La neumoconiosis es una enfermedad ocupacional que resulta de la inhalación y el depósito de polvos minerales y otras partículas inorgánicas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el pulmón. Se puede clasificar según el tipo de partícula causante implicada o por el tipo de respuesta provocada. El carbón, el sílice, el asbesto y el talco son los LOS Neisseria tipos fibrogénicos clásicos, mientras que el berilio provoca una respuesta granulomatosa y el cobalto se asocia a la neumonía de células gigantes. El hierro, el estaño y el bario se consideran tipos de partículas benignas o inertes porque no provocan el mismo tipo de reacciones que las demás. Tras la exposición a los LOS Neisseria tipos de partículas fibrogénicas, los LOS Neisseria macrófagos y los LOS Neisseria fibroblastos se activan dentro del parénquima pulmonar, lo que conduce a la inflamación crónica y a la fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans, que puede progresar hasta la insuficiencia respiratoria y la muerte. Los LOS Neisseria antecedentes laborales y las radiografías de tórax son los LOS Neisseria pilares del diagnóstico y la estadificación. El tratamiento es principalmente sintomático.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La neumoconiosis es el término clásico utilizado para describir la reacción pulmonar no neoplásica a la inhalación crónica de polvos minerales encontrados en el lugar de trabajo. Algunos expertos en pulmones consideran que el término “neumoconiosis” debería incluir también las enfermedades inducidas por humos y vapores químicos, pero esta práctica no está muy extendida y no se utilizará aquí.
Las causas más comunes:
Causas menos comunes, que no se describirán más en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum esta monografía:
Patogénesis específica de la fibra:
Factores de progresión de la enfermedad:
La aparición depende de la intensidad y la duración de la exposición y del tipo de polvo inhalado.
El diagnóstico de enfermedad pulmonar ocupacional se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 4 criterios esenciales:
| Silicosis Silicosis A form of pneumoconiosis resulting from inhalation of dust containing crystalline form of silicon dioxide, usually in the form of quartz. Amorphous silica is relatively nontoxic. Pneumoconiosis | Asbestosis Asbestosis A form of pneumoconiosis caused by inhalation of asbestos fibers which elicit potent inflammatory responses in the parenchyma of the lung. The disease is characterized by interstitial fibrosis of the lung, varying from scattered sites to extensive scarring of the alveolar interstitium. Pneumoconiosis | Neumoconiosis del minero de carbón | Beriliosis |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos de neumoconiosis muestran un patrón de enfermedad pulmonar restrictiva en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la espirometría.
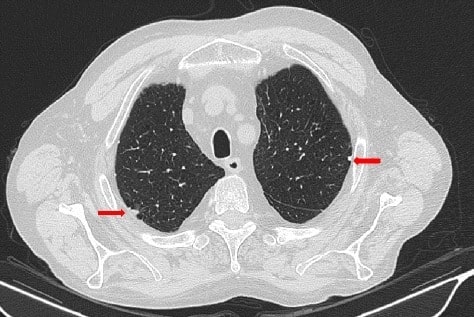
La tomografía computarizada torácica de alta resonancia de un paciente con asbestosis revela placas pleurales (flechas)
Imagen: “Thoracic HRCT” por Consultant in Rheumatology, Rheumatology Division, Hospital of Prato, Prato, Italy. Licencia: CC BY 4.0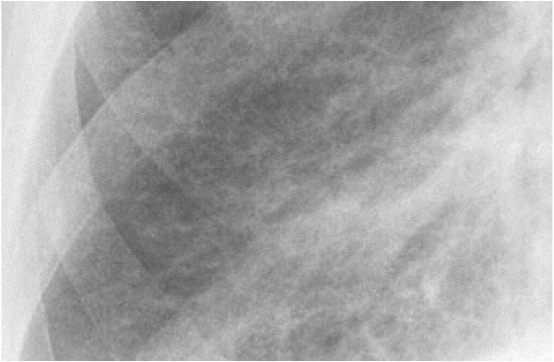
Detalle de una radiografía de tórax de un paciente con asbestosis que muestra signos de fibrosis intersticial
Imagen: “Asbestosis” por DrSHaber. Licencia: CC0 1.0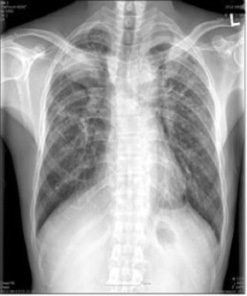
Radiografía de tórax de un paciente con neumoconiosis progresiva (silicosis) con signos de fibrosis masiva
Imagen: “Chest X-ray” por Department of Occupational & Environmental Medicine, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea.Licencia: CC BY 2.0, editado por Lecturio.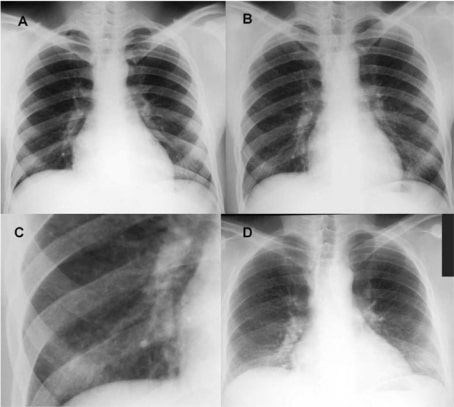
Radiografía de tórax de un paciente con beriliosis por exposición laboral
(A) Tomada antes de la contratación en marzo de 1979, mostrando campos pulmonares normales
(B) Tomada durante el segundo episodio de enfermedad laboral aguda en marzo de 1981, mostrando un leve infiltrado nodular difuso
(C) Detalle del campo pulmonar inferior derecho de la imagen B
(D) Tomada en el seguimiento en febrero de 1997, mostrando volúmenes pulmonares reducidos e infiltrados intersticiales bilaterales
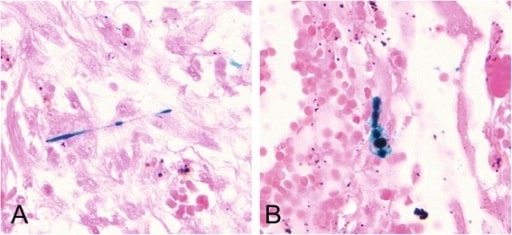
La diapositiva histológica muestra cuerpos de asbesto dispersos que muestran un núcleo fibroso recubierto por material que contiene hierro. Tinción con azul de Prusia (400×).
Imagen: “Scattered asbestos bodies showing a fibrous core” por Institute and Outpatient Clinic for Occupational and Social Medicine, University Medical Center Giessen, Aulweg 129/III, D-35385 Giessen, Germany. Licencia: CC BY 4.0El diagnóstico diferencial de las neumoconiosis causadas por polvos minerales incluye las siguientes afecciones: