La neurofibromatosis tipo 1 ( NF1 NF1 Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), also known as phakomatosis, is a neurocutaneous disorder that is most commonly of autosomal dominant inheritance due to mutations in the NF1 gene. Neurofibromatosis type 1 presents a range of clinical manifestations with the most prominent features being various pigmented skin lesions called café au lait macules (CALMs), neurofibromas, freckling of the inguinal and axillary regions, and iris hamartomas. Neurofibromatosis Type 1), también conocida como facomatosis, es un trastorno neurocutáneo que es más comúnmente de herencia autosómica dominante debido a mutaciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el gen NF1 NF1 Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), also known as phakomatosis, is a neurocutaneous disorder that is most commonly of autosomal dominant inheritance due to mutations in the NF1 gene. Neurofibromatosis type 1 presents a range of clinical manifestations with the most prominent features being various pigmented skin lesions called café au lait macules (CALMs), neurofibromas, freckling of the inguinal and axillary regions, and iris hamartomas. Neurofibromatosis Type 1. La neurofibromatosis tipo 1 presenta una serie de manifestaciones clínicas, siendo las características más destacadas diversas lesiones cutáneas pigmentadas denominadas máculas café con leche, tumores benignos de la vaina nerviosa denominados neurofibromas, pecas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las regiones inguinales y axilares y hamartomas del iris, denominados como nódulos de Lisch. Al AL Amyloidosis menos la mitad de los LOS Neisseria pacientes con NF1 NF1 Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), also known as phakomatosis, is a neurocutaneous disorder that is most commonly of autosomal dominant inheritance due to mutations in the NF1 gene. Neurofibromatosis type 1 presents a range of clinical manifestations with the most prominent features being various pigmented skin lesions called café au lait macules (CALMs), neurofibromas, freckling of the inguinal and axillary regions, and iris hamartomas. Neurofibromatosis Type 1 tienen problemas del aprendizaje. La neurofibromatosis tipo 1 también puede causar osteodisplasia y transformación maligna de tumores. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la presentación clínica típica y se puede confirmar mediante pruebas genéticas. El tratamiento depende de la presentación clínica y puede variar desde la extirpación quirúrgica hasta la quimioterapia/radioterapia para tumores, terapia ocupacional y fisioterapia para alteraciones motoras, tratamiento con hormona del crecimiento y ortesis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el caso de anomalías óseas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
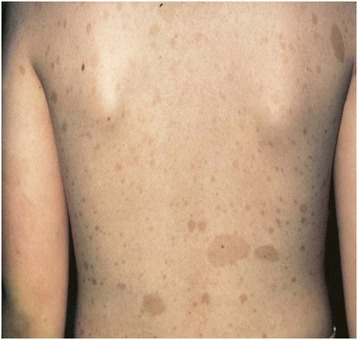
Máculas café con leche:
Imagen que muestra máculas café con leche bien delimitadas, de color marrón claro y pigmentadas que se encuentran comúnmente en la población general. Las máculas pueden ser de unos pocos milímetros a varios centímetros (> 20 cm) de tamaño y pueden aparecer al nacer o en los primeros años de vida. El desarrollo de múltiples máculas café con leche puede estar asociado con síndromes genéticos como el neurofibroma tipo 1. Las máculas se pueden tratar con terapia láser con fines cosméticos.
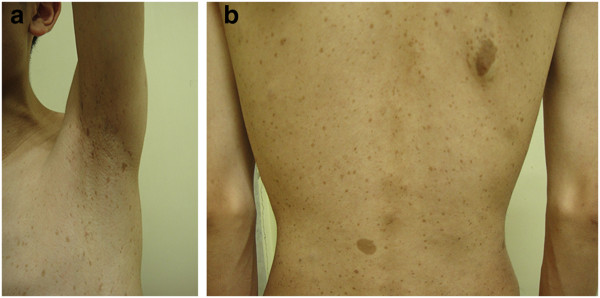
Pecas axilares y máculas café con leche:
pecas axilares (a) y múltiples máculas café con leche (b) esparcidas sobre la piel del tronco de un paciente con neurofibroma tipo 1 (NF1)
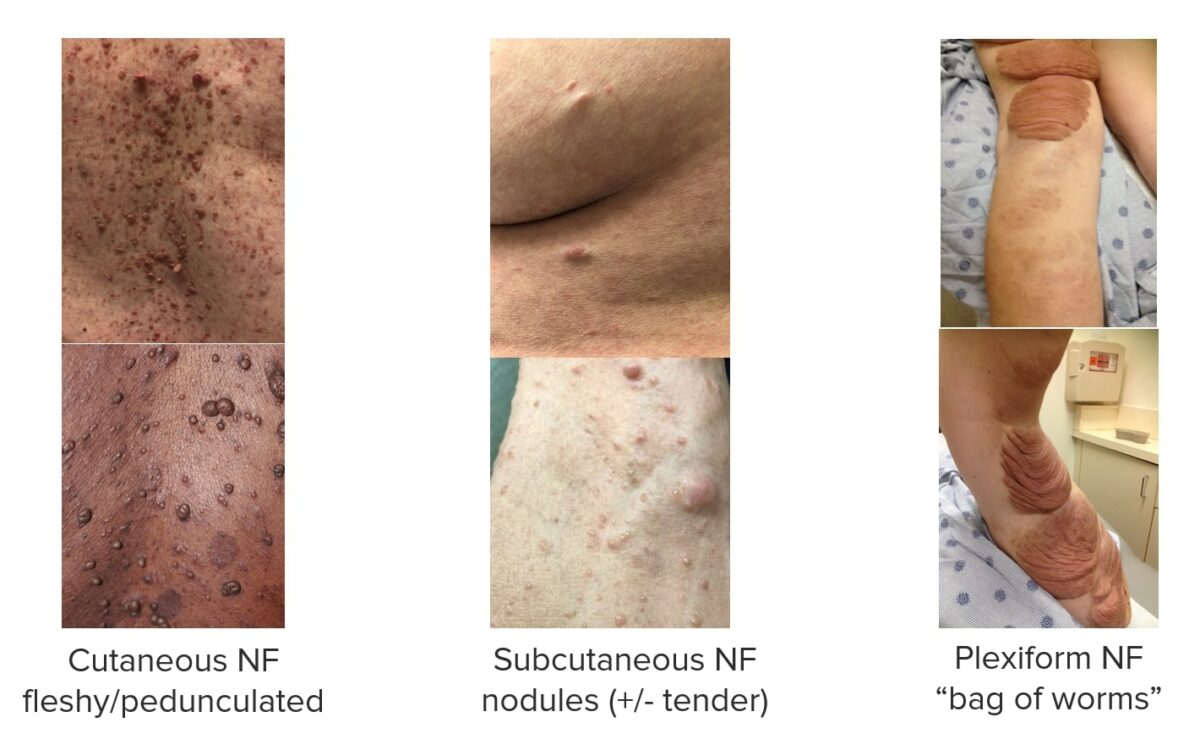
Neurofibromas (NF):
Imágenes que muestran distintos tipos de neurofibromas asociados a la NF1.
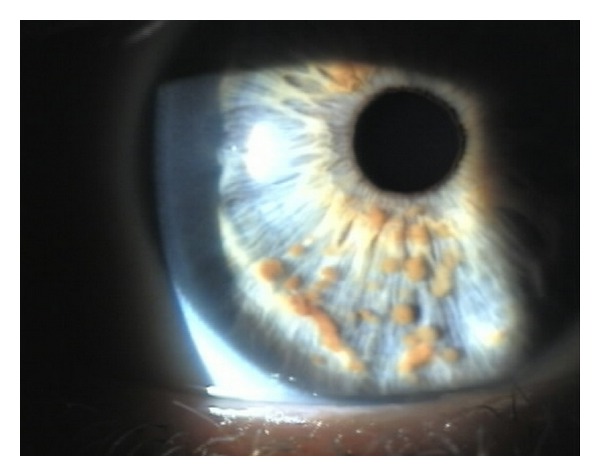
Nódulos de Lisch en el iris:
Imagen que muestra hamartomas pigmentados que se derivan de melanocitos dendríticos
Imagen: “Multiple small, oval, yellow-brown papules (Lisch nodules) in the right iris” por Adams, E. G., et al. Licencia: CC BY 3.0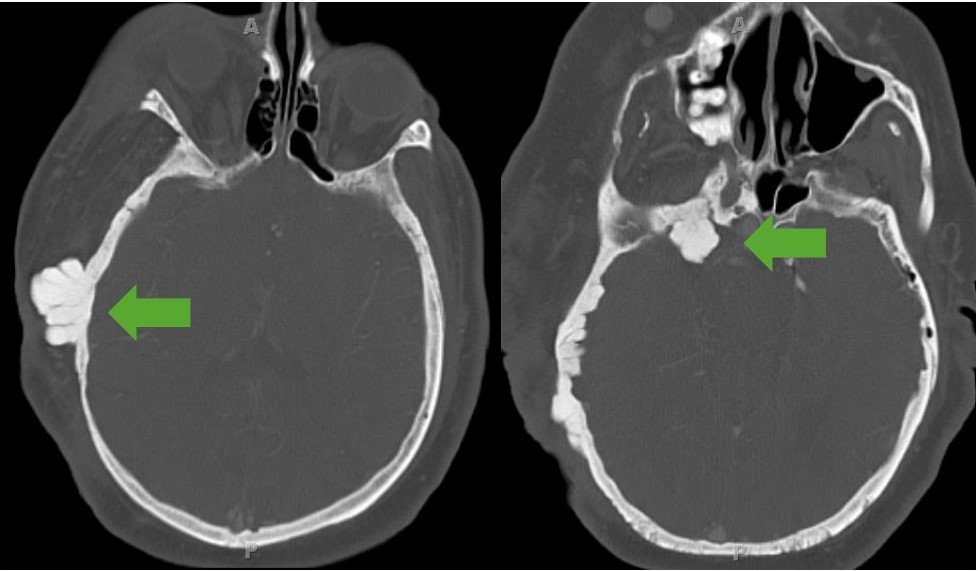
Displasia del ala esfenoidal:
Imagen de una TC que muestra displasia exofítica del hueso esfenoides. Obsérvese la afectación de los tejidos blandos que se observan como un agrandamiento de todo el lado derecho de la cara del paciente
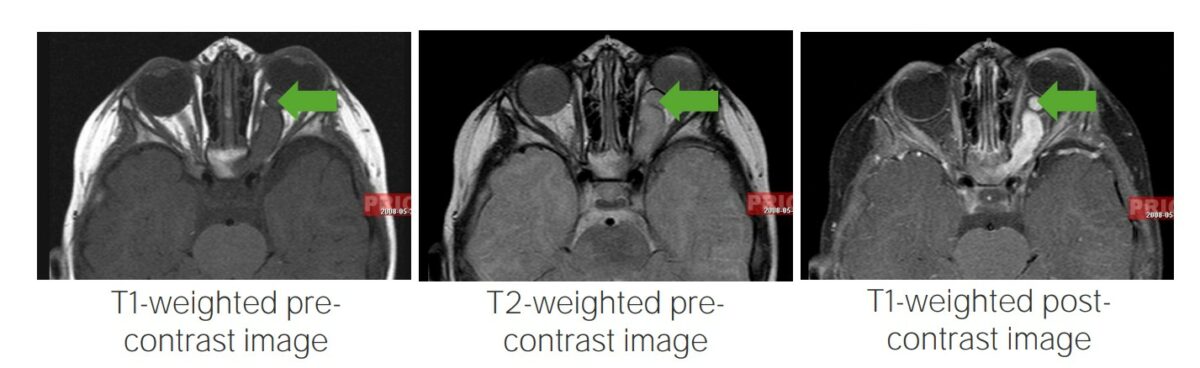
Glioma de la vía óptica:
Imágenes de resonancia magnética que muestran gliomas de la vía óptica, un hallazgo típico en pacientes con neurofibroma tipo 1
El diagnóstico de la NF1 NF1 Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), also known as phakomatosis, is a neurocutaneous disorder that is most commonly of autosomal dominant inheritance due to mutations in the NF1 gene. Neurofibromatosis type 1 presents a range of clinical manifestations with the most prominent features being various pigmented skin lesions called café au lait macules (CALMs), neurofibromas, freckling of the inguinal and axillary regions, and iris hamartomas. Neurofibromatosis Type 1 generalmente se realiza de forma clínica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de la presentación clínica típica y se confirma mediante pruebas genéticas.