Los LOS Neisseria líquidos intravenosos son una de las intervenciones más comunes administradas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum medicina para aproximarse a los LOS Neisseria líquidos corporales fisiológicos. Los LOS Neisseria líquidos intravenosos se dividen en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 2 categorías: soluciones cristaloides y coloides. Los LOS Neisseria líquidos intravenosos tienen una amplia variedad de indicaciones, incluida la expansión del volumen intravascular, la manipulación de electrolitos y los LOS Neisseria líquidos de mantenimiento. Los LOS Neisseria cristaloides y los LOS Neisseria coloides tienen diferentes composiciones generales, que afectan las distribuciones a través de los LOS Neisseria compartimentos de líquidos del cuerpo y guían el uso clínico. Las soluciones cristaloides generalmente se usan para pacientes hipovolémicos, deshidratados o que tienen pérdidas continuas de líquidos. Las soluciones coloidales se pueden utilizar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casos de baja presión oncótica. Los LOS Neisseria proveedores de salud deben elegir los LOS Neisseria tipos de líquidos según el escenario clínico y la mejor evidencia disponible. Todos los LOS Neisseria pacientes que reciben líquidos intravenosos deben ser monitoreados de cerca para determinar el objetivo y el estado de la terapia de líquidos.
Last updated: Jan 29, 2026
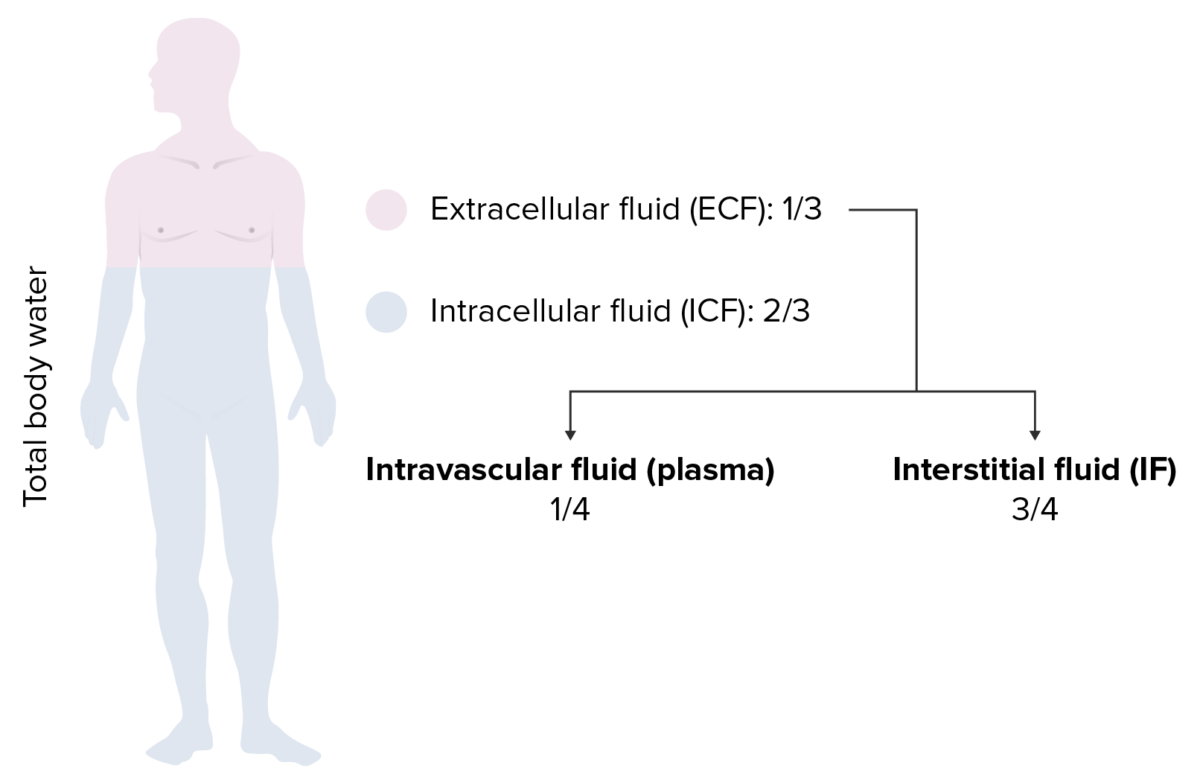
Distribución del agua corporal total:
⅔ del agua del cuerpo es líquido intracelular (ICF, por sus siglas en inglés) y ⅓ es líquido extracelular (ECF , por sus siglas en inglés). Del ECF, ¾ es líquido intersticial y solo ¼ es líquido intravascular.
Fuerzas de Starling en el intercambio transcapilar:
Las fuerzas hacia afuera del capilar incluyen la presión hidrostática de la sangre en el capilar (Pc) y la presión osmótica coloidal del líquido intersticial (πif). Las fuerzas hacia adentro del capilar incluyen la presión hidrostática del líquido intersticial (Pif) y la presión coloidosmótica del plasma (πc) del capilar.
Tonicidad: el movimiento de agua debido a la ósmosis de una célula (mostrado en 3 soluciones diferentes):
En la solución hipertónica, el agua sale de la célula. En la solución isotónica, no hay movimiento neto de agua. En la solución hipotónica, el agua entra en la célula.
| Líquido | Na mEq/L | Cl mEq/L | K mEq/L | Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts) 2 mEq/L | Glucosa g/L | Tampón mEq/L | Osmolaridad mOsm/L | Tonicidad |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products normal | 140 | 100 | 4 | 2,4 | 0,85 | HCO3 24 | 290 | N / A |
| Solución salina al AL Amyloidosis 0,9% | 154 | 154 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 308 | Isotónica |
| Solución salina al AL Amyloidosis 0,45% | 77 | 77 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 154 | Hipotónica |
| Lactato de Ringer | 130 | 109 | 4 | 3 | 0 | Lactato 28 | 273 | Isotónico |
| Dextrosa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum agua al AL Amyloidosis 5% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 252 | Hipotónica |
| Cristaloides | Coloides | |
|---|---|---|
| Ventajas | De bajo costo | Vida media más larga |
| Accesibles | Se requiere un volumen más pequeño para expandir el volumen intravascular. | |
| Desventajas | Vida media más corta | Costosos |
| Se requiere un volumen mayor para expandir el volumen intravascular. | Riesgo de reacción alérgica |
HCO3 puede estar indicado para:
La albúmina se utiliza para fines específicos:
Volver a evaluar con frecuencia los LOS Neisseria objetivos de la terapia con líquido intravenosos y adaptar el tratamiento para evitar efectos secundarios:
Anomalías ácido-base:
La hipernatremia puede resultar de:
Hiponatremia:
Hiperpotasemia:
Hiperglucemia: