Los LOS Neisseria órganos linfoides secundarios, también llamados órganos linfoides/linfáticos periféricos, incluyen el tejido linfoide asociado a mucosas ( MALT MALT Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés), los LOS Neisseria nódulos linfáticos y el bazo. Estas colecciones de tejidos linfoides proporcionan una vigilancia constante de los LOS Neisseria patógenos. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum sus distintos sitios, estos tejidos están llenos de células inmunitarias listas para montar una respuesta cuando se detectan antígenos. Los LOS Neisseria nódulos linfáticos se ven a lo largo de los LOS Neisseria vasos linfáticos y se presentan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cadenas o grupos (cuello, ingle, axilas, mesenterios, abdomen). Los LOS Neisseria MALT MALT Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy actúan como sensores inmunitarios situados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum lugares donde la luz está expuesta al AL Amyloidosis entorno externo (orofaringe, tracto gastrointestinal, tracto genitourinario). El bazo es el sitio de producción de anticuerpos y linfocitos, pero también ayuda en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la descomposición de plaquetas y eritrocitos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El sistema linfático (vasos linfáticos, líquido linfático y órganos linfoides) es parte del sistema inmunológico del cuerpo.
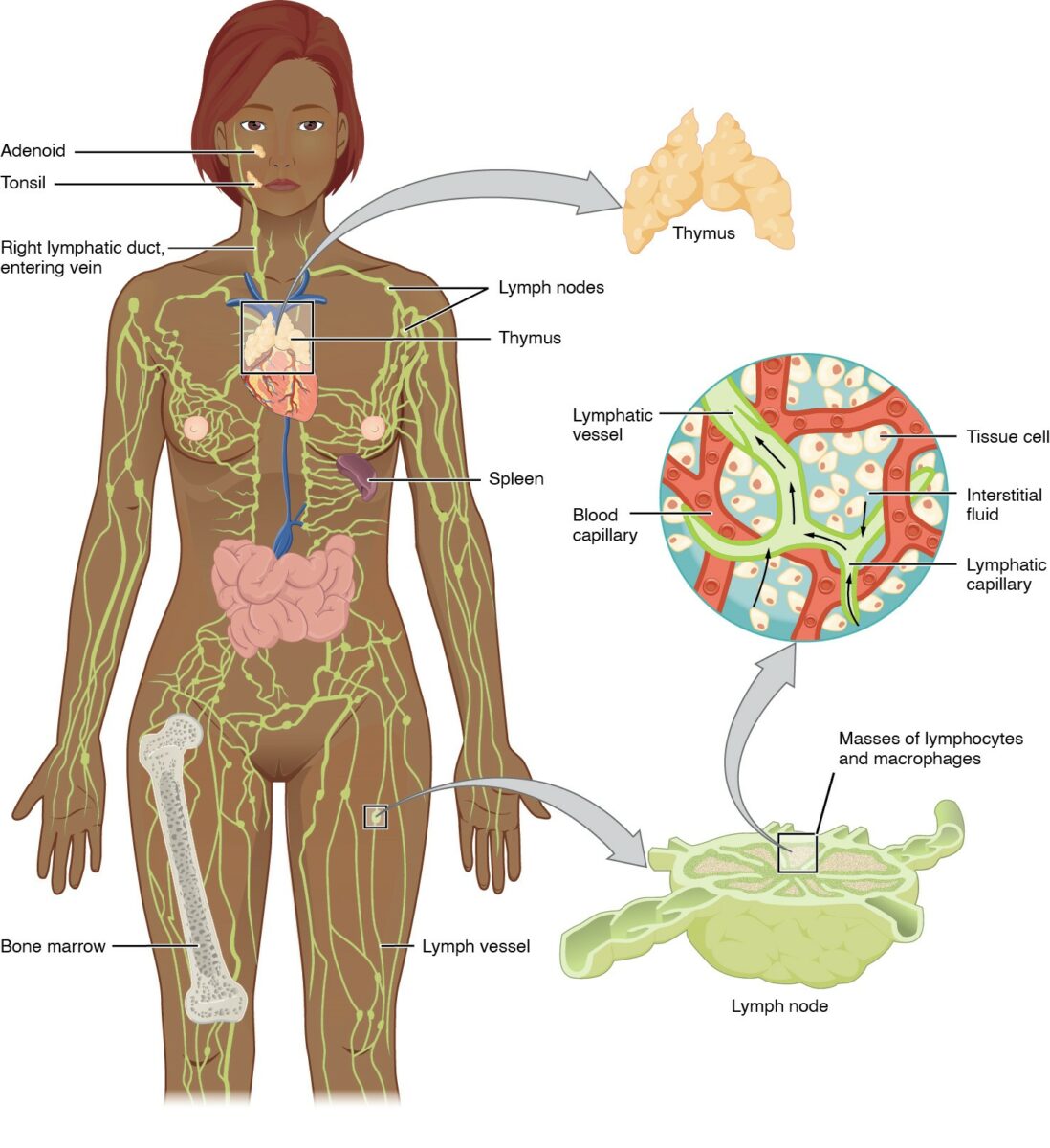
Anatomía del sistema linfático:
Incluye los órganos linfoides primarios (médula ósea, timo) y secundarios (bazo, ganglios linfáticos y MALT)
Los vasos linfáticos transportan linfa a los vasos linfáticos más grandes del tórax, transportando líquido de vuelta a la circulación venosa.
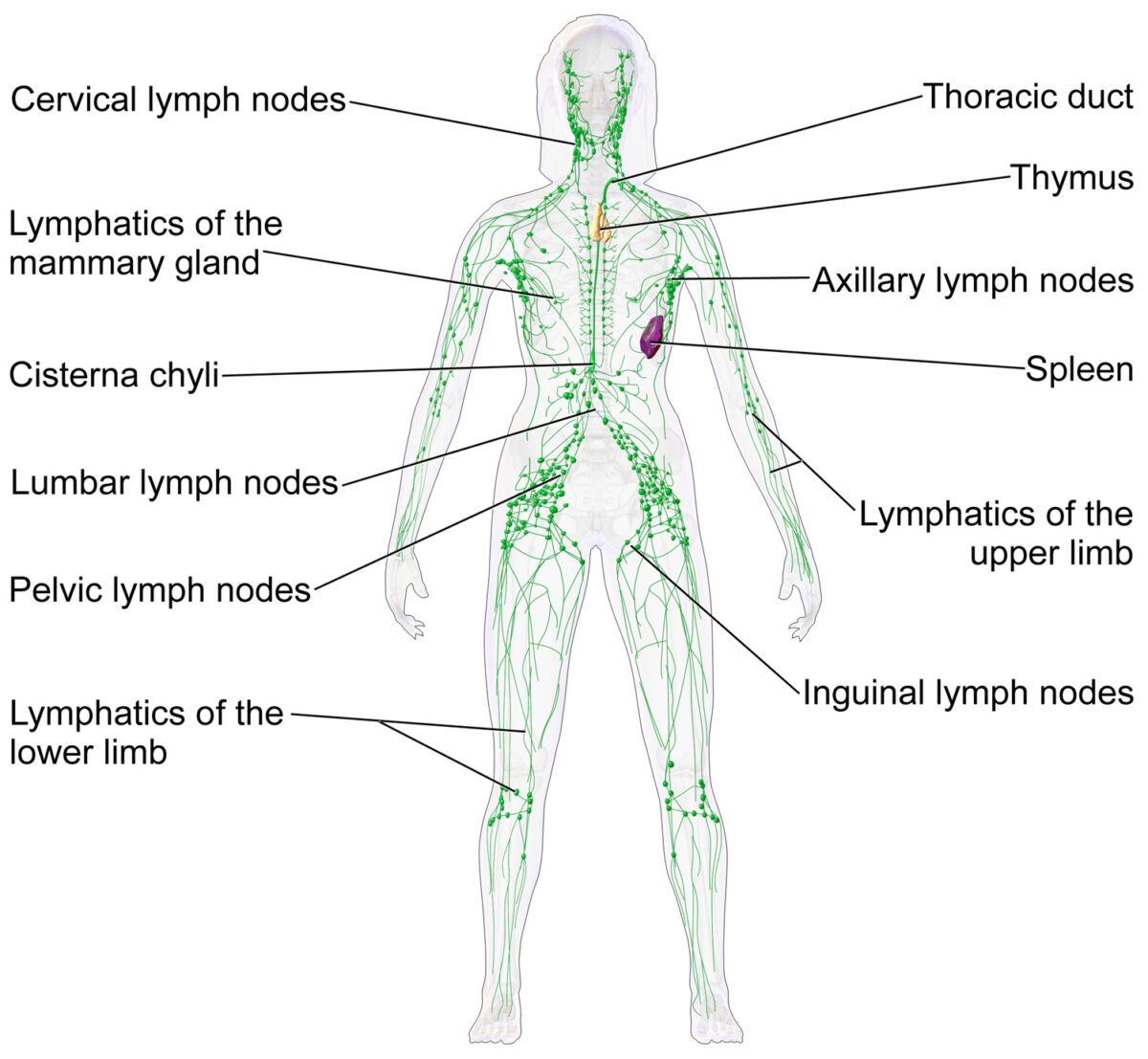
Nódulos linfáticos y el sistema linfático
Imagen: “Blausen 0623 LymphaticSystem Female” por Blausen Licencia: CC BY 3.0La función principal de los LOS Neisseria nódulos linfáticos es la defensa contra la propagación de microorganismos y células tumorales:
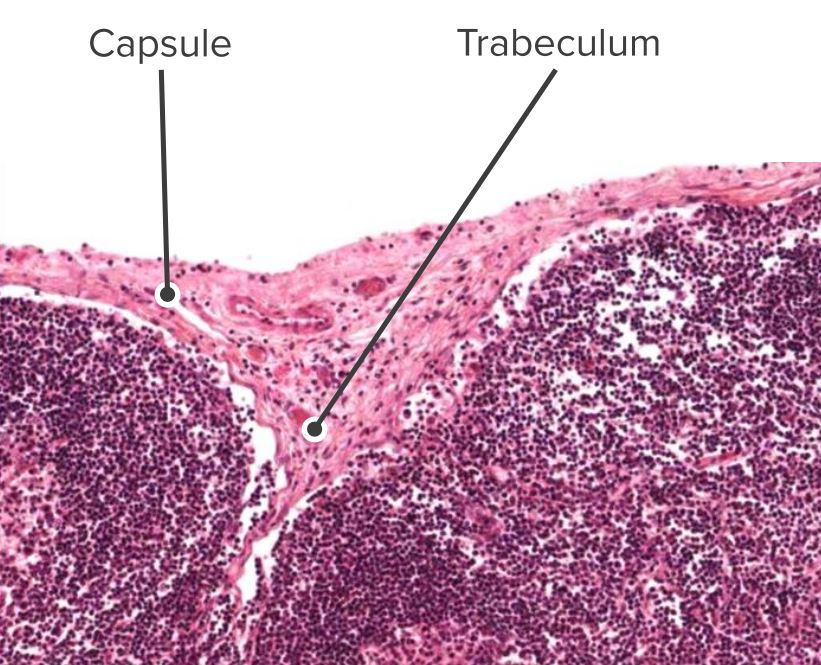
Corte histológico de un nódulo linfático, identificando la cápsula y las trabéculas
Imagen por Geoffrey Meyer, editado por Lecturio.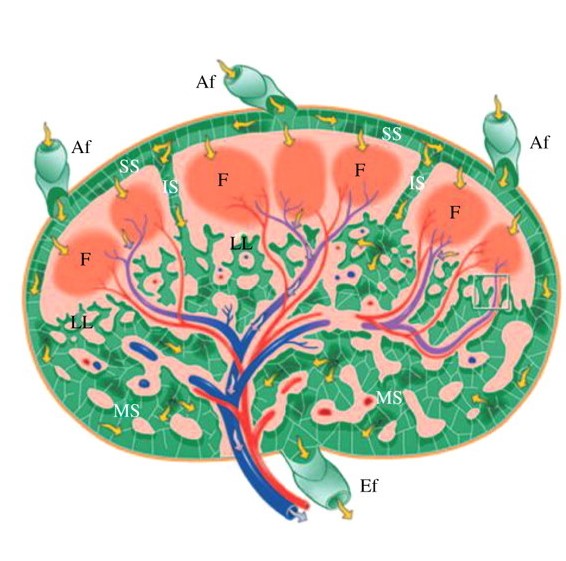
Ilustración de una sección transversal de un ganglio linfático:
El rojo y el azul indican arterias y venas, respectivamente. Las flechas amarillas indican el flujo linfático.
Af: vasos aferentes
Ef: vasos eferentes
F: folículo
IS: senos intermedios
LL: laberinto linfático
MS: senos medulares
SS: senos subcapsulares
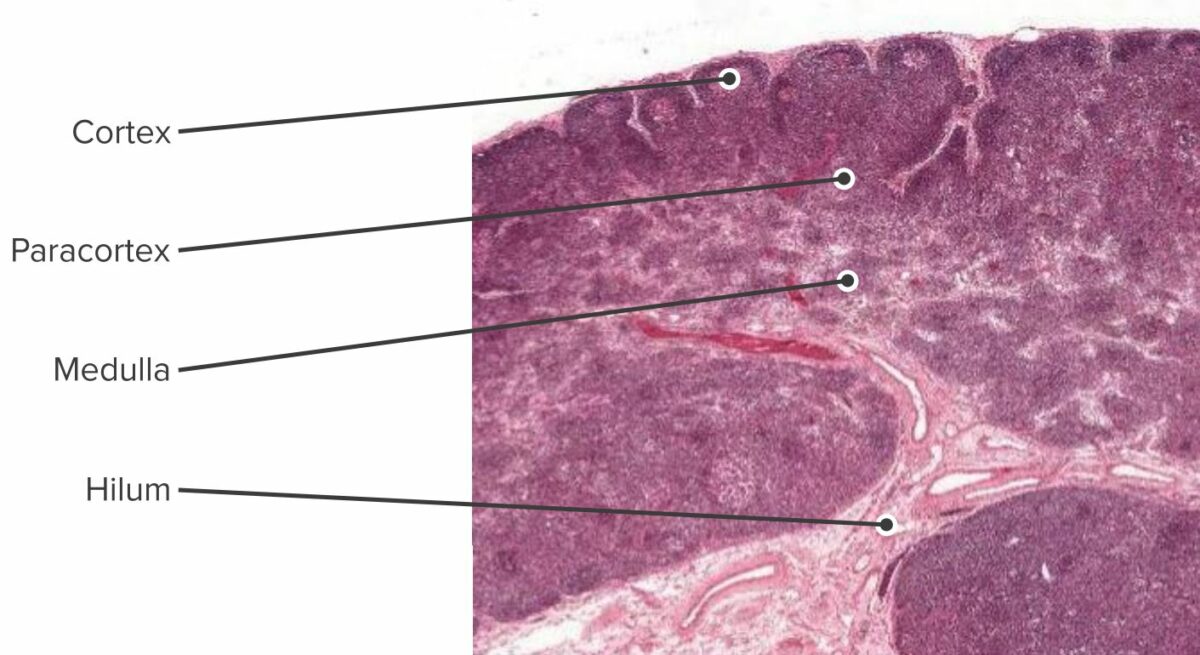
Sección histológica del ganglio linfático que muestra la corteza, paracorteza y médula
Imagen por Geoffrey Meyer, editado por Lecturio.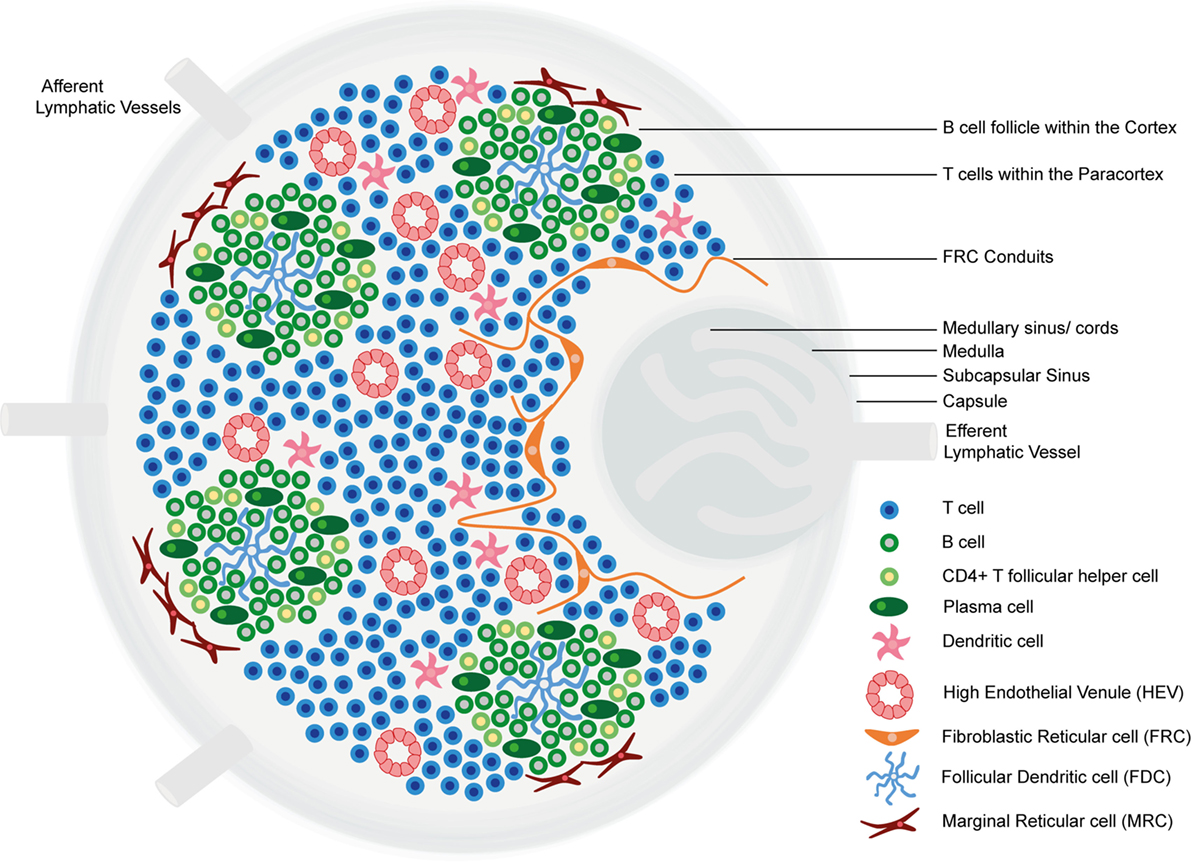
Estructura y regiones funcionales de un ganglio linfático que comprende una cápsula fibrosa rica en colágeno y un seno subcapsular subyacente (SCS).
Las células se segregan en (1) la corteza (que consiste de linfocitos B, linfocitos T cooperadores foliculares y células dendríticas foliculares dispuestas en folículos primarios, en los que los linfocitos B examinan los antígenos presentados en la red estromal de células dendríticas foliculares); y en (2) la paracorteza (que aloja a linfocitos T, células dendríticas y células reticulares fibroblásticas, que forman redes de células estromales y fibras reticulares).
La médula interna está compuesta por tejidos linfáticos (cordones medulares) separados por senos medulares compuestos por linfa.
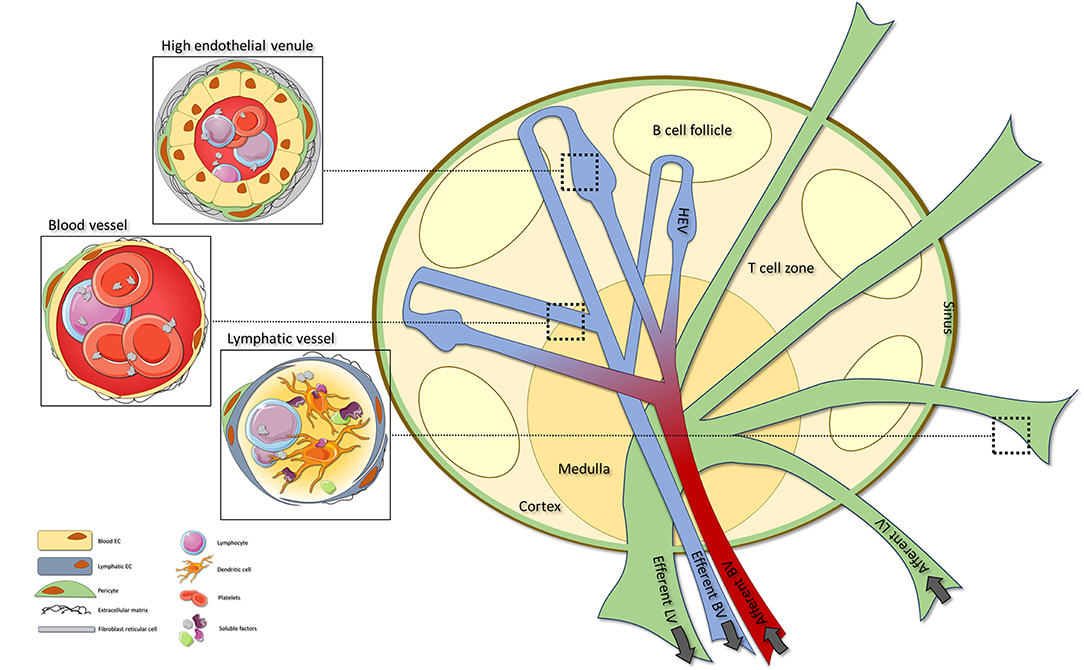
Estructura vascular de los ganglios linfáticos:
Consiste en vasos sanguíneos (BV), vénulas endoteliales altas (HEV) y vasos linfáticos (LV).
Se pueden encontrar vasos sanguíneos en todo el ganglio linfático, con HEV especializados ubicados dentro de las áreas de células T. Las vénulas endoteliales altas son vasos sanguíneos especializados que orquestan la extravasación de linfocitos en el ganglio linfático. Los vasos linfáticos aferentes ingresan al ganglio linfático, donde transitan hacia los senos que finalmente salen a través del vaso linfático eferente.
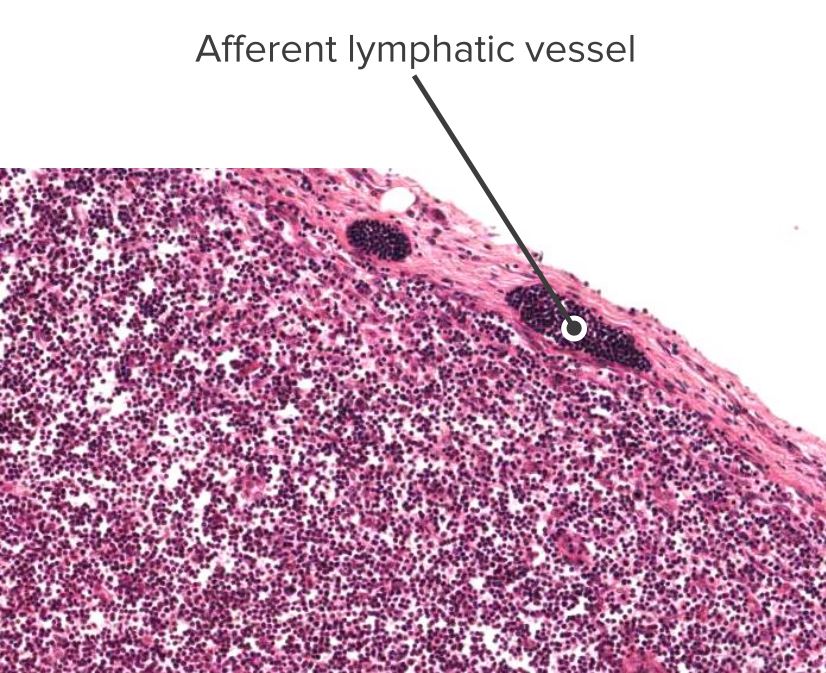
Sección histológica de un nódulo linfático que muestra un vaso linfático aferente
Imagen por Geoffrey Meyer, editado por Lecturio.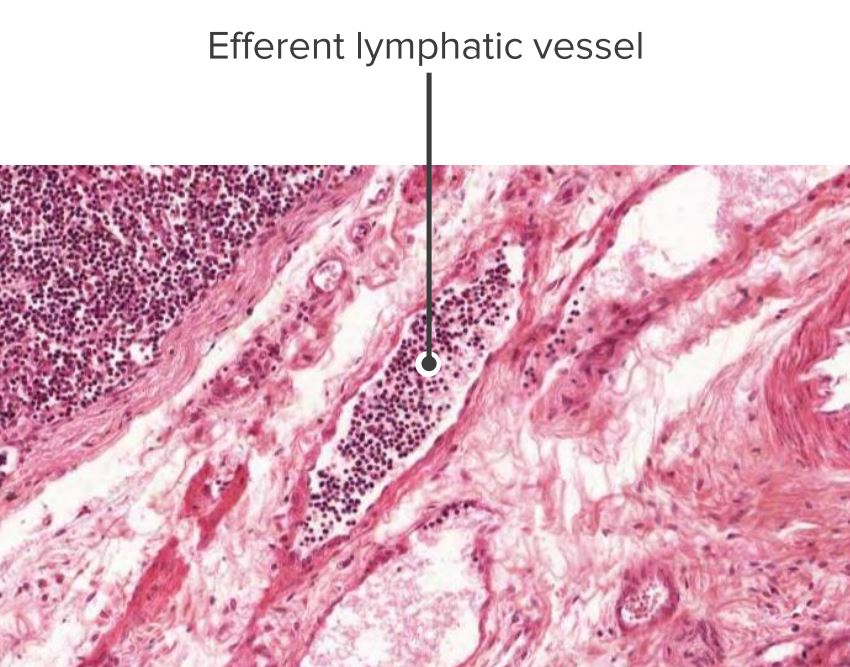
Sección histológica de un nódulo linfático que muestra un vaso linfático eferente
Imagen por Geoffrey Meyer, editado por Lecturio.Montar una respuesta inmune contra los LOS Neisseria patógenos que se encuentran en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la mucosa de los LOS Neisseria tractos gastrointestinal, respiratorio y genitourinario.
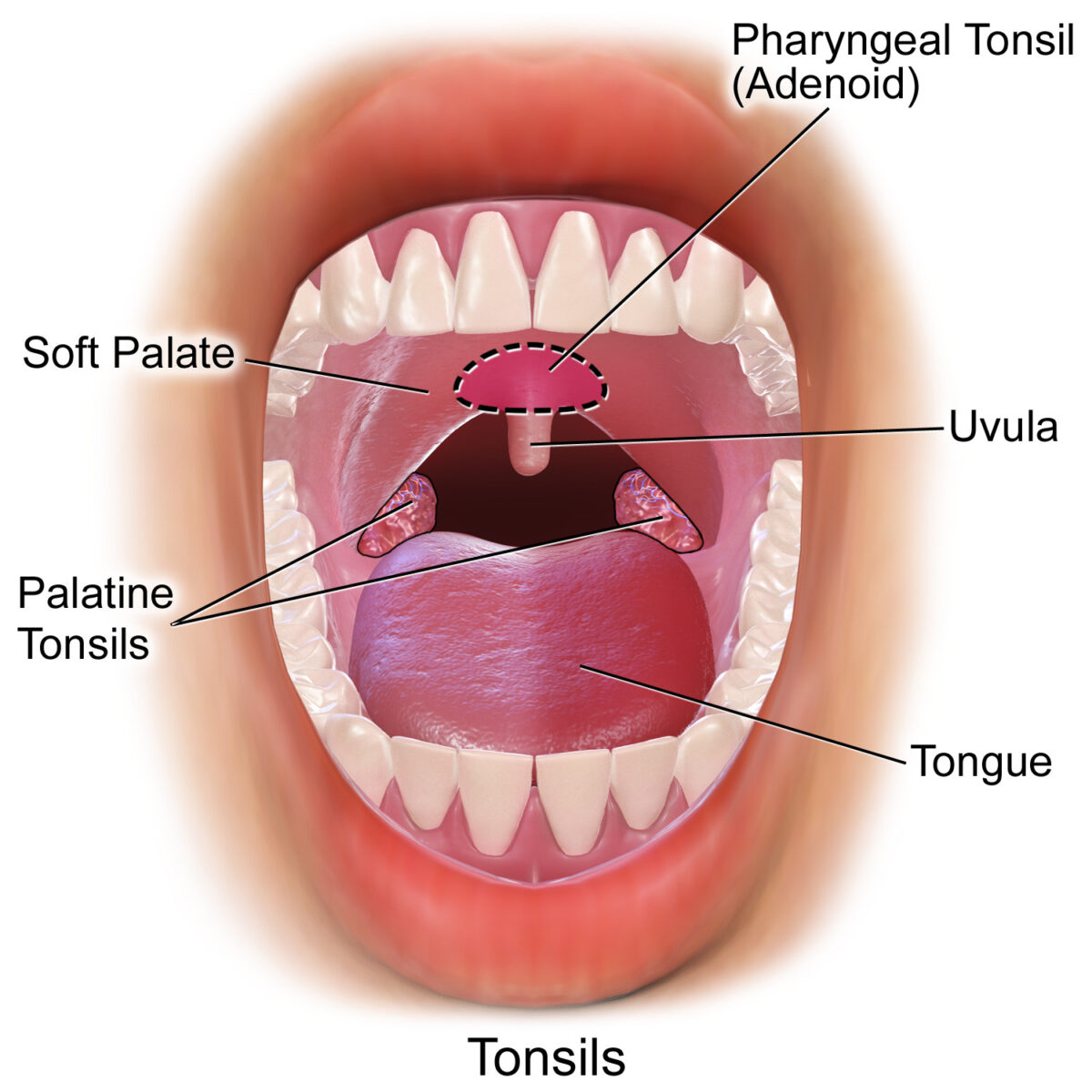
Amígdalas en el área orofaríngea, vista frontal:
Amígdalas faríngeas, palatinas y linguales
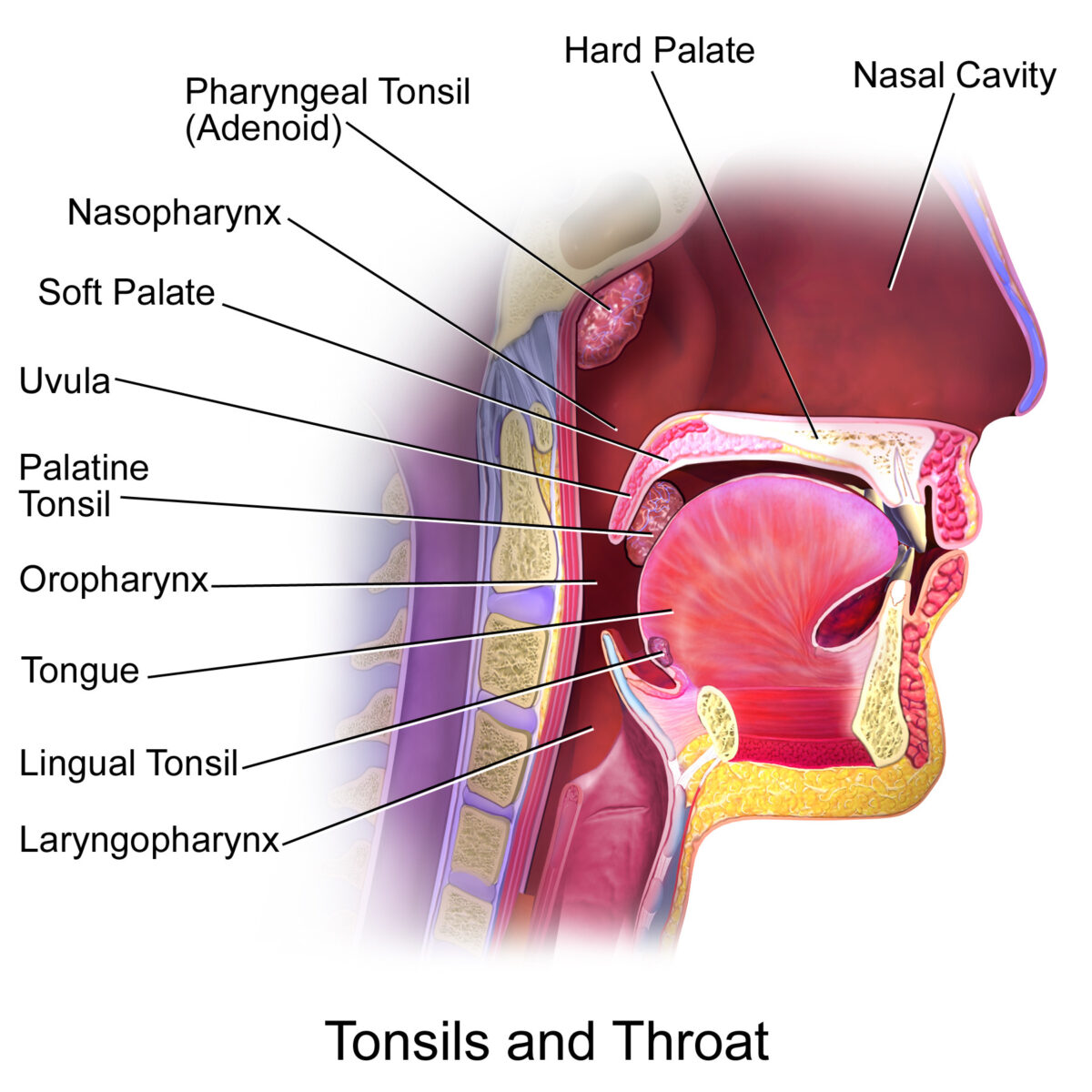
Amígdalas en el área orofaríngea, vista lateral:
Amígdalas faríngeas, palatinas y linguales.
Las amígdalas tubáricas (no representadas) se encuentran en el área de la nasofaringe.
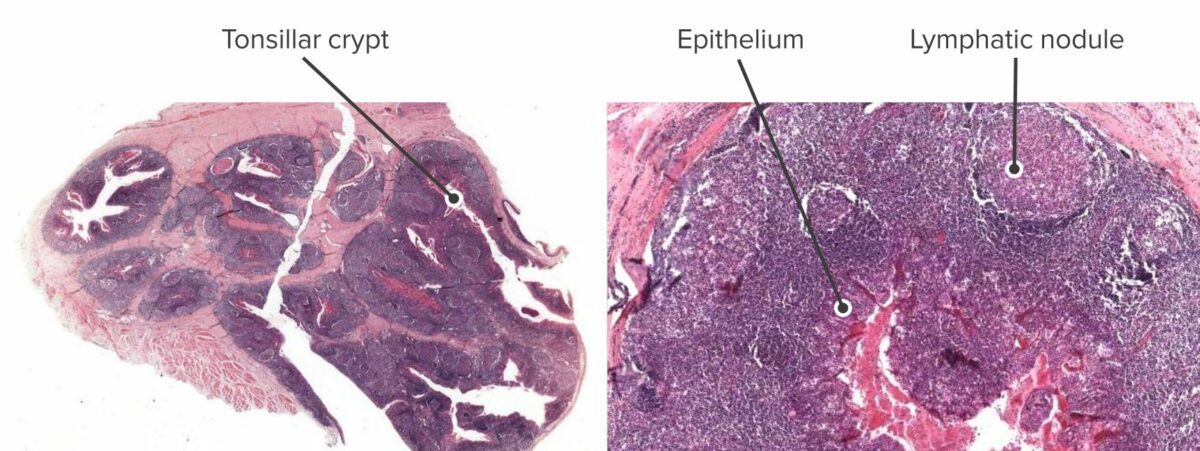
Corte transversal de una amígdala (izquierda) y primer plano de la parte inferior de una cripta amigdalina (derecha).
A la derecha se aprecia un nódulo linfático (tejido linfoide activado) muy cerca del fondo de la cripta.
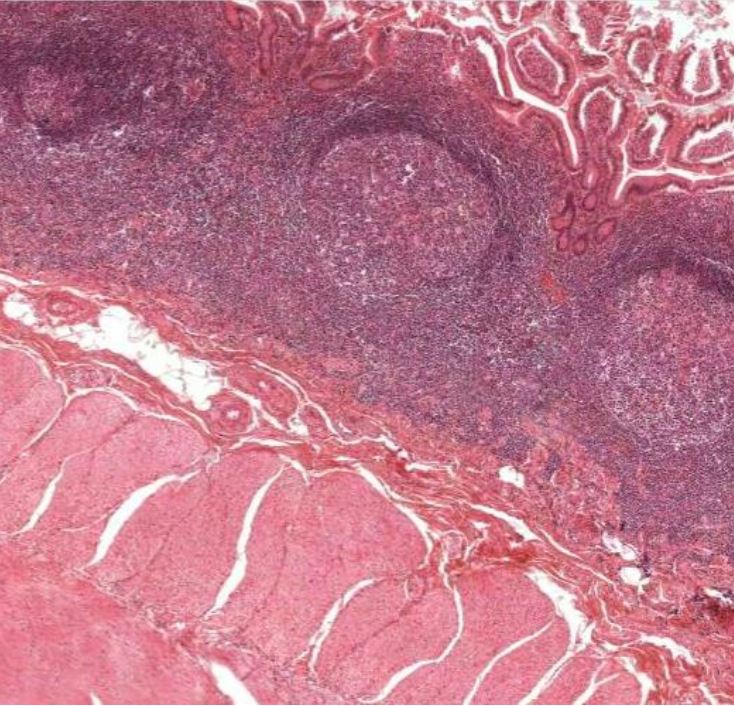
Sección histológica del íleon que muestra las placas de Peyer
Imagen por Geoffrey Meyer.
Sección transversal de un apéndice:
Los nódulos linfoides pueden verse reaccionando a un antígeno de la luz.
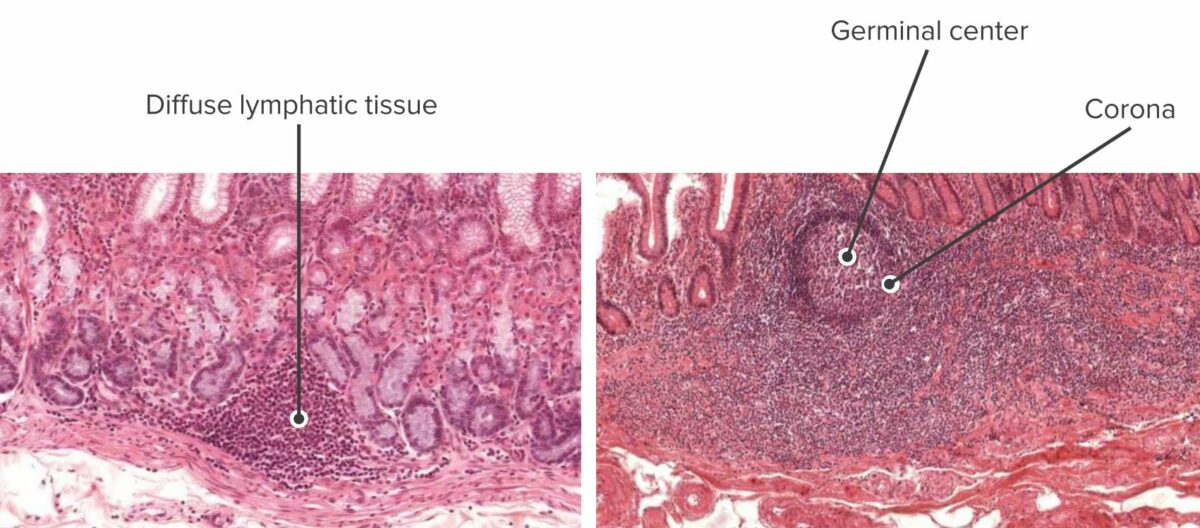
Sección transversal de la mucosa del estómago que muestra tejido linfoide inactivo (izquierda) y sección transversal de la mucosa del intestino que muestra tejido linfoide activo (derecha):
Los tejidos linfoides protegen hasta que se activan y se forman nódulos, con centros germinales.
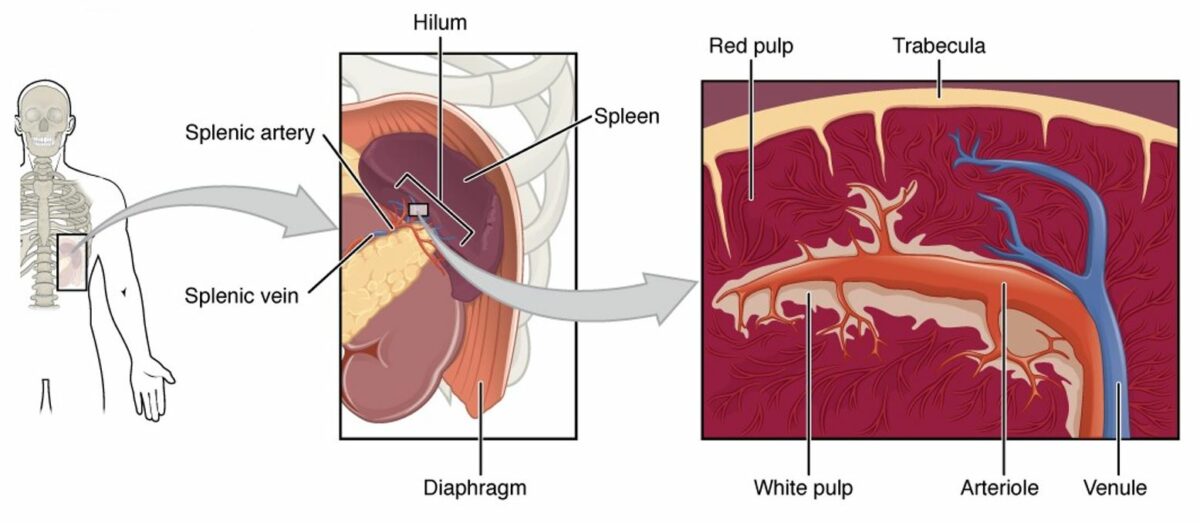
Diagrama del bazo (de izquierda a derecha):
El bazo es un órgano altamente vascularizado en el cuadrante superior izquierdo del abdomen.
El hilio es el área donde entra la arteria esplénica y la vena esplénica sale del bazo. Una sección transversal del bazo mostraría que la mayor parte del parénquima esplénico contiene pulpa roja (llena de todo tipo de elementos formes de la sangre). La pulpa blanca contiene principalmente nódulos linfoides y la vaina linfoide periarteriolar, que rodean la arteriola central.
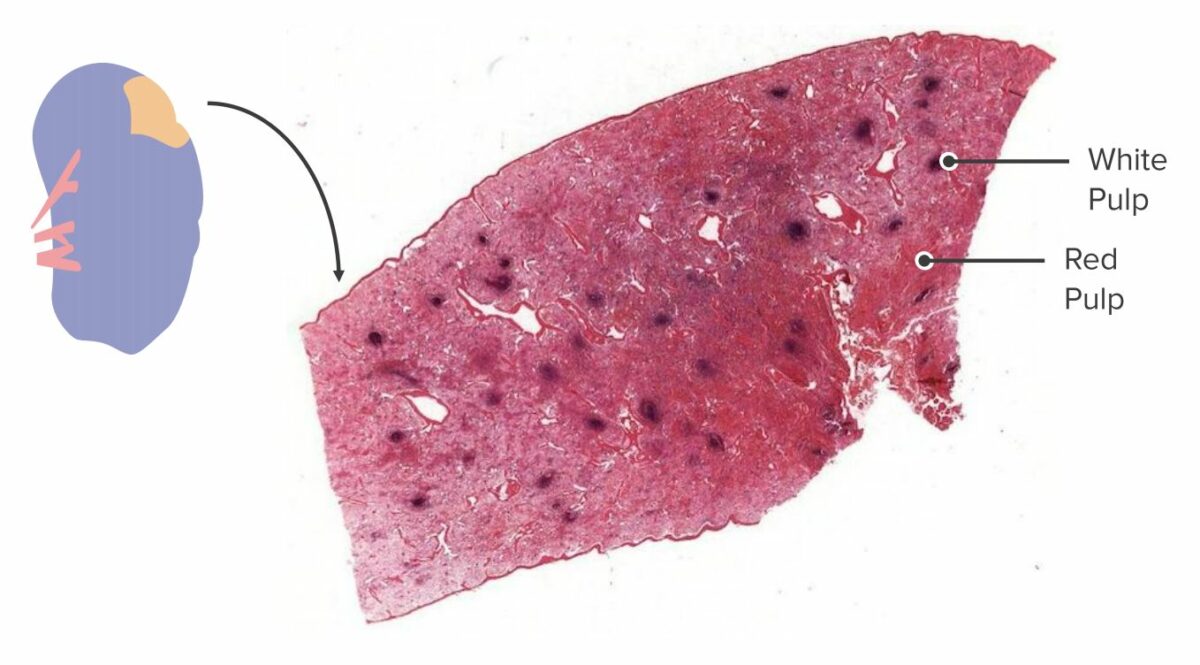
Sección transversal de un bazo:
En un espécimen macroscópico, la pulpa blanca y la pulpa roja se pueden identificar y diferenciar debido a su diferencia de color y ubicación. La pulpa blanca se aglomera alrededor de los vasos sanguíneos, mientras que la pulpa roja constituye el resto del parénquima.

Corte histológico del bazo:
La vaina linfoide periarterial (PALS) envuelve una arteriola central. Se formó un nódulo linfoide, rodeado de células T, lo que indica que se detectó un antígeno en el suministro de sangre del bazo y se inició una respuesta inmunitaria.