La atelectasia es el colapso parcial o total de una parte del pulmón. La atelectasia es casi siempre un fenómeno secundario de condiciones que causan obstrucción bronquial, compresión externa, deficiencia de surfactante o cicatrización. La hipoxemia puede ocurrir como resultado de la sangre que fluye a través de segmentos pulmonares no ventilados. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes suelen ser asintomáticos. Sin embargo, también pueden aparecer disnea, tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome, dolor Dolor Inflammation torácico y fiebre. El diagnóstico se realiza por imagenología. El manejo incluye el tratamiento de la etiología subyacente, ejercicios de expansión pulmonar, fisioterapia torácica, broncodilatadores y broncoscopia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casos seleccionados.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La atelectasia es el colapso parcial o total del tejido pulmonar.
La atelectasia se clasifica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de la fisiopatología subyacente.
Etiología:
Fisiopatología:
Atelectasia por relajación:
Atelectasia compresiva:
Atelectasia adhesiva:
Atelectasia cicatricial:
Atelectasia de reemplazo:
Atelectasia redonda:
Hallazgos:
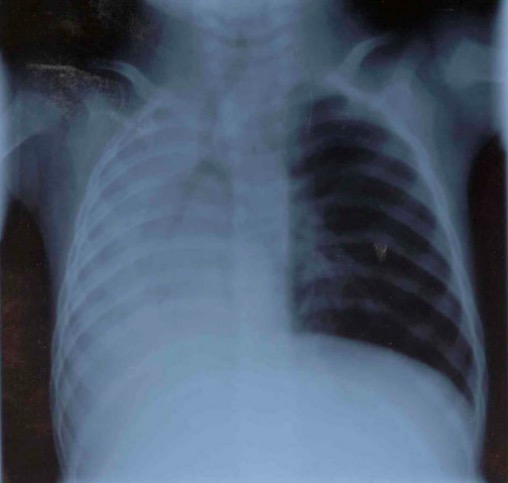
Atelectasia total de pulmón derecho en radiografía de tórax:
Nótese el desplazamiento traqueal y mediastínico hacia la derecha, con hiperinflación compensatoria del pulmón izquierdo.
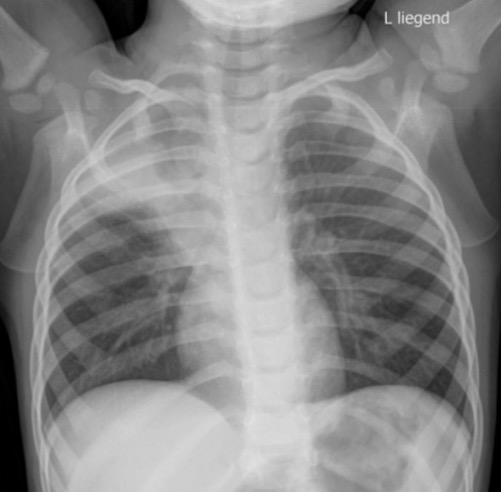
Radiografía de tórax que muestra atelectasia del lóbulo superior derecho con opacificación pulmonar y evidencia de pérdida de volumen
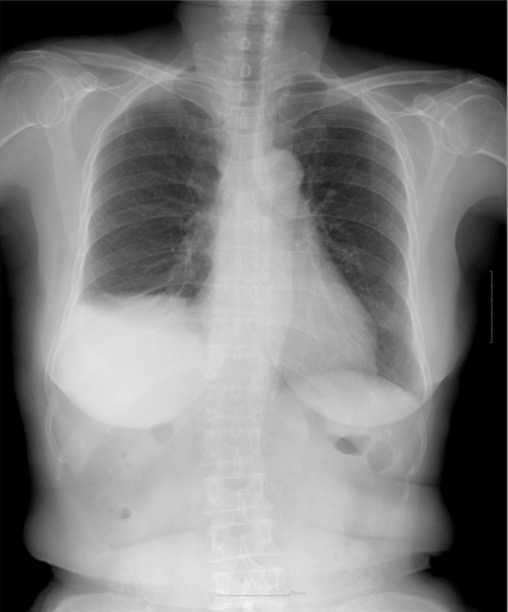
Radiografía de tórax que muestra atelectasia basilar derecha con derrame pleural derecho y elevación del hemidiafragma
Los LOS Neisseria hallazgos son similares a la radiografía de tórax, pero la TC puede ser más sensible para determinar una etiología:
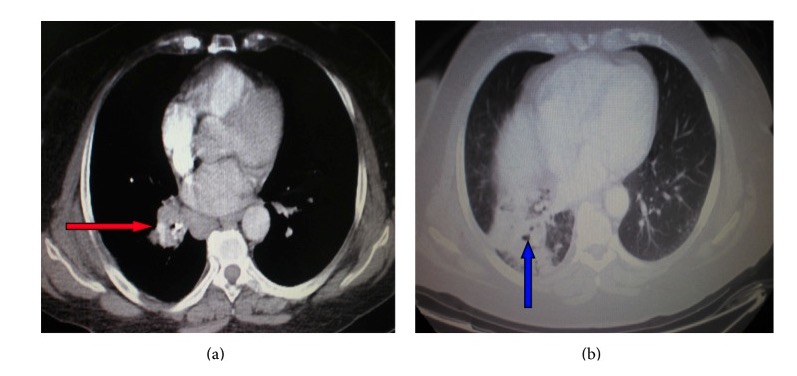
TC de tórax que muestra una masa hiliar derecha (flecha roja) que comprime el bronquio y conduce a atelectasia del lóbulo inferior derecho (flecha azul)
Imagen : “Atelectasia” por el Departamento de Neumonología, Hospital General del Ejército de Atenas, 138 Mesogion & Katehaki Avenue, 115 25 Atenas, Grecia. Licencia: CC BY 3.0Además de tratar la etiología subyacente de la atelectasia, se pueden utilizar las siguientes opciones para la prevención y el tratamiento:
La broncoscopia es un procedimiento que permite la visualización de las vías respiratorias mediante un broncoscopio.
Imagen por Lecturio.