La hemorragia uterina anormal es el término médico empleado para anomalías en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la frecuencia, el volumen, la duración y la regularidad del ciclo menstrual. La hemorragia uterina anormal se clasifica mediante el acrónimo PALM-COEIN PALM-COEIN Abnormal uterine bleeding is the medical term for abnormalities in the frequency, volume, duration, and regularity of the menstrual cycle. Abnormal uterine bleeding is classified using the acronym palm-coein, with palm representing the structural causes and coein indicating the non-structural causes. Abnormal Uterine Bleeding, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el que PALM representa las causas estructurales y COEIN indica las causas no estructurales. Las etiologías incluyen pólipo (P), adenomiosis (A), leiomioma (L), malignidad/hiperplasia (M), coagulopatía (C), disfunción ovulatoria (O); patología endometrial incluyendo endometritis Endometritis Endometritis is an inflammation of the endometrium, the inner layer of the uterus. The most common subtype is postpartum endometritis, resulting from the ascension of normal vaginal flora to the previously aseptic uterus. Postpartum Endometritis y atrofia (E), causas iatrogénicas (I) y etiologías no clasificadas (N). El diagnóstico suele requerir una anamnesis y un examen físico minuciosos, pruebas de laboratorio básicas, un ultrasonido transvaginal y una biopsia endometrial en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de la edad y los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo. El tratamiento depende de la etiología subyacente, pero suele incluir anticonceptivos orales, dispositivos intrauterinos que contienen levonorgestrel Levonorgestrel A synthetic progestational hormone with actions similar to those of progesterone and about twice as potent as its racemic or (+-)-isomer (norgestrel). It is used for contraception, control of menstrual disorders, and treatment of endometriosis. Hormonal Contraceptives y cirugía.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Hemorragia uterina anormal (HUA):
Debido a la anterior falta de coherencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las terminologías en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum torno a las HUA, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 2011 se desarrolló un nuevo sistema para describir y clasificar las HUA.
| Término antiguo | Nuevo término preferido |
|---|---|
| Oligomenorrea | Sangrado uterino infrecuente |
| Polimenorrea | Sangrado uterino frecuente |
| Menorragia | Hemorragia uterina anormal (HUA)/sangrado menstrual abundante |
| Metrorragia | Hemorragia uterina anormal (HUA)/sangrado intermenstrual |
| Amenorrea | Amenorrea (sin cambios) |
| Sangrado uterino disfuncional | Utilizar trastornos específicos (o los LOS Neisseria nuevos términos) |
Las causas de HUA se clasifican según el sistema PALM-COEIN PALM-COEIN Abnormal uterine bleeding is the medical term for abnormalities in the frequency, volume, duration, and regularity of the menstrual cycle. Abnormal uterine bleeding is classified using the acronym palm-coein, with palm representing the structural causes and coein indicating the non-structural causes. Abnormal Uterine Bleeding, que es un acrónimo.
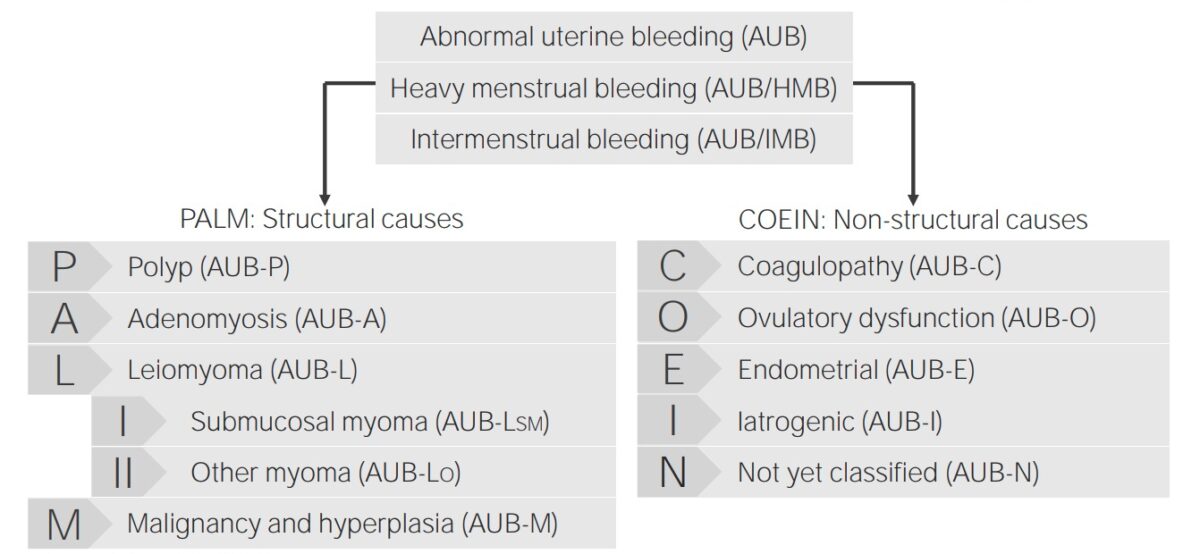
Clasificación de la hemorragia uterina anormal y sus causas
Imagen por Lecturio.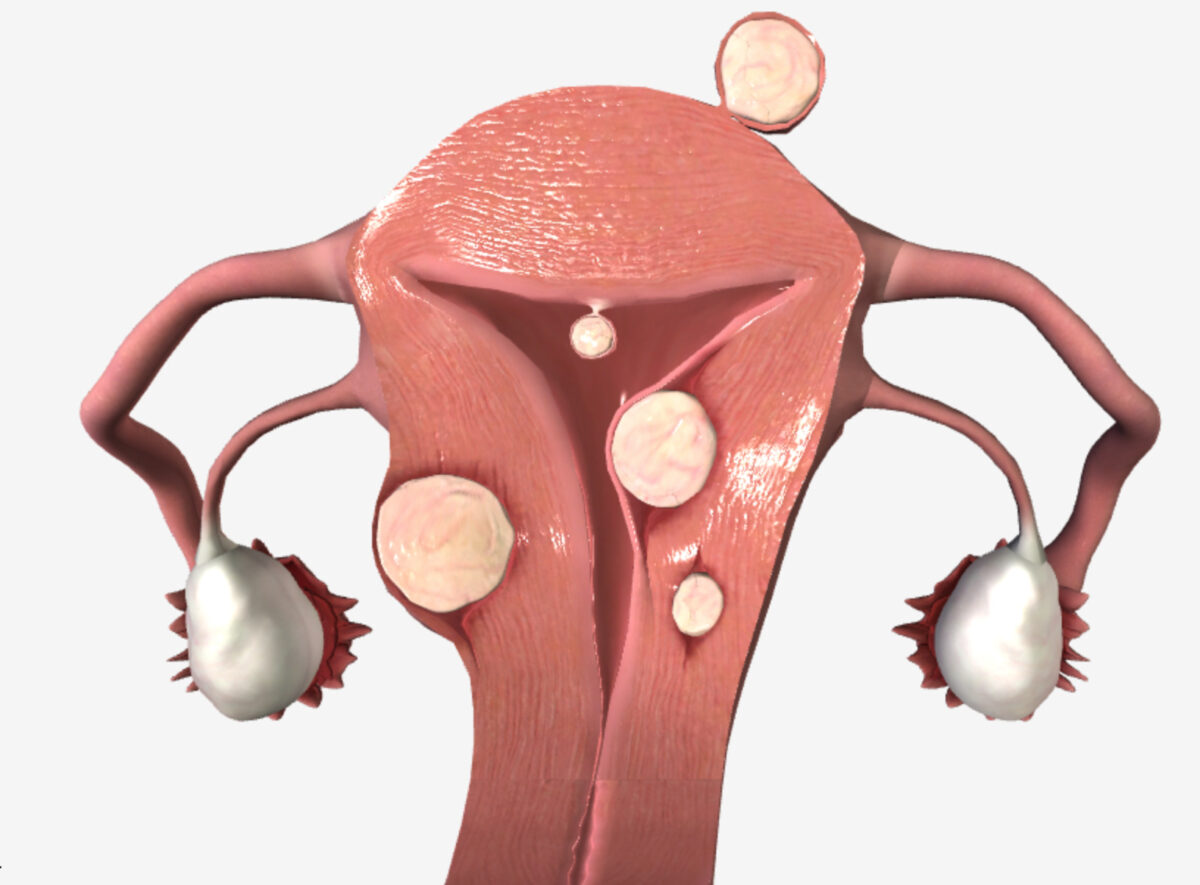
Miomas uterinos (localización): mioma subseroso (por debajo de la serosa), mioma submucoso (por debajo del endometrio), mioma intramural (en la pared miometrial), mioma pedunculado (que crece del cuerpo uterino en un pedúnculo)
Imagen por Lecturio.| Etiología | Presentación de la hemorragia | Otros hallazgos clínicos |
|---|---|---|
| Pólipo (HUA-P) | Sangrado menstrual abundante, sangrado intermenstrual y/o sangrado uterino prolongado |
|
| Adenomiosis (HUA-A) | Sangrado menstrual abundante, sangrado intermenstrual y/o sangrado uterino prolongado |
|
| Leiomioma (HUA-L) | Sangrado menstrual abundante, sangrado intermenstrual y/o sangrado uterino prolongado |
|
| Malignidad e hiperplasia (HUA-M) |
|
|
| Etiología | Presentación de la hemorragia | Otros hallazgos clínicos |
|---|---|---|
| Coagulopatía (HUA-C) | HUA/sangrado menstrual abundante desde la menarquia | Antecedente de sangrado fácil (e.g., sangrado dental, hemorragia posparto) |
| Disfunción ovulatoria (HUA-O) | Sangrado infrecuente | Amenorrea hipotalámica funcional (trastorno de la alimentación): pérdida de peso |
|
Amenorrea hipotalámica funcional (estrés): factores psicológicos | |
|
Síndrome de ovario poliquístico (SOP):
|
|
| Amenorrea | Insuficiencia ovárica primaria: | |
|
Signos y síntomas de otros trastornos endocrinos que afectan a la ovulación (e.g., hipertiroidismo, hipotiroidismo, hiperprolactinemia) | |
| Sangrado irregular | Anovulación relacionada con la edad cerca de la menarquia o la menopausia | |
| Endometrial (HUA-E) | Sangrado menstrual abundante, sangrado intermenstrual, o sangrado prolongado | EIP:
|
| Sangrado intermenstrual | Atrofia endometrial: acompañada de atrofia vaginal | |
| Iatrogénica (HUA-I) | HUA/sangrado intermenstrual | Depende de los LOS Neisseria agentes |
| No clasificada (HUA-N) | Mal definidas o extremadamente raras (e.g., malformación arteriovenosa, istmocele) | |
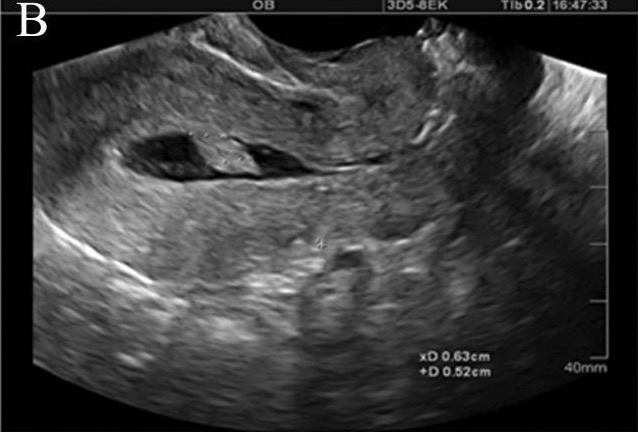
Ultrasonido con infusión de solución salina que demuestra una lesión intracavitaria pedunculada, probablemente un pólipo endometrial:
La inyección de líquido estéril en la cavidad endometrial distiende la cavidad y permite descartar patología endometrial estructural, incluyendo pólipos, fibromas submucosos y sinequias.