcripción del ADN en ARN
6. Traducción del ARN a proteínas
7. Ensamblaje en unidades virales
8. Lisis celular
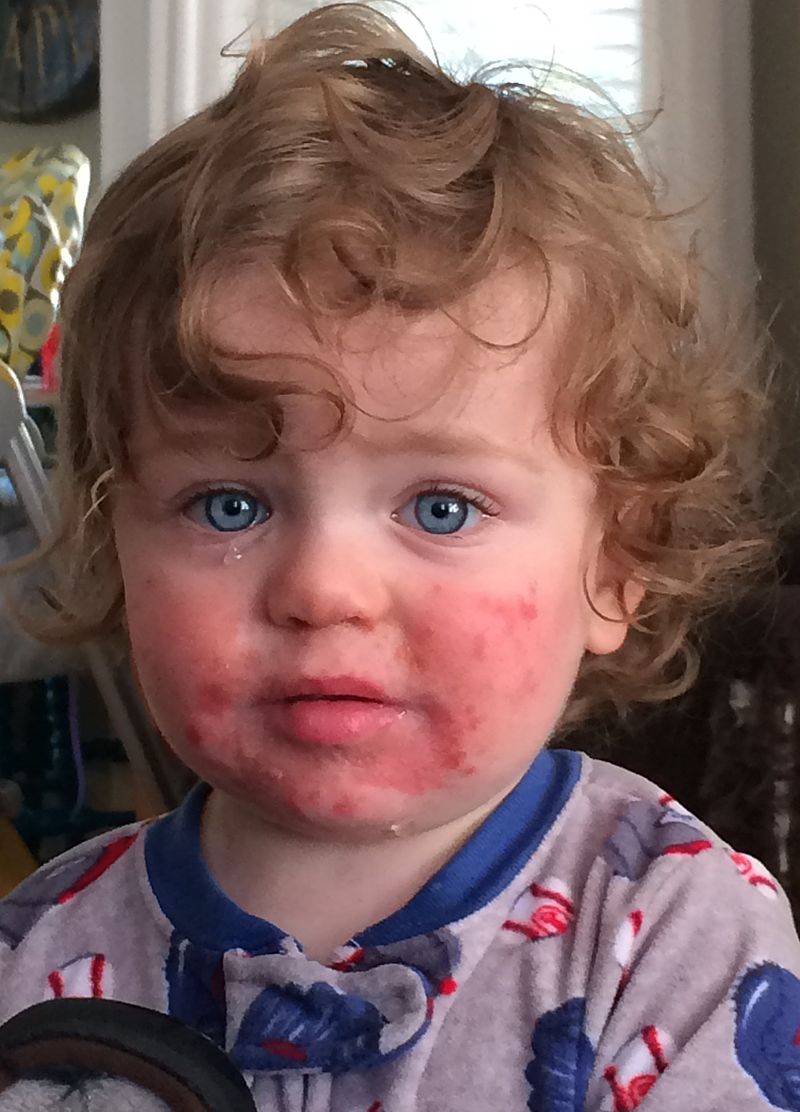
“Erupción de mejilla abofeteada”:
También llamada eritema infeccioso, esta erupción característica se observa en las infecciones por parvovirus B19, o 5ta enfermedad, en individuos inmunocompetentes. La erupción maculopapular es eritematosa y pruriginosa; comienza con una distribución malar y a menudo se extiende a las extremidades.
Aplasia Aplasia Cranial Nerve Palsies pura de eritrocitos:
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las personas con hemoglobinopatías (e.g., enfermedad de células falciformes) puede producirse una crisis aplásica transitoria:
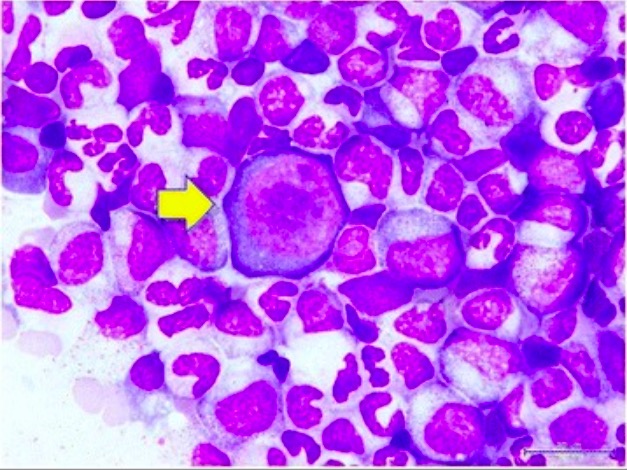
Histología de la médula ósea durante la crisis aplásica transitoria en la infección por parvovirus B19:
La imagen muestra la citología de la médula ósea. La flecha amarilla indica un pronormoblasto gigante.
| Número | Otros nombres de la enfermedad | Etiología | Síntomas | Descripción de la erupción |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1ra enfermedad |
|
Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology del sarampión |
|
La erupción maculopapular Maculopapular Dermatologic Examination comienza en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la cara y detrás de las orejas → se extiende al AL Amyloidosis tronco/extremidades |
| 2da enfermedad |
|
Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus pyogenes |
|
|
| 3ra enfermedad |
|
Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la rubéola |
|
Máculas discretas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la cara → se extienden al AL Amyloidosis cuello, tronco y extremidades |
| 4ta enfermedad |
|
|
Erupción |
|
| 5ta enfermedad |
|
Parvovirus (eritrovirus) B19 | Erupción |
|
| 6ta enfermedad | Herpesvirus humano 6B o herpesvirus humano 7 |
|
|