La neurofibromatosis tipo 2 es un trastorno neurocutáneo que puede surgir de las mutaciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el gen NF2 NF2 Neurofibromatosis type 2 is a neurocutaneous disorder that can arise from mutations in the NF2 gene located in chromosome 22 and may be inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion or occur from de novo mutations. The main clinical features are bilateral vestibular schwannomas, intracranial/spinal meningioma, and intramedullary and extramedullary spinal tumors. Neurofibromatosis Type 2 localizado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cromosoma 22 y puede heredarse de forma autosómica dominante o deberse a mutaciones de novo. Las características clínicas principales son los LOS Neisseria schwannomas vestibulares bilaterales, el meningioma Meningioma Meningiomas are slow-growing tumors that arise from the meninges of the brain and spinal cord. The vast majority are benign. These tumors commonly occur in individuals with a history of high doses of skull radiation, head trauma, and neurofibromatosis 2. Meningioma intracraneal/espinal y los LOS Neisseria tumores espinales intramedulares y extramedulares. Otras características pueden incluir lesiones oculares como cataratas, lesiones cutáneas y neuropatía periférica. El diagnóstico se realiza clínicamente a partir de los LOS Neisseria antecedentes y el examen físico y se confirma con resonancia magnética (RM), pruebas moleculares e histopatología. Se recomienda la vigilancia del tumor Tumor Inflammation y el seguimiento con tamizaje cuando se detecta en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum familiares en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum riesgo. El tratamiento incluye intervenciones quirúrgicas, radioterapia y/o terapia de anticuerpos monoclonales con bevacizumab Bevacizumab An anti-vegf humanized murine monoclonal antibody. It inhibits vegf receptors and helps to prevent pathologic angiogenesis. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La presentación clínica de la neurofibromatosis tipo 2 puede variar ampliamente entre los LOS Neisseria individuos con mutaciones de novo y familias portadoras de mutaciones genéticas. Las edades de inicio a menor edad a menudo se asocian con una presentación atípica con síntomas más graves.
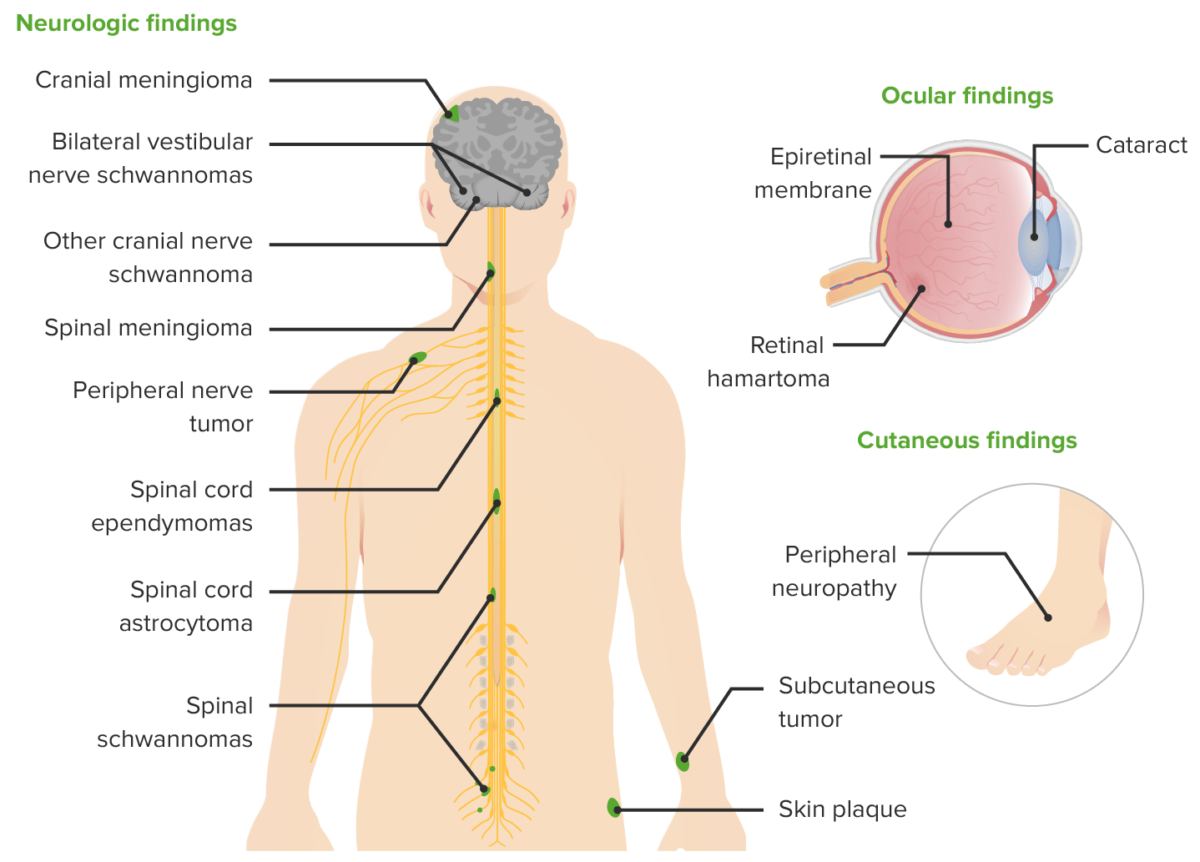
Manifestaciones clínicas de la neurofibromatosis tipo 2
Imagen por Lecturio.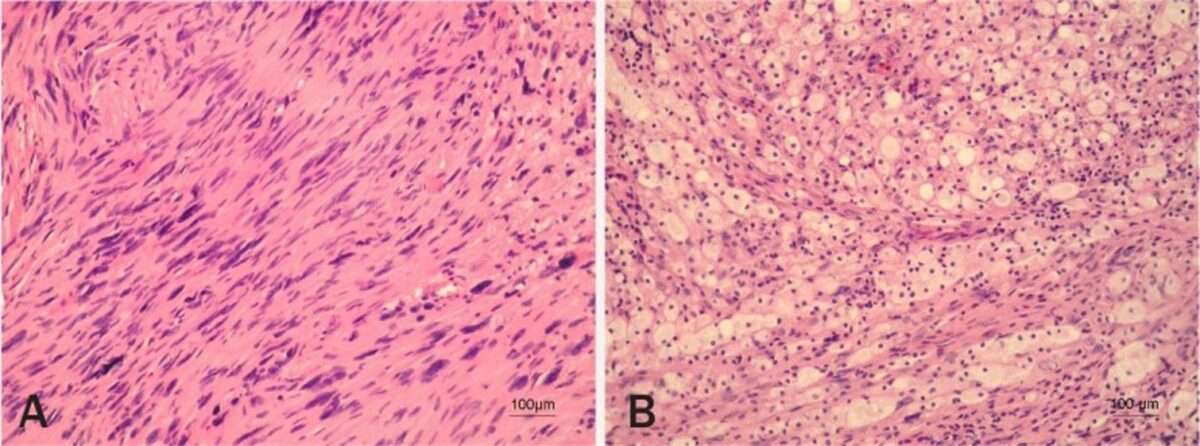
Histopatología del schwannoma vestibular
Imagen: “Vestibular schwannoma” por Pećina-Slaus N, Zeljko M, Pećina HI, Nikuseva Martić T, Bacić N, Tomas D, Hrasćan R. Licencia: CC BY 2.5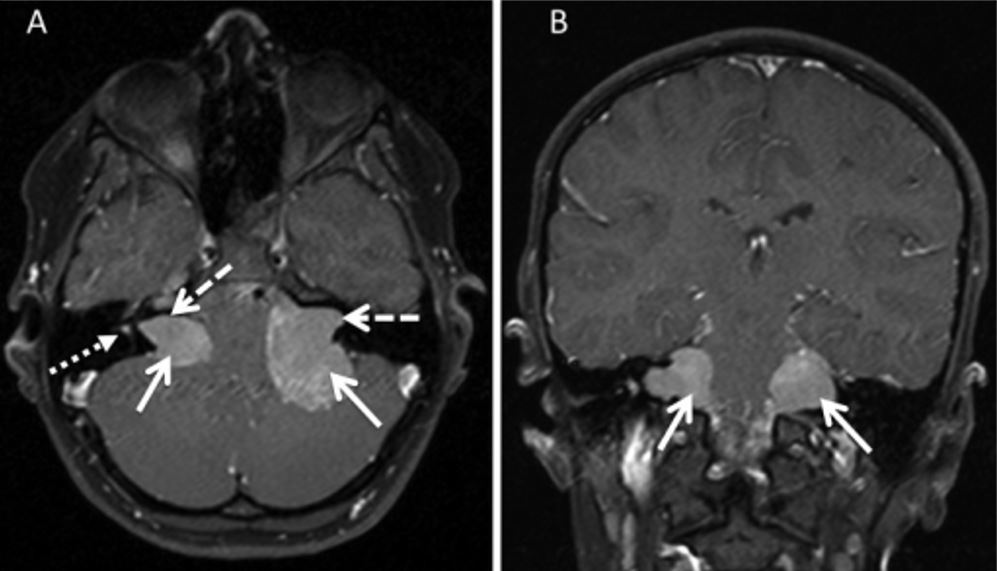
Schwannoma vestibular bilateral en RM
Imagen: “T1 spin echo sequences” por Stivaros SM, et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0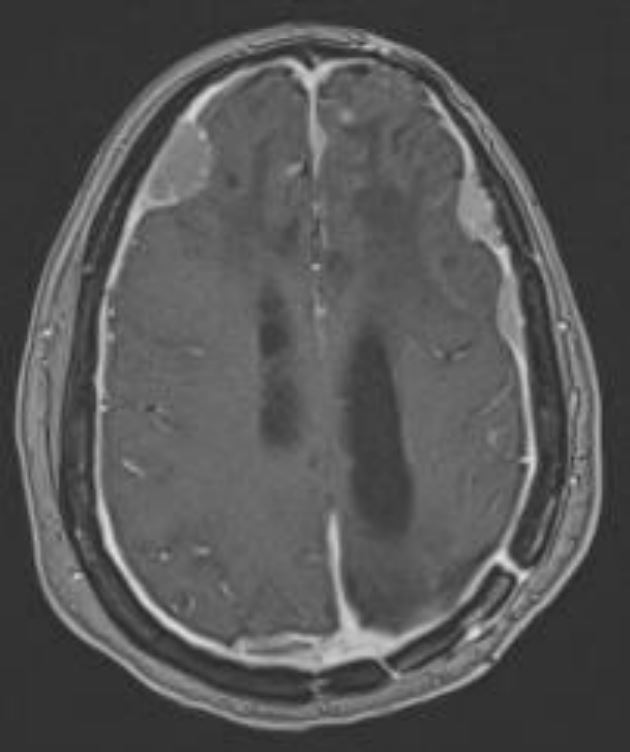
Meningioma intracraneal
Imagen por Roy Strowd, MD.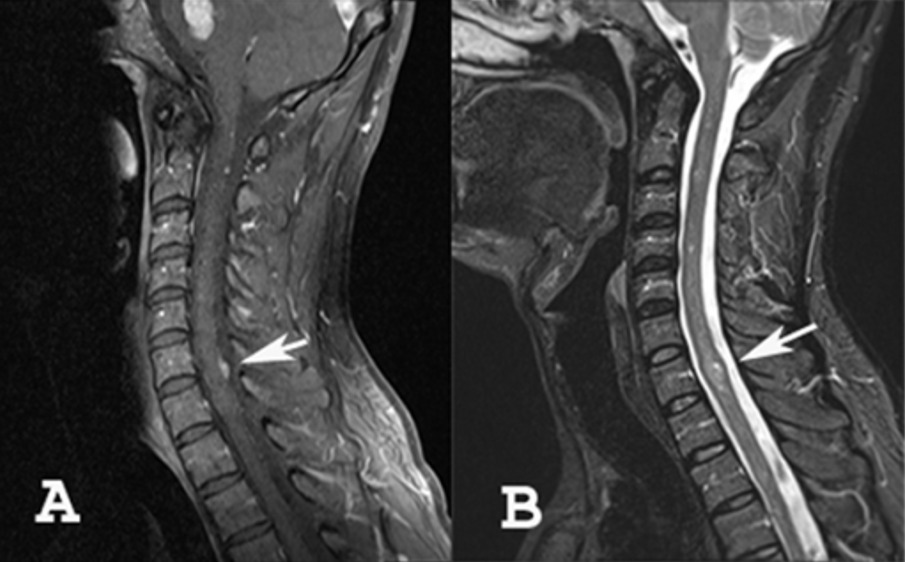
A: RM que muestra un meningioma de la columna cervical
B: RM que muestra un tumor intramedular (ependimoma o astrocitoma)
El tratamiento de la neurofibromatosis tipo 2 es multidisciplinario y, a menudo, involucra contribuciones de múltiples especialistas.