Las Corynebacteria son bacilos gram-positivos con forma de maza. Las Corynebacteria se aíslan comúnmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum medios de telurito o Loeffler y tienen gránulos metacromáticos característicos. La principal especie patógena es Corynebacterium diphtheriae Corynebacterium diphtheriae Diphtheria is an infectious disease caused by corynebacterium diphtheriae that most often results in respiratory disease with membranous inflammation of the pharynx, sore throat, fever, swollen glands, and weakness. The hallmark sign is a sheet of thick, gray material covering the back of the throat. Diphtheria, que causa la difteria, una infección grave de las vías respiratorias superiores. Los LOS Neisseria hallazgos característicos de la difteria incluyen pseudomembranas faríngeas (exudados amigdalinos grisáceos), faringitis grave y linfadenopatía en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum “cuello de toro”. El tratamiento es principalmente a través de la inmunización pasiva con antitoxina y antibióticos. La prevención es a través de la vacuna con toxoide diftérico.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
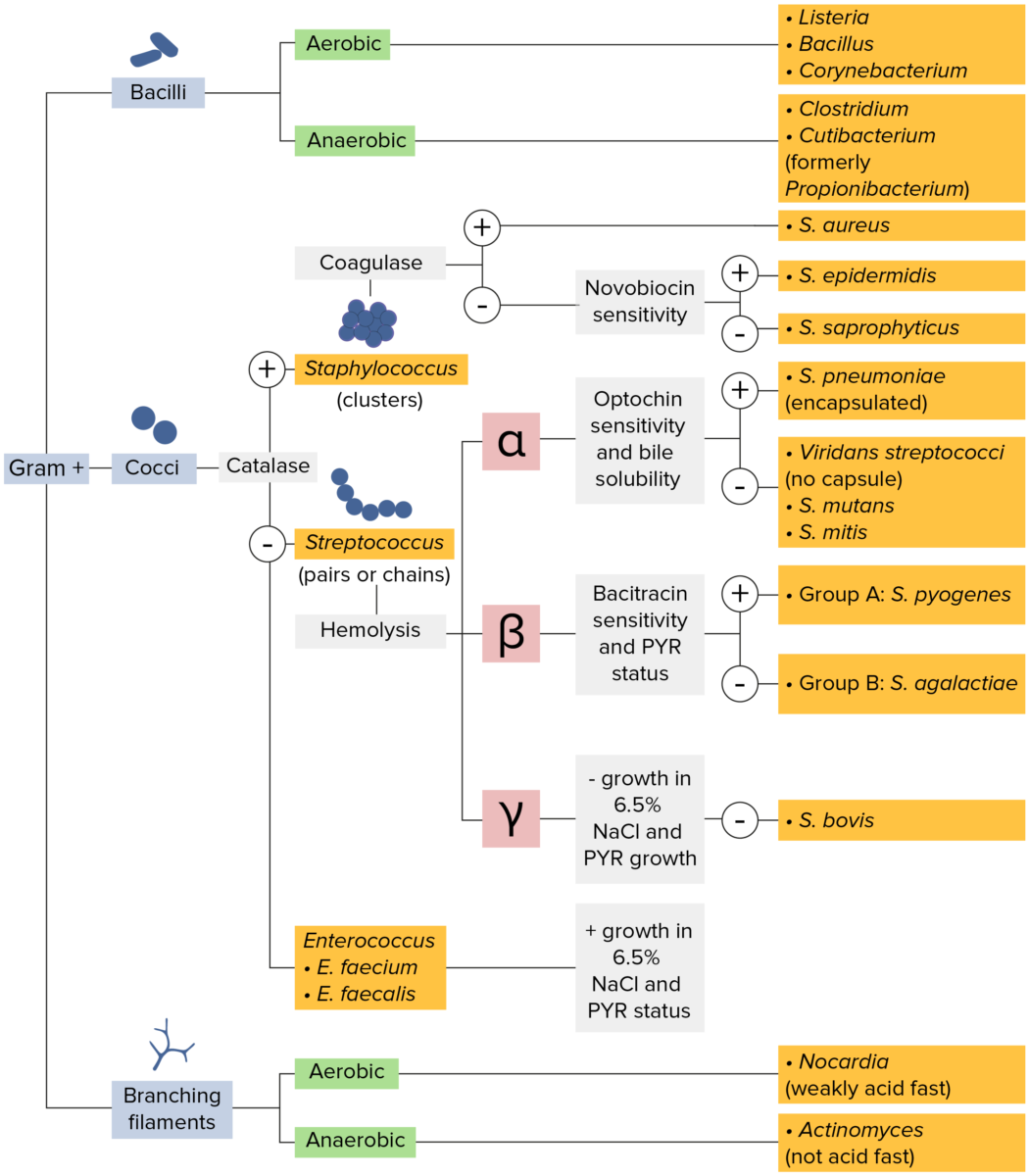
Bacterias gram-positivas:
La mayoría de las bacterias se pueden clasificar de acuerdo con un procedimiento de laboratorio llamado tinción de Gram.
Las bacterias con paredes celulares que tienen una capa gruesa de peptidoglicano retienen la tinción cristal violeta utilizada en la tinción de Gram, pero no se ven afectadas por la contratinción de safranina. Estas bacterias aparecen como azul púrpura en la tinción, lo que indica que son gram-positivas. Las bacterias pueden clasificarse además según su morfología (filamentos ramificados, bacilos y cocos en grupos o cadenas) y su capacidad para crecer en presencia de oxígeno (aeróbicos versus anaeróbicos). Los cocos también pueden identificarse con mayor profundidad. Los estafilococos pueden reducirse en función de la presencia de la enzima coagulasa y de su sensibilidad al antibiótico novobiocina. Los estreptococos se cultivan en agar sangre y se clasifican según la forma de hemólisis que emplean (α, β o γ). Los estreptococos se reducen aún más en función de su respuesta a la prueba de pirrolidonil-β-naftilamida, su sensibilidad a antimicrobianos específicos (optoquina y bacitracina) y su capacidad para crecer en medios de cloruro de sodio (NaCl).
Las características generales de las especies de Corynebacterium Corynebacterium Corynebacteria are gram-positive, club-shaped bacilli. Corynebacteria are commonly isolated on tellurite or Loeffler’s media and have characteristic metachromatic granules. The major pathogenic species is Corynebacterium diphtheriae, which causes a severe respiratory infection called diphtheria. Corynebacterium incluyen:
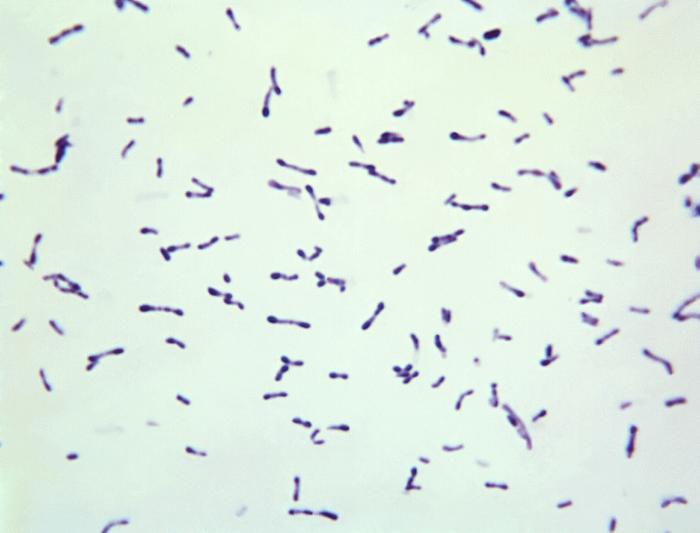
Micrografía de Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Imagen: “12163” por CDC/Graham Heid. Licencia: Dominio Público.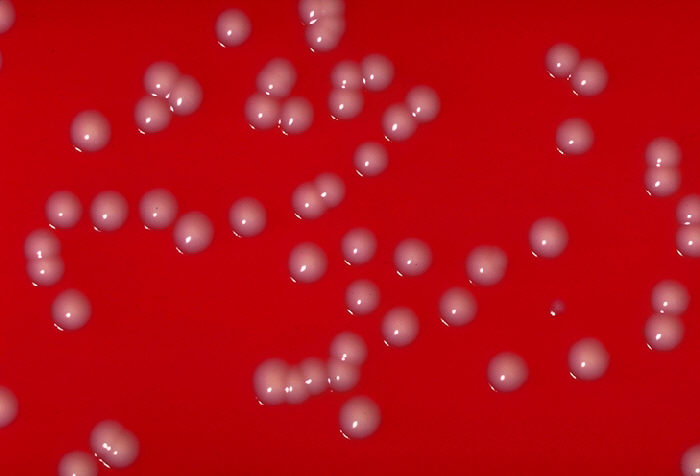
Colonias de Corynebacterium ulcerans en una placa de agar sangre
Imagen: “Corynebacterium ulcerans 01” por CDC/Dr. W. A. Clark. Licencia: Dominio Público.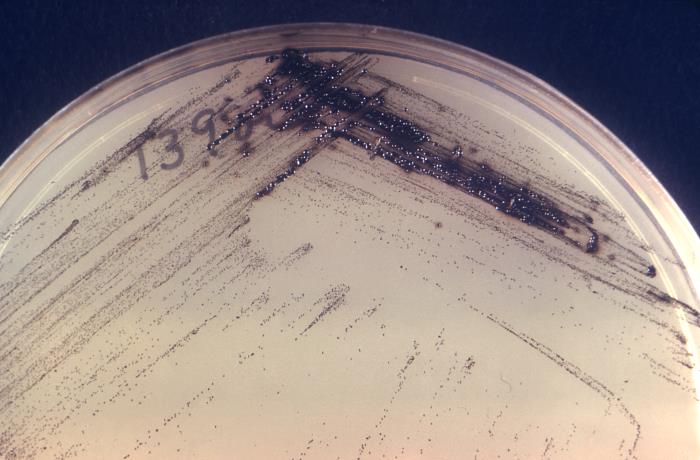
Corynebacterium diphtheriae en placa de agar de Tinsdale
Imagen: “16561” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público.Difteria (respiratoria):
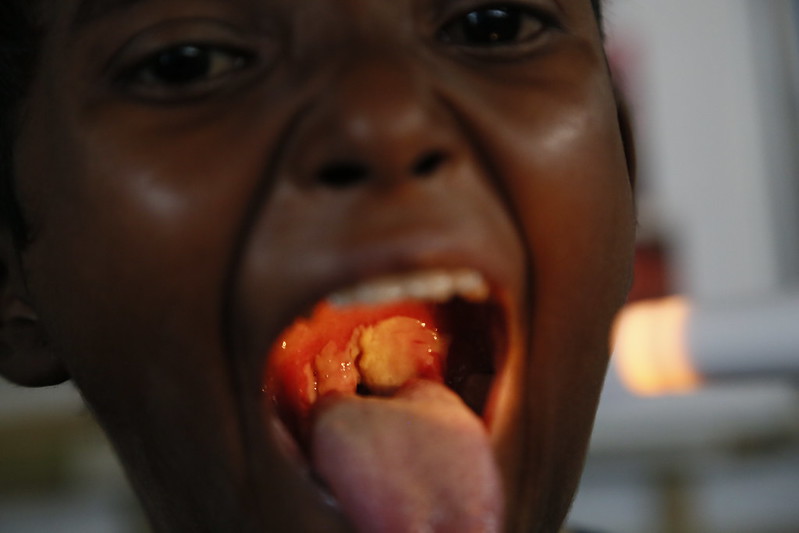
Difteria: paciente pediátrico con difteria que presenta la característica membrana de color blanco grisáceo que cubre la pared faríngea posterior
Imagen: “39015940254_849c8705a0_c” por Russell Watkins/Department for International Development. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.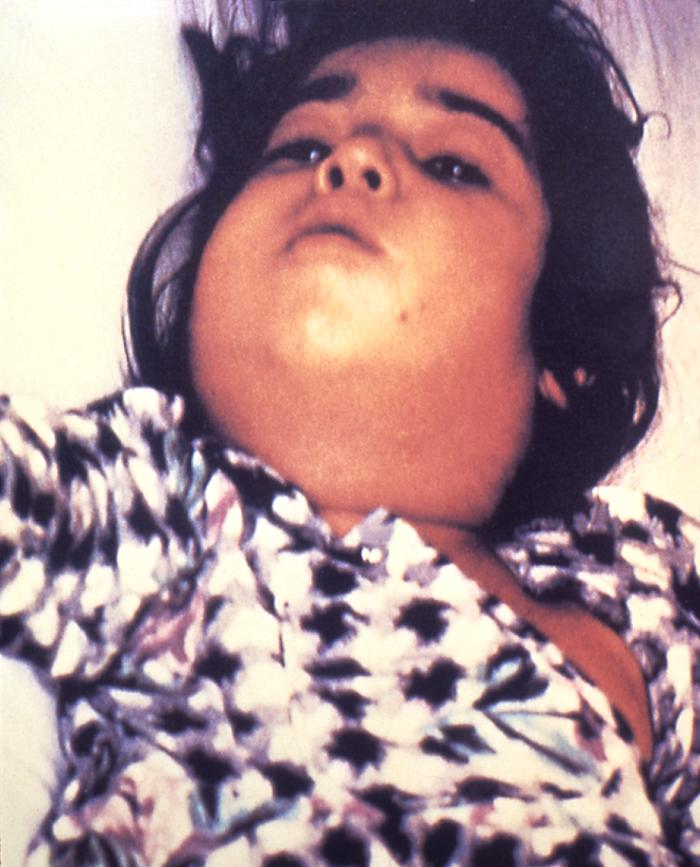
Paciente infectado por Corynebacterium: linfadenopatía severa, conocida como “cuello de toro”
Imagen: “5325” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público.Complicaciones/toxemia sistémica:
Difteria cutánea (herida):
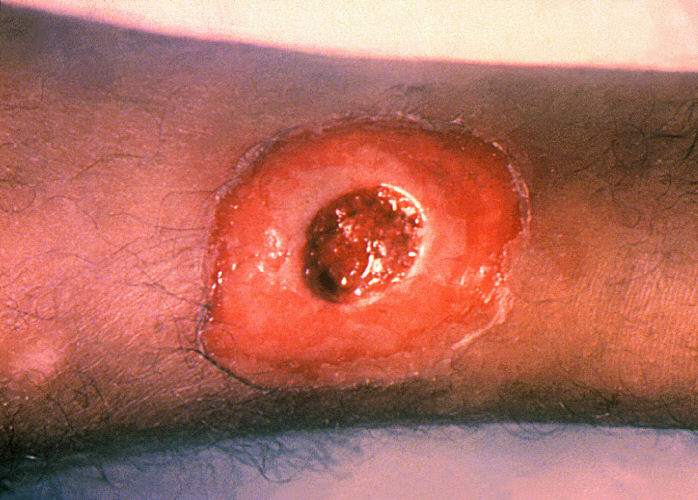
Difteria cutánea: úlcera crónica que no cicatriza
Imagen: “1941” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público.“’ABCDEFG‘ de Corynebacterium diphtheriae Corynebacterium diphtheriae Diphtheria is an infectious disease caused by corynebacterium diphtheriae that most often results in respiratory disease with membranous inflammation of the pharynx, sore throat, fever, swollen glands, and weakness. The hallmark sign is a sheet of thick, gray material covering the back of the throat. Diphtheria”: