La disfagia es la sensación subjetiva de dificultad para tragar. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas pueden variar desde una incapacidad total para tragar hasta la sensación de que los LOS Neisseria sólidos o líquidos se “atascan”. La disfagia se clasifica como orofaríngea o esofágica, y la disfagia esofágica tiene 2 subtipos: funcional y mecánica. Las causas comunes de disfagia funcional incluyen acalasia, esclerodermia y espasmo esofágico difuso. Las causas mecánicas de disfagia incluyen anillos esofágicos, membranas, estenosis y cáncer. La disfagia orofaríngea puede deberse a anomalías estructurales o a una función y coordinación neuromuscular anormales. El estudio diagnóstico depende de los LOS Neisseria síntomas que presente el paciente, pero puede incluir manometría, esofagograma con bario o visualización directa con laringoscopia o endoscopia esofágica. El tratamiento varía según la causa subyacente.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La disfagia es una condición en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la que hay una interrupción del proceso de deglución, lo que generalmente interfiere con la capacidad de comer y beber.
La deglución consta de 3 fases:
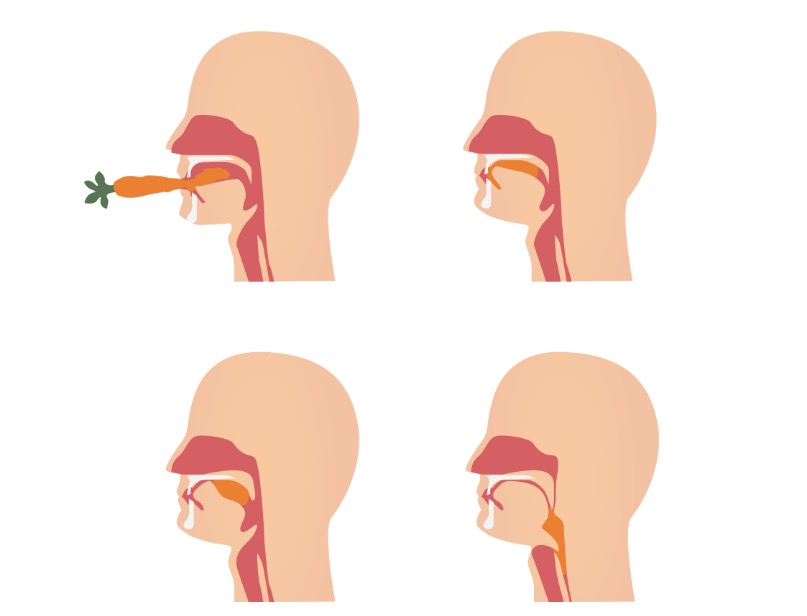
Movimiento de un bolo alimenticio a través de las fases oral y faríngea de la deglución
Imagen por Lecturio.Hay 2 categorías de disfagia:
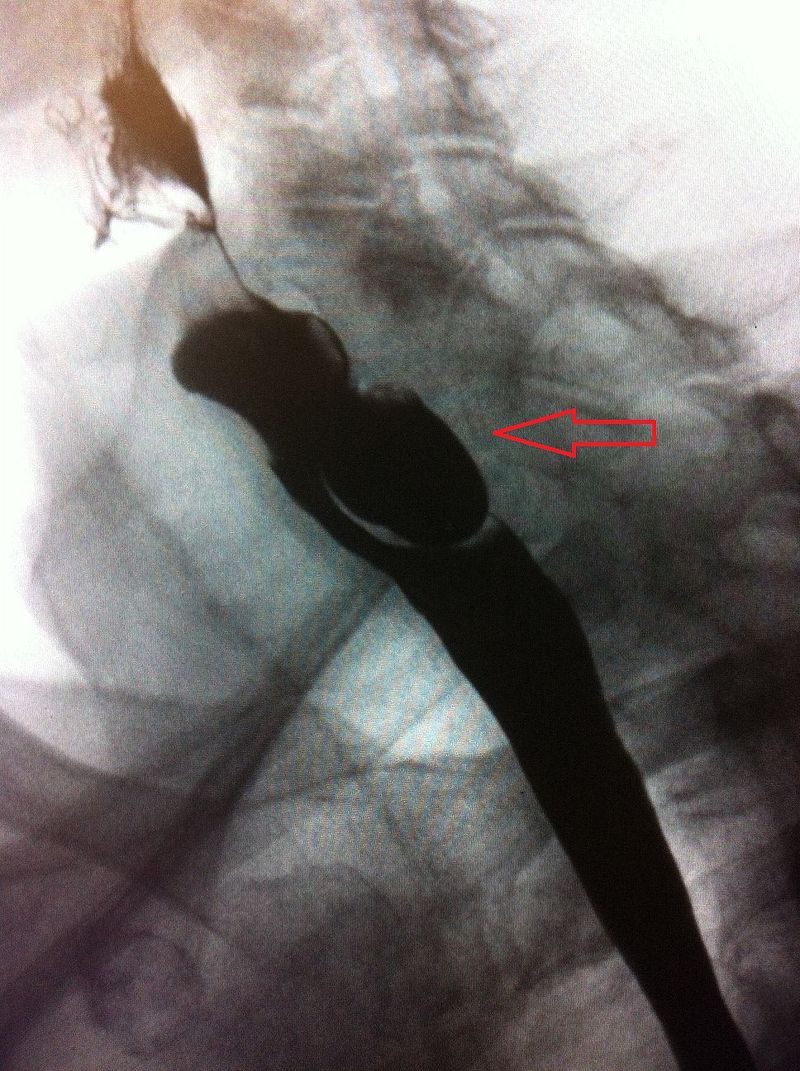
Un estudio con trago de bario que identifica un divertículo falso que surge de la pared posterior del esófago superior, lo que es compatible con un divertículo de Zenker
Imagen: “Lateral X-ray of a Zenker’s diverticula” por James Heilman, MD. Licencia: CC BY-SA 4.0.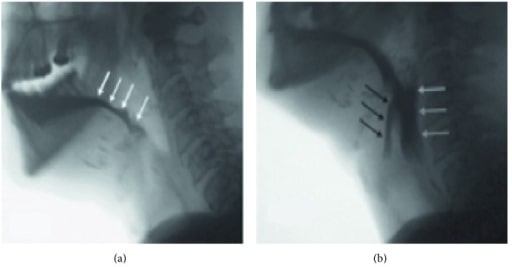
Vista video fluoroscópica en un paciente que se ha sometido a una glosectomía casi total por cáncer avanzado de cabeza y cuello. El paciente tiene un control deficiente del bolo oral y una pérdida temprana en la orofaringe (A, flechas blancas). Ha perdido la capacidad de tirar del hioides y la laringe hacia arriba y hacia adelante para abrir el esfínter esofágico superior, lo que provoca disfagia faríngea y restos de comida en la faringe (B, flechas blancas) con penetración por encima de las cuerdas vocales (flechas negras). Se determinó que este paciente tenía un alto riesgo de aspiración.
Imagen: “Lateral fluoroscopic view” por Caterina Giannitto. Licencia: CC BY 4.0.El tratamiento se guía por la evaluación diagnóstica y se enfoca en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum mejorar el paso de alimentos y prevenir la aspiración:
Los LOS Neisseria trastornos esofágicos funcionales y de la motilidad ocurren típicamente debido a una patología de los LOS Neisseria músculos del esófago, lo que provoca una interrupción en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el peristaltismo. Todos los LOS Neisseria trastornos funcionales y de la motilidad presentan disfagia con líquidos y sólidos al AL Amyloidosis inicio.
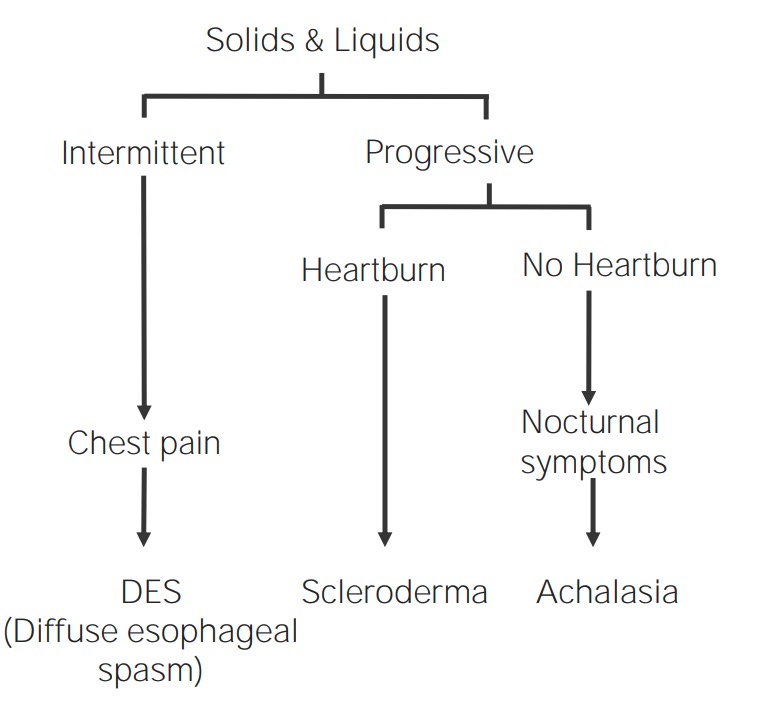
Descripción general de los trastornos funcionales y de la motilidad
Imagen por Lecturio.Un trastorno de la motilidad esofágica caracterizado por contracciones hiperdinámicas y no propulsoras:
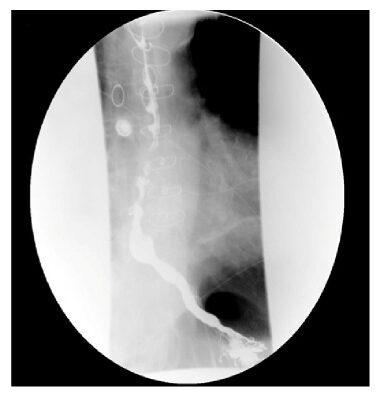
Espasmo esofágico difuso: esofagograma de bario que muestra el típico patrón en “sacacorchos”
Imagen: “Smooth short stricture in the distal esophagus” por Chui Man Carmen Hui et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0.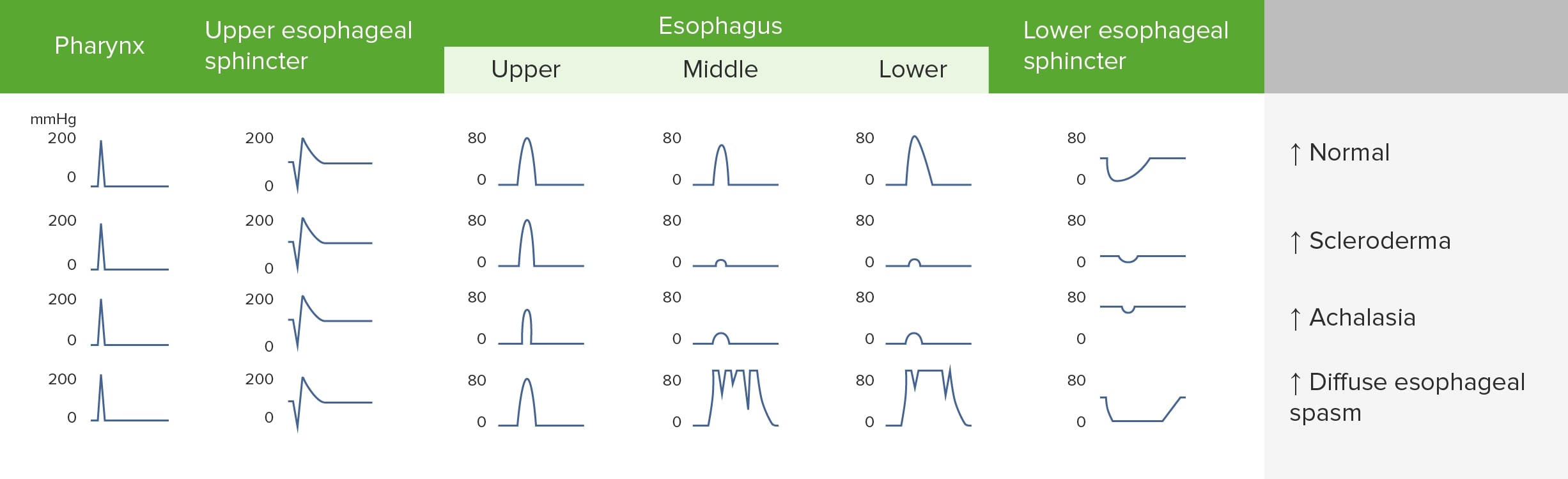
Hallazgos de la manometría en los trastornos de la motilidad esofágica
Imagen por Lecturio.La esclerodermia es un trastorno autoinmune que puede causar atrofia y esclerosis del esófago distal, lo que resulta en una disminución (o ausencia) del peristaltismo y la presión del esfínter esofágico inferior.
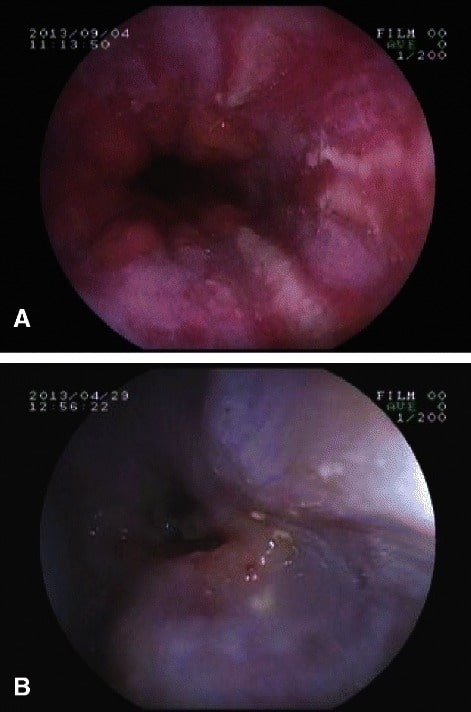
A: endoscopia superior que demuestra esofagitis por reflujo; B: endoscopia superior que demuestra una estenosis esofágica en un paciente con esclerodermia
Imagen: “EGD in systemic sclerosis” por the Postgraduate Department of Dermatology, STDs & Leprosy, Government Medical College, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India. Licencia: CC BY 4.0.Un trastorno neurogénico de la motilidad esofágica que resulta en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una alteración de la relajación del esfínter esofágico inferior y una disminución del peristaltismo:
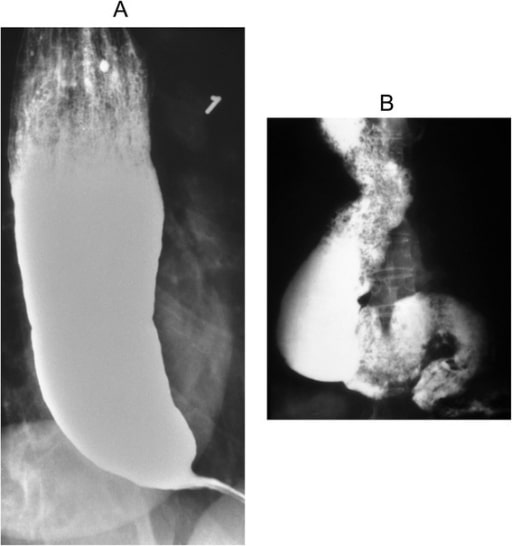
Acalasia: apariencia de “pico de pájaro” en un esofagograma de bario
Imagen: “Barium swallow” por the Department of Internal Medicine, Nashville, TN, USA. Licencia: CC BY 4.0.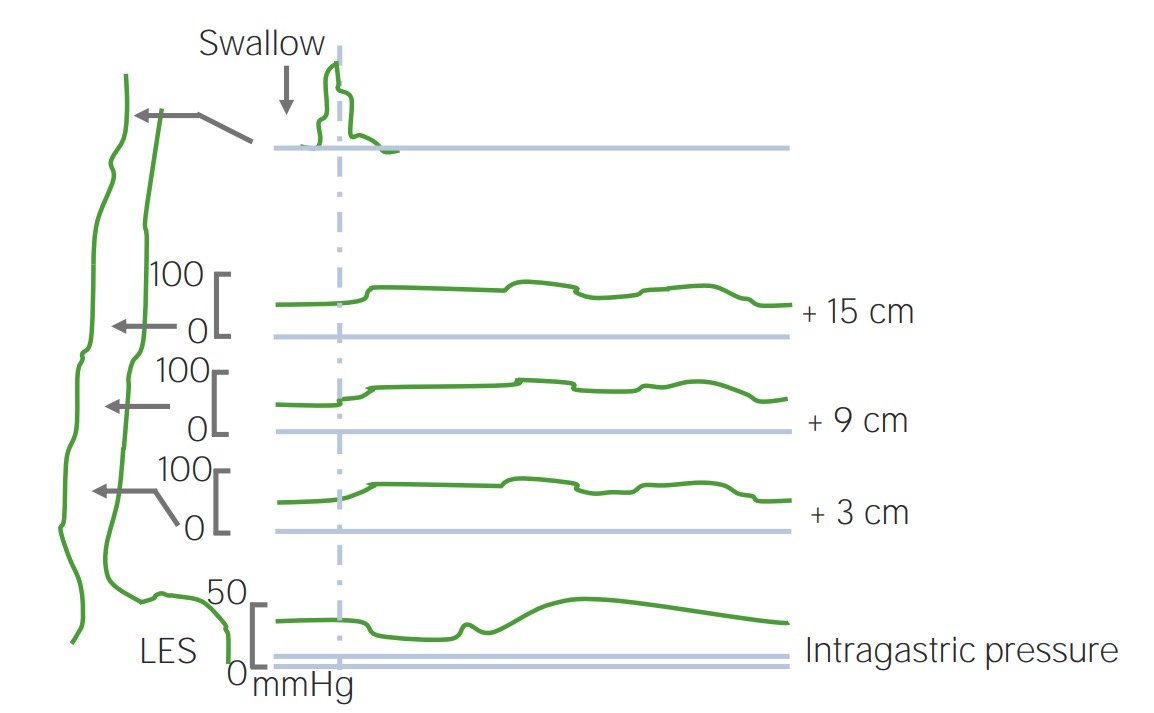
Acalasia: manometría que muestra presión alta en esfínter esofágico inferior (línea superior)
Imagen por Lecturio.Los LOS Neisseria trastornos mecánicos y obstructivos esofágicos ocurren típicamente debido a la obstrucción de la luz esofágica. Todos los LOS Neisseria trastornos mecánicos y obstructivos presentan disfagia con sólidos con progresión a líquidos.
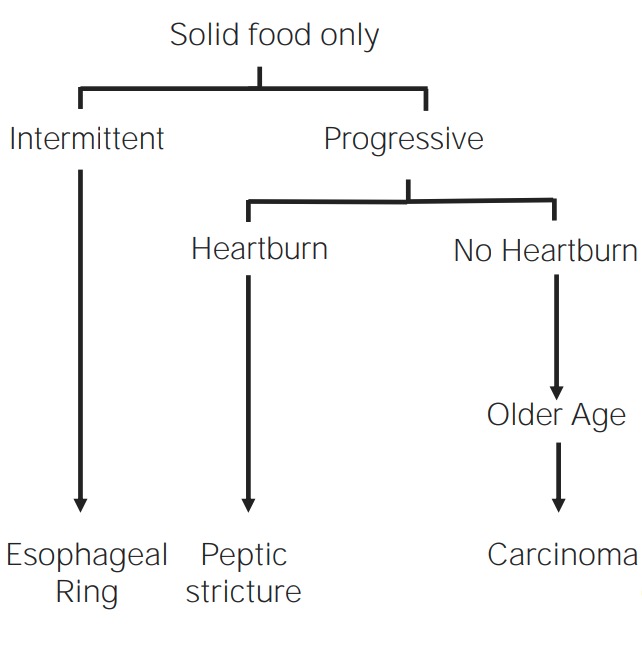
Descripción general de los trastornos mecánicos y obstructivos
Imagen por Lecturio.Los LOS Neisseria anillos y las membranas son estenosis mucosas delgadas que ocluyen parcialmente la luz esofágica:
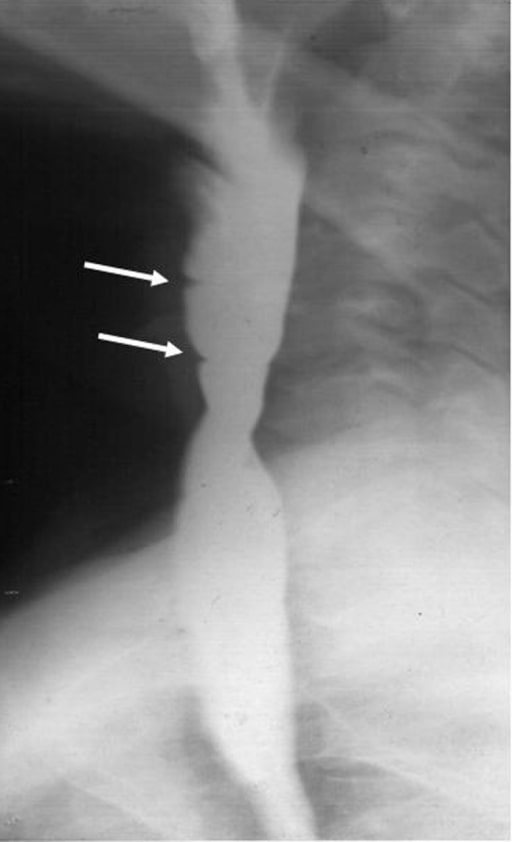
Esofagograma de bario que muestra membranas esofágicas en la parte superior del esófago
Imagen: “Barium swallow examination” por Usha Dutta et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.Una estenosis esofágica es un estrechamiento anormal de la luz esofágica:
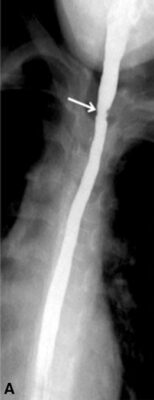
Esofagograma con bario que muestra una estenosis esofágica (flecha), que muestra una estenosis en el esófago proximal, pero las estenosis generalmente estarán en el esófago distal
Imagen: “Barium esophagogram” por the Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Children’s Hospital, King Fahad Medical City, P. O. Box 59046, Riyadh, 11525, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Licencia: CC BY 4.0.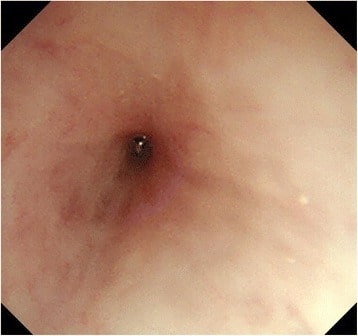
Imagen de endoscopia que muestra una estenosis esofágica importante
Imagen: “Esophagogastroduodenoscopy” por the Department of Gastroenterological Surgery, Tokai University School of Medicine, 143 Shimokasuya, Isehara, Kanagawa, 259-1193, Japan. Licencia: CC BY 4.0.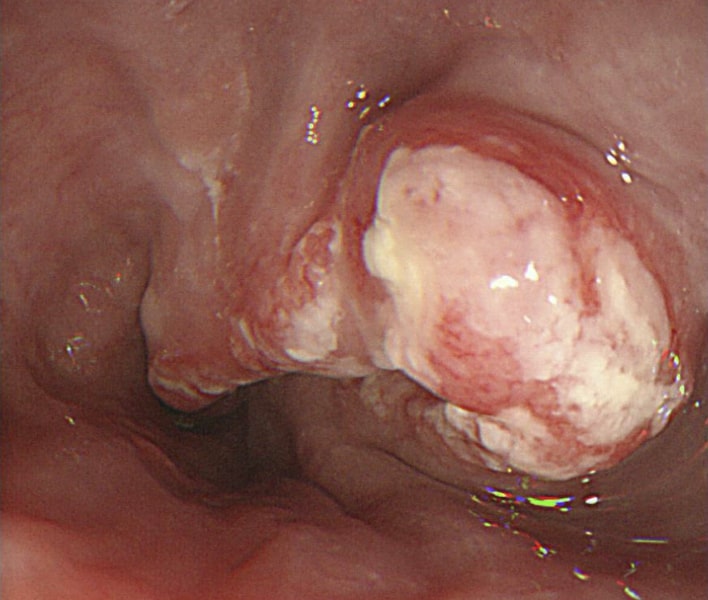
Esofagogastroduodenoscopia (EGD) que muestra el crecimiento del cáncer (carcinoma de células escamosas) , lo que provoca un estrechamiento de la luz
Imagen: “A Late-Stage Squamous Cell Carcinoma” por Brooks PJ, Enoch M-A, Goldman D, Li T-K, Yokoyama A. Licencia: C BY 2.5.