Un lipoma Lipoma A lipoma is a benign neoplasm of fat cells (adipocytes) and the most common soft tissue tumor in adults. The etiology is unknown, but obesity is a predisposing factor; genetics also play a role, with multiple lipomas occurring in various inherited disorders. Lipoma es una neoplasia benigna de células grasas (adipocitos) y el tumor Tumor Inflammation de tejidos blandos más común en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum adultos. La etiología es desconocida, pero la obesidad es un factor predisponente; la genética también juega un papel, con la aparición de múltiples lipomas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum varios trastornos hereditarios. Los LOS Neisseria lipomas pueden surgir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cualquier sitio con tejido adiposo (incluido el tracto gastrointestinal, la cavidad torácica, el retroperitoneo y las glándulas), pero son más comunes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria tejidos subcutáneos del tronco o las extremidades proximales. El tratamiento no es necesario en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum caso de lipomas pequeños asintomáticos. La escisión quirúrgica es el tratamiento si existe un problema estético, funcional o de diagnóstico.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El lipoma Lipoma A lipoma is a benign neoplasm of fat cells (adipocytes) and the most common soft tissue tumor in adults. The etiology is unknown, but obesity is a predisposing factor; genetics also play a role, with multiple lipomas occurring in various inherited disorders. Lipoma es una neoplasia benigna de las células grasas (adipocitos).
Sitios anatómicos:
Morfología:
Histología:
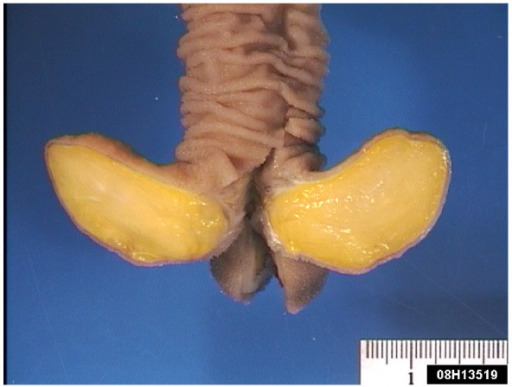
Lipoma submucoso pedunculado en íleon, que provocaba o una obstrucción
Imagen: “Gastric lipoma presenting as a giant bulging mass in an oligosymptomatic patient: a case report” por Abbasakoor NO, Kavanagh DO, Moran DC, Ryan B, Neary PC. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.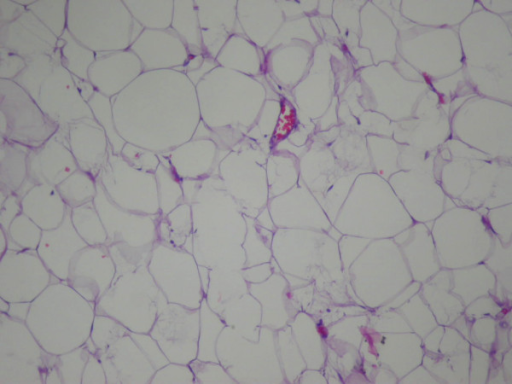
Fotomicrografía de un lipoma convencional que muestra adipocitos maduros con escasa vascularización
Imagen: “Gastric lipoma presenting as a giant bulging mass in an oligosymptomatic patient: a case report” por Neto FA, Ferreira MC, Bertoncello LC, Neto AA, de Aveiro WC, Bento CA, Cecchino GN, Rocha MA. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.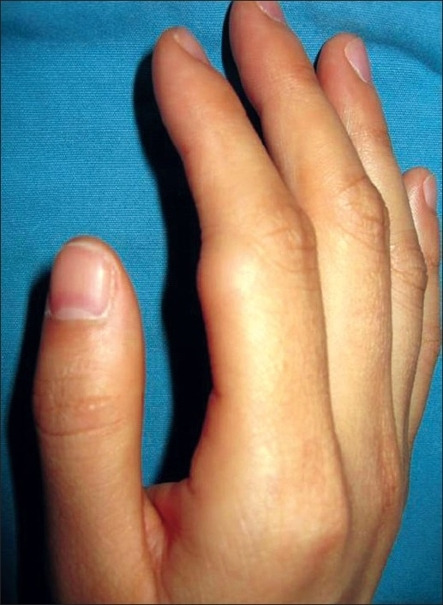
Lipoma subcutáneo de 1,5 cm en la articulación interfalángica proximal del dedo índice derecho de una mujer de 35 años
Imagen: “Lipoma of the finger presenting as restricted motion” por Yoon S, Jung SN. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.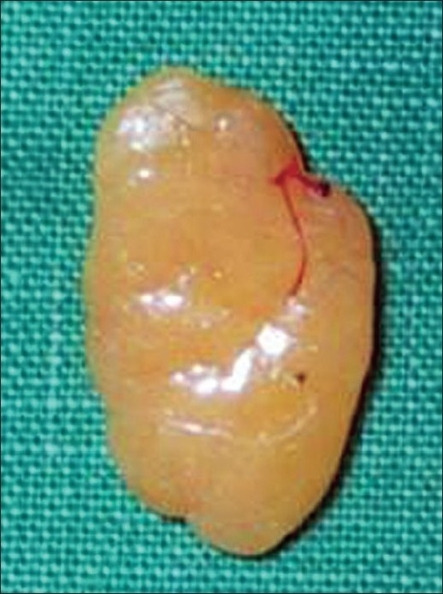
Lipoma subcutáneo de 1,5 cm
El lipoma del dedo se presenta como una restricción del movimiento.
Antecedentes clínicos:
Examen físico:
Imagenología:
Endoscopia y ultrasonido endoscópico:
Biopsia:
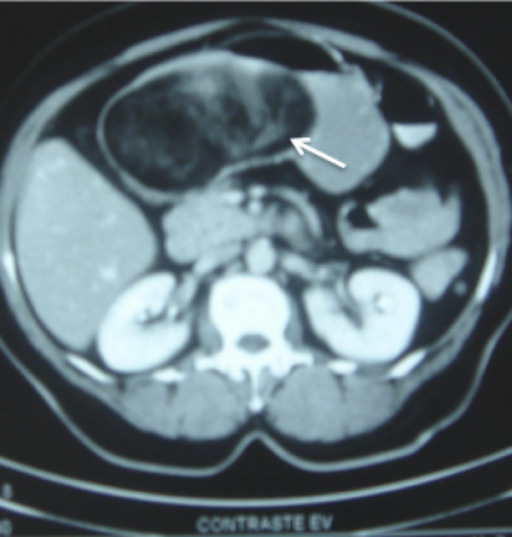
Un lipoma gástrico submucoso grande (12 x 8 x 6 cm) (flecha)
Parte del medio de contraste se ha filtrado hacia el lipoma a través de áreas ulceradas focales en la mucosa suprayacente, y se puede ver penetrando en el centro desde la superficie.
Tratamiento expectante: adecuado para lipomas pequeños (< 5 cm) asintomáticos subcutáneos
Extirpación quirúrgica:
Complicaciones de la cirugía:
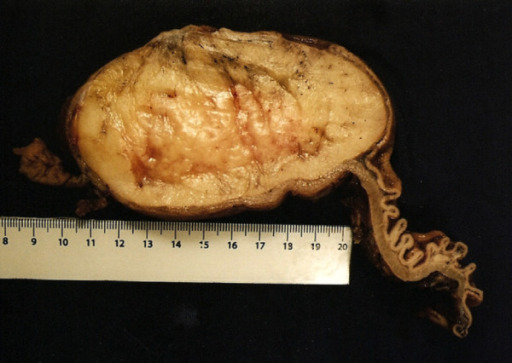
Lipoma gástrico submucoso (muestra quirúrgica)
Obsérvese la pared engrosada de la pared gástrica proximal en el lado derecho y la mucosa gástrica suprayacente focalmente ulcerada atenuada.