Los LOS Neisseria diuréticos ahorradores de potasio son medicamentos que actúan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las células principales de los LOS Neisseria conductos colectores para inducir una diuresis, pero evitando la excreción de potasio. Estos diuréticos incluyen 2 subclases: los LOS Neisseria bloqueadores de los LOS Neisseria canales de sodio y los LOS Neisseria antagonistas de la aldosterona. Debido a que estos agentes actúan tan distalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la nefrona, no hay una pérdida significativa de potasio asociada a su uso. Estos agentes se utilizan normalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento del exceso de mineralocorticoides, que puede ser primario (e.g., el síndrome de Conn) o secundario (e.g., estados de disminución del volumen intravascular, especialmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca). Además, la espironolactona puede utilizarse por sus propiedades antiandrogénicas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum mujeres con exceso de andrógenos (e.g., hirsutismo) y para la supresión de andrógenos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum mujeres transgénero (de hombre a mujer). Estos medicamentos están contraindicados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum caso de hiperpotasemia.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria diuréticos ahorradores de potasio son medicamentos que actúan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las células principales de los LOS Neisseria conductos colectores para inducir una diuresis, pero evitando la excreción de potasio.
Los diuréticos ahorradores de potasio actúan en los conductos colectores de la nefrona.
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0| Sitio de acción | Clase | Subclases |
|---|---|---|
| Medicamentos renales | Medicamentos que afectan al AL Amyloidosis SRAA |
|
| Diuréticos |
|
|
| Medicamentos extrarrenales | Vasodilatadores directos | |
| Agentes que actúan a través del sistema nervioso simpático |
|
Estructura del triamtereno
Imagen: “Estructura del triamtereno” por NEUROtiker. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoAntagonistas de la aldosterona (espironolactona, eplerenona):
Bloqueadores de los LOS Neisseria canales de sodio (triamtereno, amilorida):
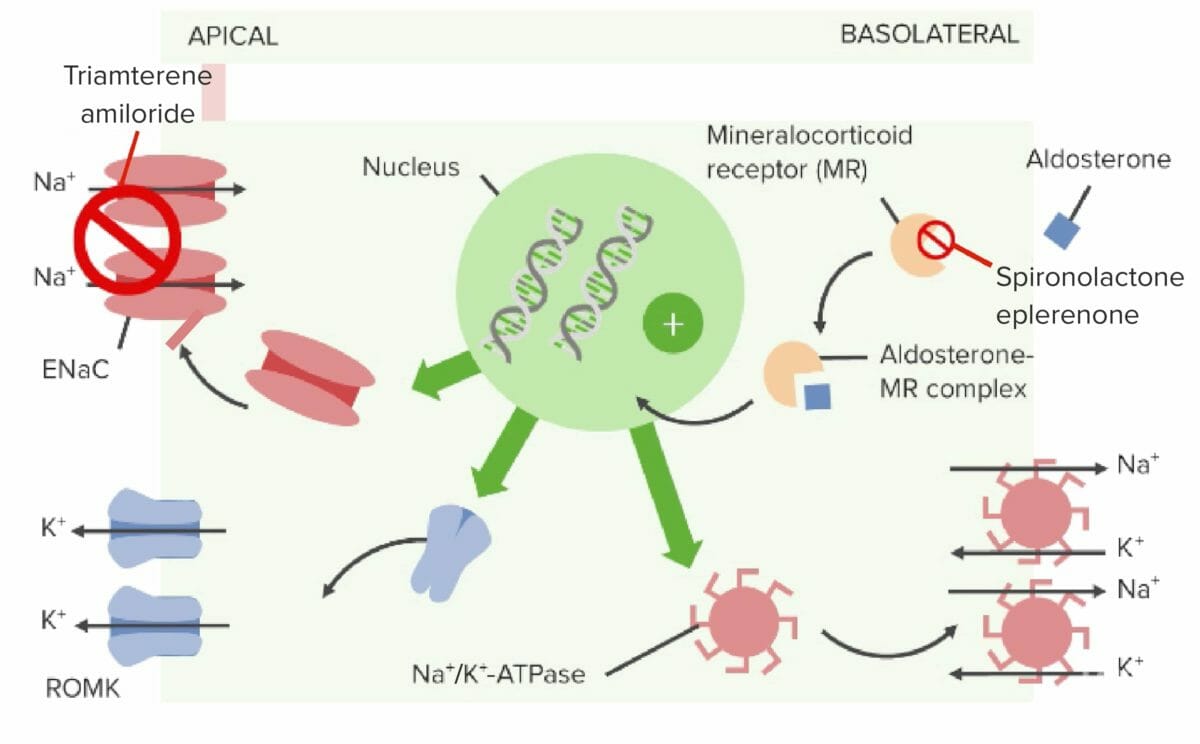
Mecanismo de acción de los antagonistas de la aldosterona y los bloqueadores de los canales de sodio
Imagen por Lecturio.| Medicamento | Absorción | Distribución | Metabolismo | Excreción |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Espironolactona |
|
Unión a proteínas: > 90% | Metabolismo hepático rápido y extenso a metabolitos activos |
|
| Eplerenona |
|
|
Metabolismo hepático por CYP3A4 CYP3A4 Class 3 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Potassium Channel Blockers) a metabolitos inactivos |
|
| Triamtereno |
|
VD: 1,5 L/kg | Metabolismo hepático por CYP1A2 a metabolitos activos | Se excreta por vía renal. |
| Amilorida |
|
|
No se metaboliza. |
|
Los LOS Neisseria diuréticos ahorradores de potasio son los LOS Neisseria más útiles para tratar el edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema relacionado con estados de exceso de mineralocorticoides, que pueden ser primarios o secundarios. Las indicaciones incluyen:
La espironolactona tiene indicaciones adicionales debido a sus propiedades antiandrogénicas:
Algunos de los LOS Neisseria otros diuréticos más comunes son los LOS Neisseria diuréticos tiazídicos (e.g., la hidroclorotiazida), los LOS Neisseria diuréticos de asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome (e.g., la furosemida), los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la anhidrasa carbónica (e.g., la acetazolamida) y los LOS Neisseria diuréticos osmóticos (e.g., el manitol).
| Medicamento | Mecanismo | Efecto fisiológico | Indicación |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diurético tiazídico: Hidroclorotiazida | ↓ Reabsorción de NaCl en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el DCT a través de la inhibición del cotransportador de Na+/Cl– |
|
|
| Diurético de asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome: Furosemida | Inhibe el cotransportador luminal de Na+/K+/Cl– en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la rama ascendente gruesa del asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome de Henle. |
|
|
| Diurético ahorrador de potasio: Espironolactona |
|
|
|
| Inhibidor de la anhidrasa carbónica: Acetazolamida | Inhibe tanto la hidratación del CO2 en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las células epiteliales del PCT como la deshidratación del H2CO3 en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el lumen del PCT; provocando una excreción ↑ HCO3–y Na+. |
|
|
| Diuréticos osmóticos: Manitol | ↑ Presión osmótica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el filtrado glomerular → ↑ líquido tubular e impide la reabsorción de agua. |
|
|
Sitios de acción, dentro de la nefrona, para las clases de medicamentos diuréticos
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0