La apófisis es un centro de osificación secundario que se encuentra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum segmentos de huesos que no soportan peso. Es el sitio de inserción de ligamentos o tendones y está involucrado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el crecimiento periférico de los LOS Neisseria huesos. Estos centros de crecimiento secundarios generalmente están abiertos durante la niñez y no se cierran hasta la adultez temprana. La lesión apofisaria crónica (apofisitis por tracción) casi siempre ocurre en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum atletas adolescentes durante los LOS Neisseria períodos de crecimiento. Los LOS Neisseria tipos de lesiones apofisarias crónicas incluyen la enfermedad de Sever (apofisitis del calcáneo posterior), la enfermedad de Osgood-Schlatter (apofisitis de la tuberosidad tibial), el codo de las ligas menores (apofisitis del epicóndilo medial) y el síndrome de Sinding-Larsen-Johansson (apofisitis de la rótula inferior). El diagnóstico generalmente se hace HACE Altitude Sickness clínicamente. Las lesiones apofisarias crónicas generalmente se tratan con un abordaje conservador y rara vez requieren intervención quirúrgica.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La apófisis, un centro de osificación secundario, puede ser susceptible a cargas físicas agudas o repetitivas, que pueden provocar lesiones.
| Enfermedad | Factor de riesgo |
|---|---|
| Enfermedad de Osgood-Schlatter (apofisitis del tuberosidad tibial) |
|
| Enfermedad de Sinding-Larsen-Johansson (apofisitis del polo inferior de la rótula) | Los LOS Neisseria deportes que implican correr y saltar ejercen una tensión repetitiva sobre el ligamento rotuliano y pueden provocar irritación o incluso avulsión de la apófisis del polo inferior de la rótula. |
| Apofisitis pélvica (múltiples sitios) |
|
| Codo de las ligas menores (apofisitis del epicóndilo medial) | Los LOS Neisseria lanzamientos repetitivos ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el béisbol) imponen una tensión repetitiva en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la apófisis del epicóndilo medial—una lesión por tracción. |
| Enfermedad de Sever (apofisitis del calcáneo) |
|
| Enfermedad de Iselin (apofisitis por tracción del 5to metatarsiano) |
|
Las lesiones relacionadas con deportes y actividades en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum edad escolar son de presentación común:
| Enfermedad | Epidemiología |
|---|---|
| Enfermedad de Osgood-Schlatter |
|
| Enfermedad de Sinding-Larsen-Johansson | Similar a la enfermedad de Osgood-Schlatter, pero comúnmente ocurre en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños un poco más pequeños, entre 10 y 13 años |
| Apofisitis pélvica | El rango de edad es amplio; relacionado con la variación en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el crecimiento de la apófisis |
| Codo de ligas menores |
|
| Enfermedad de Sever |
|
| Enfermedad de Iselin |
|
La mayoría de las apofisitis por tracción se presenta con aumento de volumen y dolor Dolor Inflammation localizados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el sitio de la apófisis, que empeora con el movimiento contra resistencia o la activación muscular del complejo músculo-tendón asociado.
| Enfermedad | Presentación clínica |
|---|---|
| Enfermedad de Osgood-Schlatter |
|
| Enfermedad de Sinding-Larsen-Johansson |
|
| Apofisitis pélvica (ubicaciones múltiples) |
|
| Codo de ligas menores |
|
| Enfermedad de Sever |
|
| Enfermedad de Iselin |
|
Hay trastornos apofisarios específicos de la pelvis Pelvis The pelvis consists of the bony pelvic girdle, the muscular and ligamentous pelvic floor, and the pelvic cavity, which contains viscera, vessels, and multiple nerves and muscles. The pelvic girdle, composed of 2 “hip” bones and the sacrum, is a ring-like bony structure of the axial skeleton that links the vertebral column with the lower extremities. Pelvis: Anatomy con sus músculos asociados. Estos trastornos pueden presentarse como consecuencia de traumatismos repetitivos, traumatismos directos o avulsiones agudas:
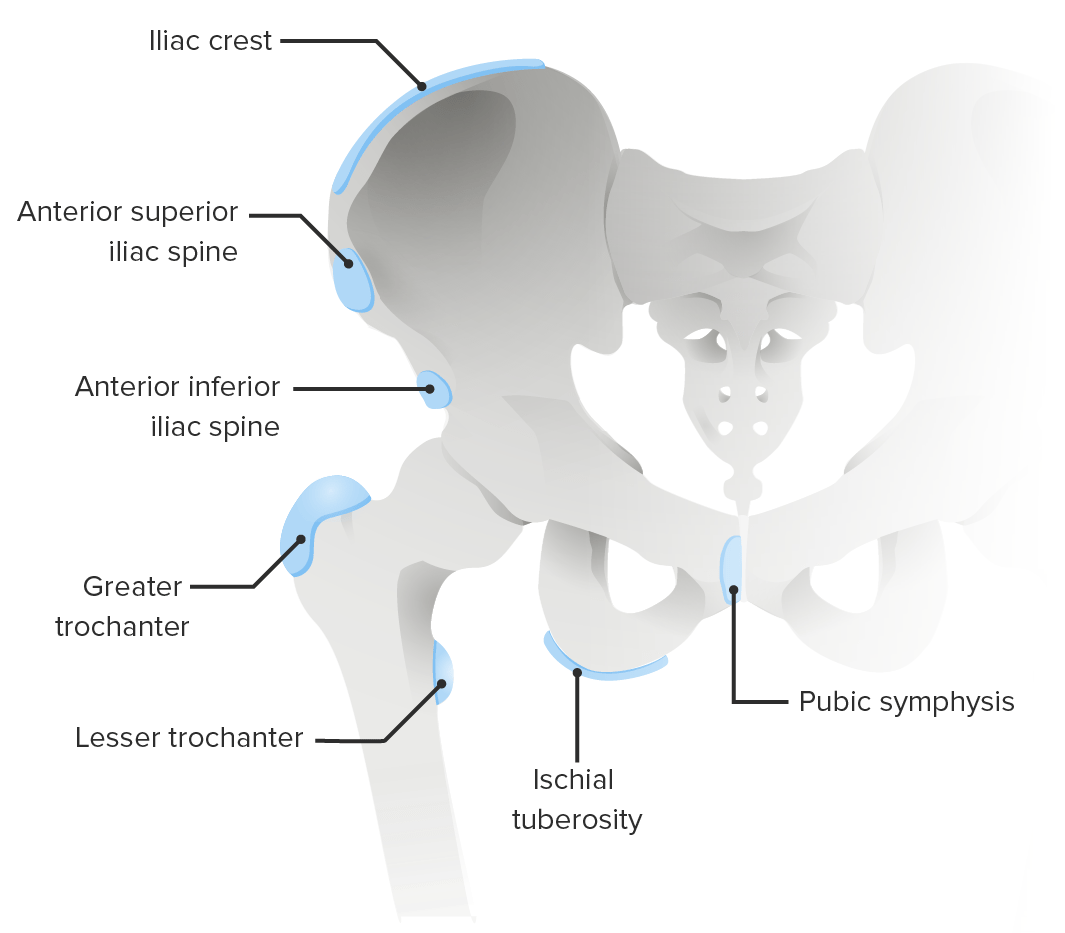
Sitios comunes de trastornos apofisarios de la pelvis
Imagen por Lecturio.| Enfermedad | Hallazgos radiográficos |
|---|---|
| Enfermedad de Osgood-Schlatter | Inflamación de partes blandas y fragmentación de la tuberosidad tibial |
| Enfermedad de Sinding-Larsen-Johansson | Inflamación y calcificación o fragmentación de los LOS Neisseria tejidos blandos del polo inferior de la rótula |
| Apofisitis de la pelvis Pelvis The pelvis consists of the bony pelvic girdle, the muscular and ligamentous pelvic floor, and the pelvic cavity, which contains viscera, vessels, and multiple nerves and muscles. The pelvic girdle, composed of 2 “hip” bones and the sacrum, is a ring-like bony structure of the axial skeleton that links the vertebral column with the lower extremities. Pelvis: Anatomy/cadera |
|
| Codo de ligas menores | Puede mostrar fragmentación o ensanchamiento de la apófisis del epicóndilo medial |
| Enfermedad de Sever | Con frecuencia normal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la radiografía simple |
| Enfermedad de Iselin | Apófisis normal o ensanchada del 5to metatarsiano proximal |
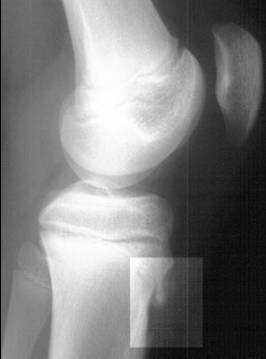
Radiografía lateral que muestra fragmentación de la tuberosidad tibial, lo que indica enfermedad de Osgood-Schlatter
Imagen: “Osgood-Schlatter disease X-ray” por Kristin M Houghton; Radiograph courtesy of BC Children’s Hospital. Licencia: CC BY 2.0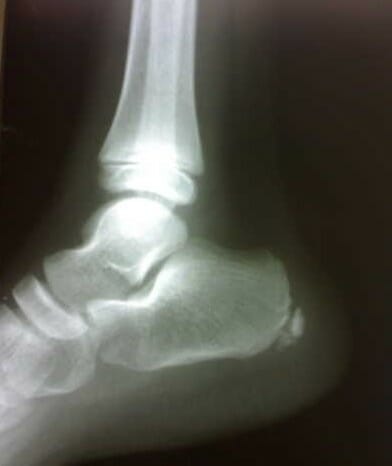
Radiografía del pie derecho que muestra esclerosis y fragmentación de la apófisis del calcáneo, lo que indica enfermedad de Sever
Imagen: “Figure 1 Lateral radiograph of the right foot” por Sitati, F. C. and Kingori, J. Licencia: CC BY 2.0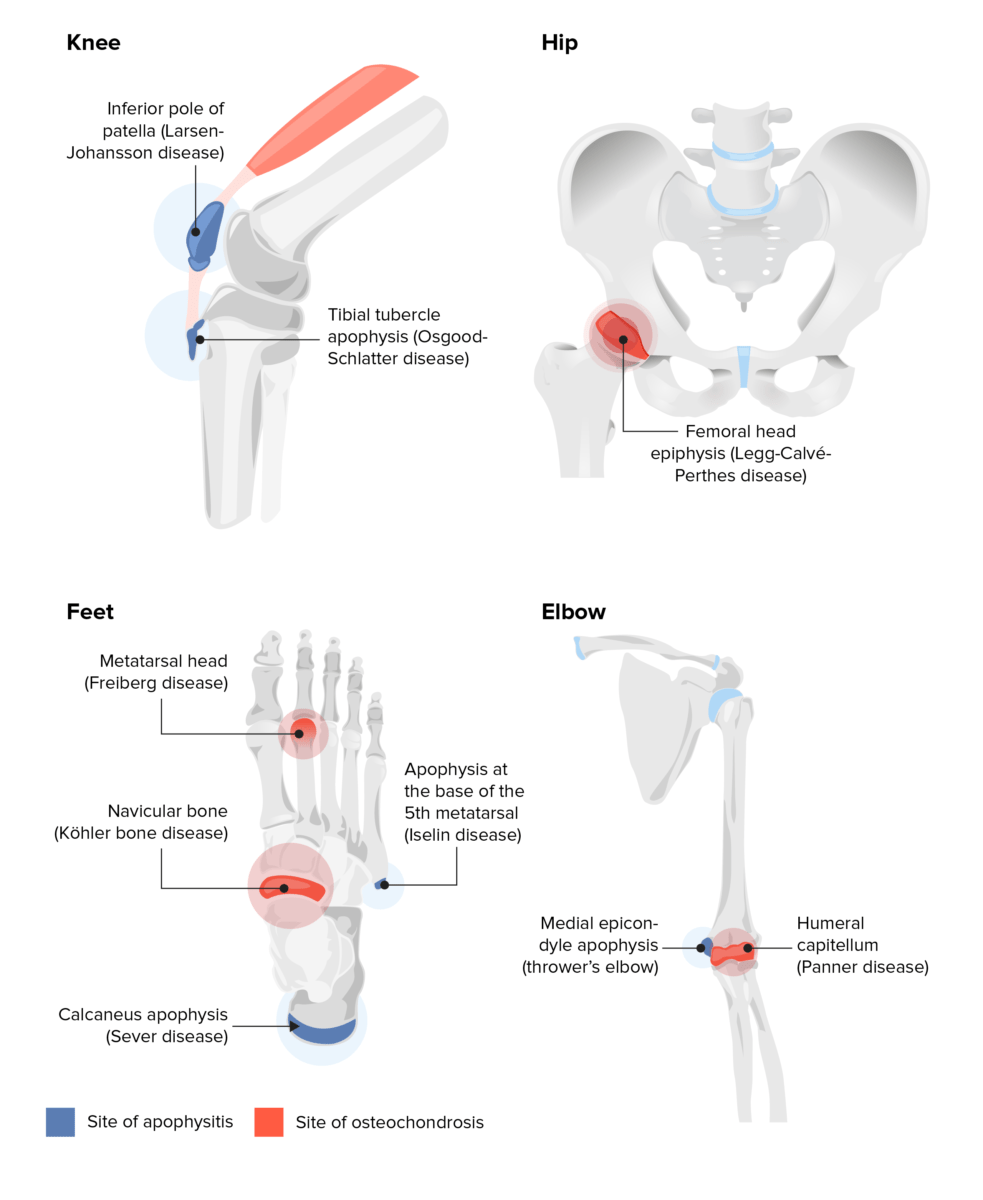
Sitios de apofisitis y osteocondrosis
Imagen por Lecturio.| Enfermedad | Tratamiento | Indicación de referencia ortopédica |
|---|---|---|
| Enfermedad de Osgood-Schlatter |
|
|
| Enfermedad de Sinding-Larsen-Johansson |
|
|
| Codo de ligas menores |
|
|
| Apofisitis de cadera |
|
|
| Enfermedad de Sever |
|
Pacientes que no responden a las modificaciones de la actividad y al AL Amyloidosis tratamiento inicial |
| Enfermedad de Iselin |
|
|