Bacteroides Bacteroides Bacteroides is a genus of opportunistic, anaerobic, gram-negative bacilli. Bacteroides fragilis is the most common species involved in human disease and is part of the normal flora of the large intestine. Bacteroides es un género de bacilos gram-negativos, anaerobios, oportunistas. Bacteroides fragilis Bacteroides fragilis Gram-negative bacteria occurring in the lower intestinal tracts of man and other animals. It is the most common species of anaerobic bacteria isolated from human soft tissue infections. Bacteroides es la especie más común implicada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum enfermedades humanas y forma parte de la flora normal del intestino grueso. La infección ocurre más comúnmente cuando la pared del colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy se ve VE Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing afectada y las bacterias ingresan a la cavidad peritoneal, lo que puede causar infecciones intraabdominales y formación de abscesos intraabdominales. El tratamiento involucra antibióticos y drenaje de abscesos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Bacterias gram-negativas:
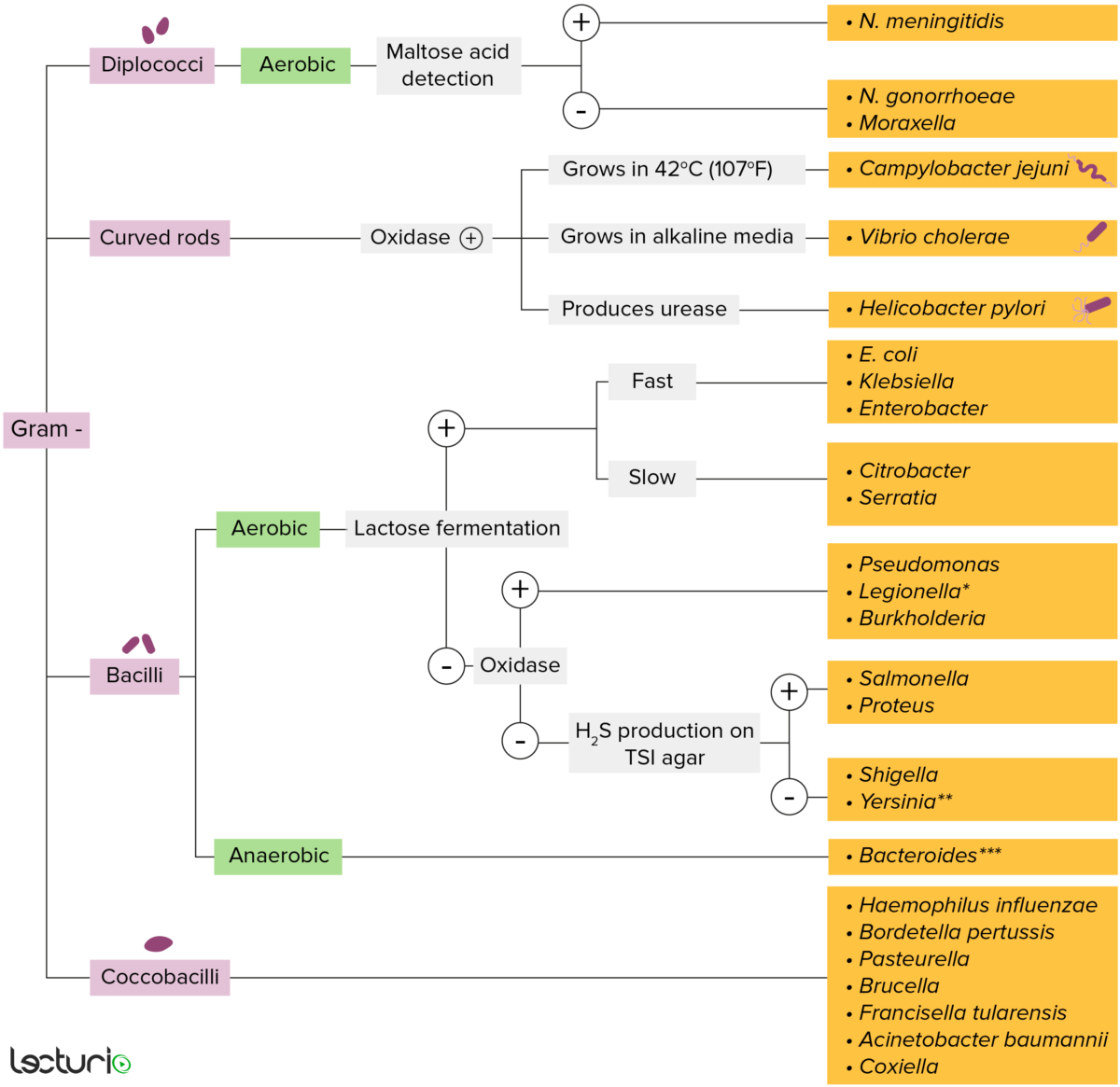
La mayoría de las bacterias se pueden clasificar de acuerdo a un procedimiento de laboratorio llamado tinción de Gram.
Las bacterias con paredes celulares que tienen una capa delgada de peptidoglicano no retienen la tinción de cristal violeta utilizada en la tinción de Gram. Sin embargo, estas bacterias retienen la contratinción de safranina y, por lo tanto, adoptan un color rojo-rosado en la tinción, lo que las hace gram-negativas. Estas bacterias pueden clasificarse además según su morfología (diplococos, bastones curvos, bacilos y cocobacilos) y su capacidad para crecer en presencia de oxígeno (aeróbicos versus anaeróbicos). Las bacterias se pueden identificar de manera más profunda cultivándolas en medios específicos (agar hierro triple azúcar) donde se pueden identificar sus enzimas (ureasa, oxidasa) y se puede probar su capacidad para fermentar lactosa.
* Se tiñe mal en la tinción de Gram
** Bastón/cocobacilo pleomórfico
*** Requiere medios de transporte especiales
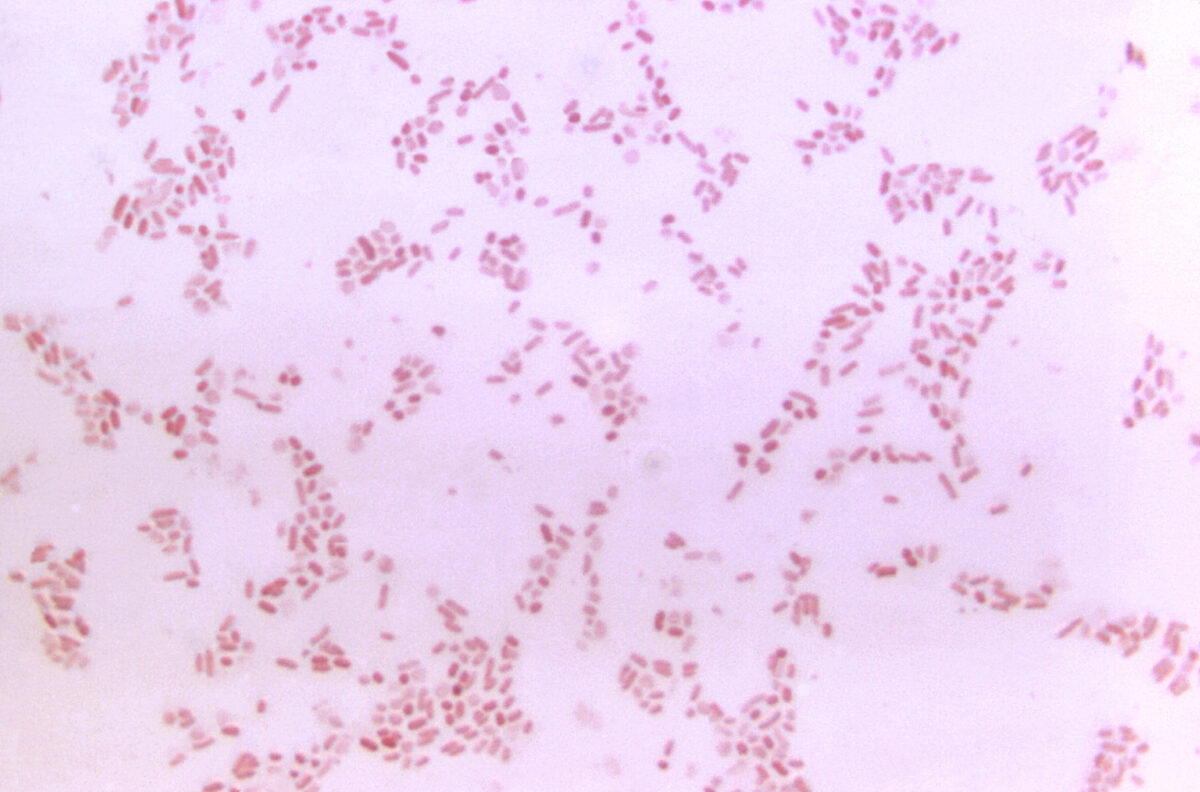
Micrografía de Bacteroides
La microfotografía muestra la bacteria gram-negativa Bacteroides fragilis.
La transmisión y la infección por la translocación de bacterias de las superficies mucosas a otros tejidos pueden deberse a:
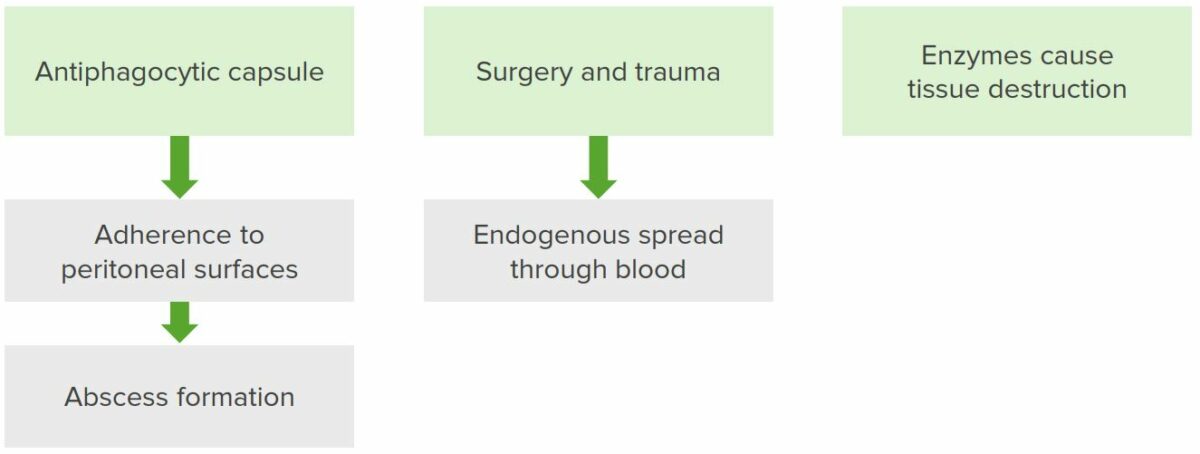
Patogénesis de Bacteroides fragilis
El patógeno contiene una cápsula antifagocítica que se adhiere a la superficie peritoneal. Esto resulta en la formación de abscesos. La cirugía y el traumatismo acentúan el problema, ya que rompen el absceso, lo que permite la propagación endógena del organismo hacia el torrente sanguíneo. Cuando esto ocurre, el patógeno libera enzimas degradantes que destruyen las células del huésped.
Bacteroides fragilis Bacteroides fragilis Gram-negative bacteria occurring in the lower intestinal tracts of man and other animals. It is the most common species of anaerobic bacteria isolated from human soft tissue infections. Bacteroides (B. fragilis) se encuentra naturalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el intestino grueso como parte de la flora natural. B. fragilis es un patógeno oportunista que rara vez infecta el sistema gastrointestinal y que con mayor frecuencia causa enfermedades cuando las bacterias escapan del intestino grueso.
| Afección | Características | Tipo de infección |
|---|---|---|
| Intraabdominal | Infección intraabdominal |
|
| Apendicitis perforada |
|
|
| Gastrointestinal | Diarrea inflamatoria |
|
| Ginecológica | Infecciones pélvicas |
|
| Abscesos ováricos y de las trompas de Falopio |
|
|
| Piel y tejidos blandos | Infección de pie diabético |
|
| Infecciones por mordedura de animales |
|
|
| Cerebral | Meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis y absceso cerebral |
|
| Diseminada | Bacteriemia |
|