El asma ASMA Autoimmune Hepatitis es una afección inflamatoria crónica que provoca una obstrucción intermitente de las vías respiratorias, sibilancias, tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome y disnea. La genética y los LOS Neisseria factores ambientales desempeñan un papel importante en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la etiología. El diagnóstico de asma ASMA Autoimmune Hepatitis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria niños suele implicar una toma cuidadosa de los LOS Neisseria antecedentes, un examen físico, pruebas de función pulmonar y estudios radiológicos para descartar otras afecciones. El objetivo es minimizar los LOS Neisseria síntomas, las exacerbaciones y la morbilidad funcional y psicológica. El tratamiento incluye el alivio clínico y la farmacoterapia a largo plazo.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El asma ASMA Autoimmune Hepatitis se define como la obstrucción episódica de las vías respiratorias pulmonares resultante de una afección inflamatoria crónica.
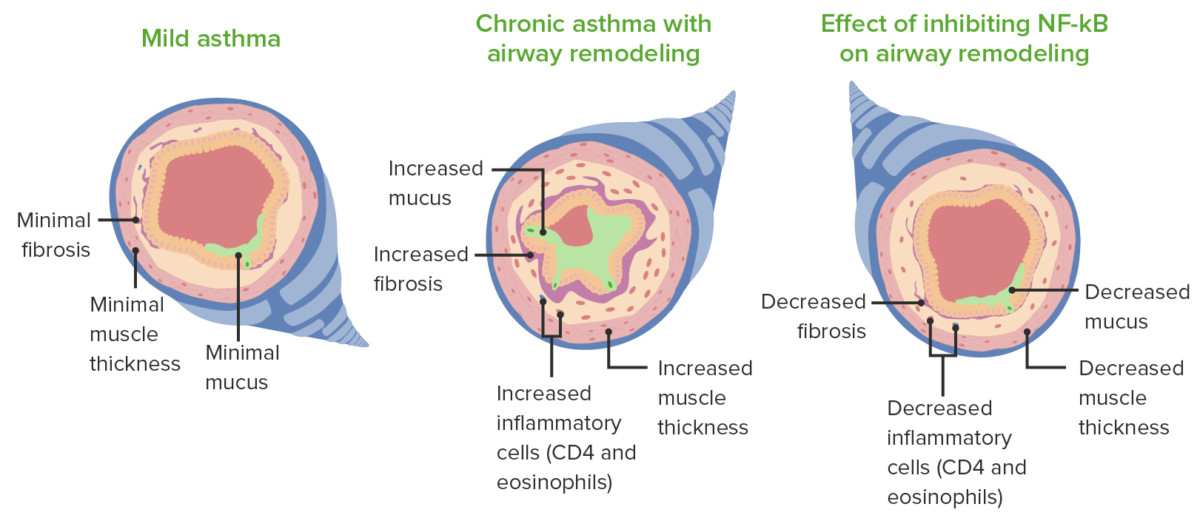
Remodelación y cambios patológicos observados en el asma.
Imagen por Lecturio.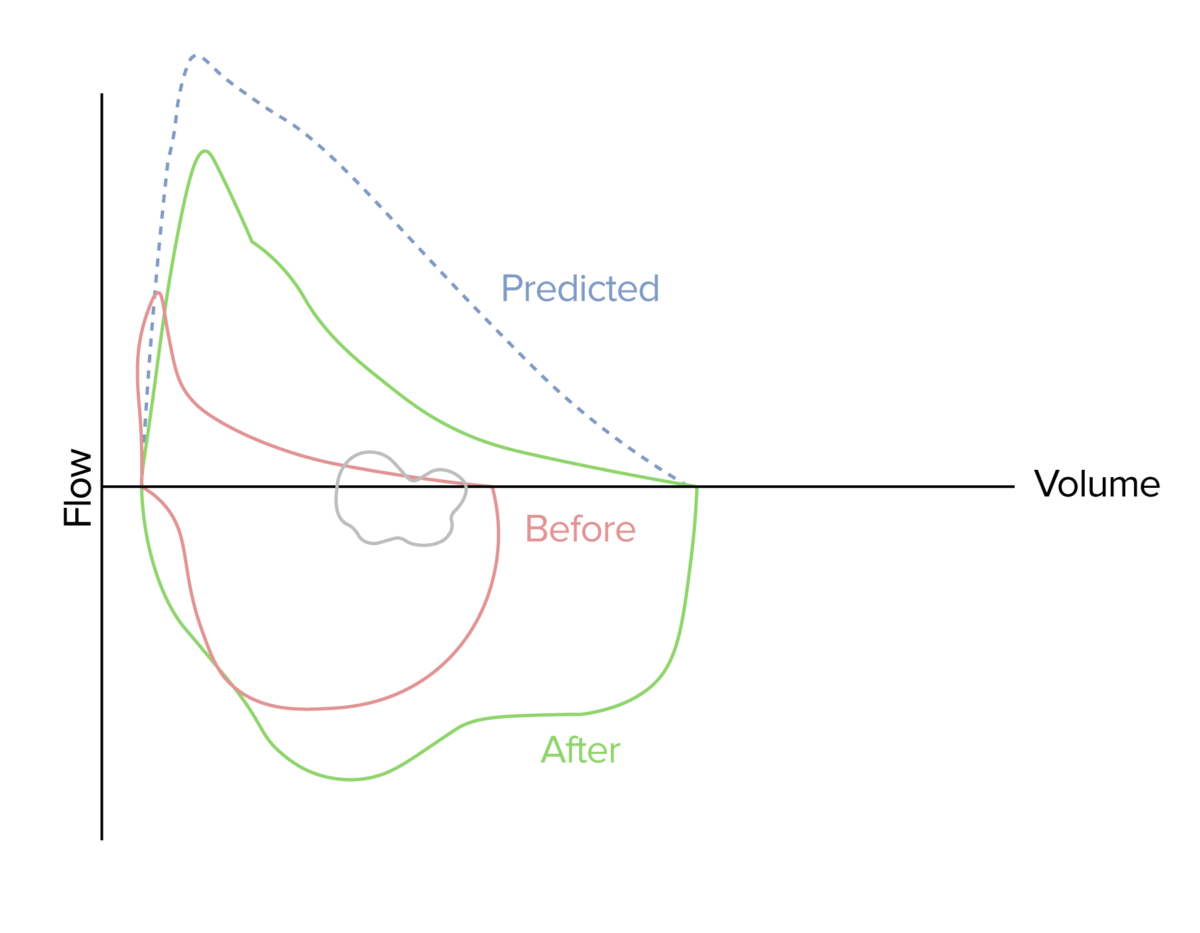
Curva de flujo-volumen que demuestra la mejora del flujo de aire (curva verde) tras la administración de un broncodilatador de acción corta en un paciente con una crisis de asma aguda (curva roja)
Imagen por Lecturio.
Una niña utilizando un medidor de flujo máximo en una clínica
Imagen: A child using a peak expiratory flow meter in a pediatric clinic. Por: National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Licencia: Dominio públicoEl objetivo del tratamiento es prevenir/minimizar los LOS Neisseria síntomas, las exacerbaciones y la morbilidad funcional y psicológica para proporcionar un estilo de vida saludable adecuado a la edad del niño.
El tratamiento del asma ASMA Autoimmune Hepatitis tiene 4 componentes:
| Componente de gravedad | Clasificación de la gravedad del asma ASMA Autoimmune Hepatitis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intermitente | Persistente | |||
| Leve | Moderada | Severa | ||
| Síntomas | ≤ 2 días/semana | > 2 días/semana | Diario | A lo largo del día |
| Uso de agonistas beta 2 de acción corta | ≤ 2 días/semana | > 2 días/semana | Diario | Varias veces al AL Amyloidosis día |
| Despertares nocturnos | ≤ 2/mes | 3–4/mes | ≥ 1/semana | Cada noche |
| Limitación de la actividad | Ninguna | Menor | Cierto grado | Extrema |
| Función pulmonar (solo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños > 5 años) |
|
|
|
|
| Exacerbación que requiere el uso de corticosteroides orales | 0–1 veces/año | ≥ 2 veces/año | ||
| Acción recomendada para el tratamiento | Paso 1 | Paso 2 | Paso 3 + dosis media de corticosteroides inhalados | Paso 3 + dosis media de corticosteroides inhalados, o Paso 4 o 5 |
| Considerar un curso corto de corticosteroides orales. | ||||
| En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 2–6 semanas, evaluar como control y ajustar la dosis. | ||||
| Componente de control | Bien controlada | Mal controlada | Muy mal controlada |
|---|---|---|---|
| Síntomas | ≤ 2 días/semana | > 2 días/semana o varias veces en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ≤ 2 días/semana | A lo largo del día |
| Uso de agonistas beta 2 de acción corta | ≤ 2 días/semana | > 2 días/semana o varias veces en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ≤ 2 días/semana | Varias veces al AL Amyloidosis día |
| Síntomas | ≤ 2 días/semana | > 2 días/semana | A lo largo del día |
| Despertares nocturnos | ≤ 1/mes | ≥ 2/mes | ≥ 2/semana |
| Limitación de la actividad | Ninguna | Cierto grado | Extrema |
| Función pulmonar | |||
| VEF1 | > 80% | 60%–80% | < 60% |
| VEF1/CVF | > 80% | 75%–80% | < 75% |
| Exacerbación que requiere el uso de corticosteroides orales | 0–1/año | ≥ 2/año | |
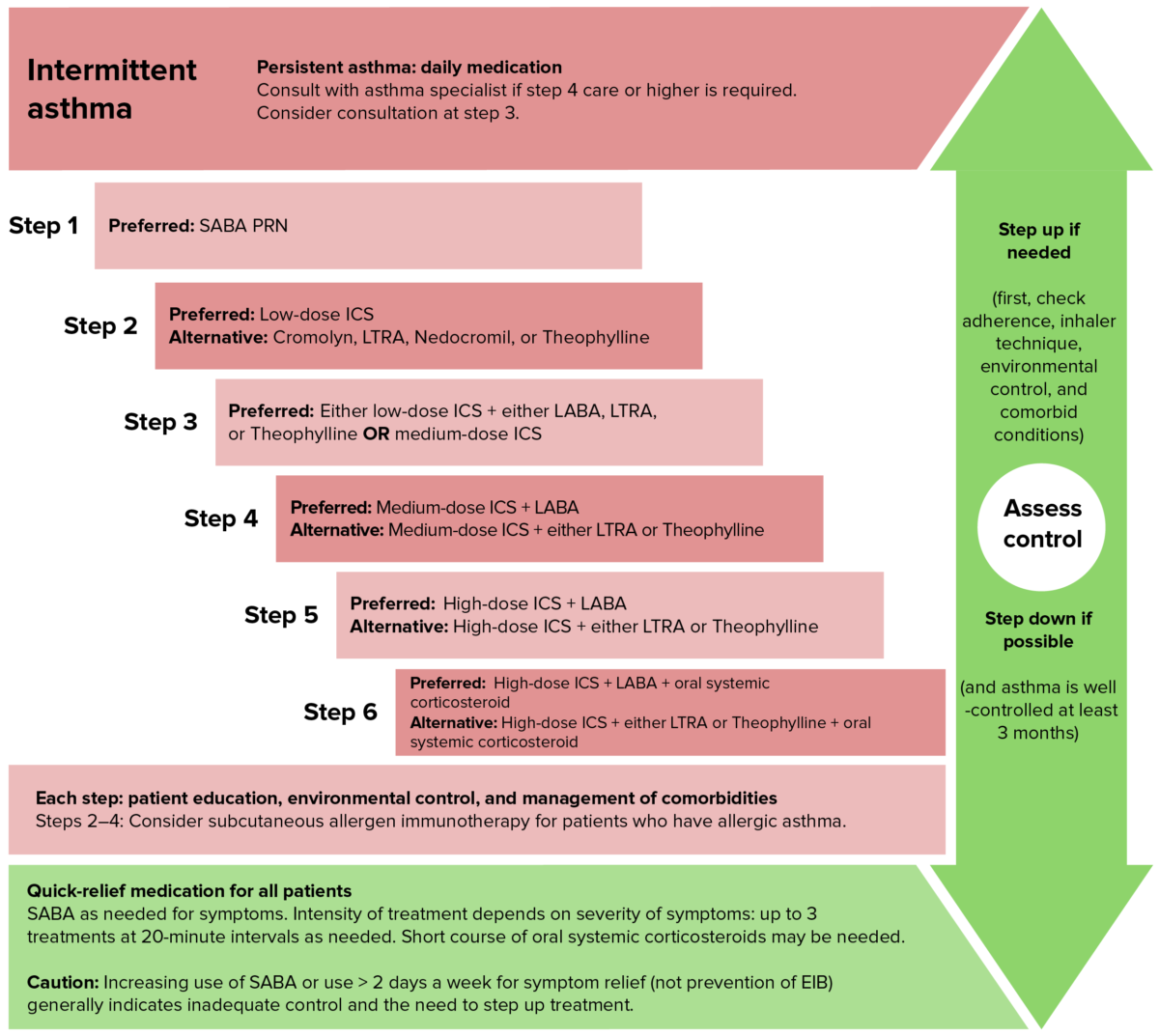
Abordaje de escalera ascendente en el tratamiento del asma en niños de 5–11 años. Obsérvese que en los niños no se utilizan inicialmente broncodilatadores de acción prolongada y que el objetivo es disponer de dosis más bajas de corticosteroides inhalados.
Imagen por Lecturio.La exacerbación aguda del asma ASMA Autoimmune Hepatitis es el empeoramiento progresivo agudo o subagudo de la inflamación y la obstrucción de las vías respiratorias en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un paciente asmático.
| Leve | Moderada | Severa | Paro respiratorio inminente | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nivel de alerta | Normal | Generalmente agitado | Agitado | Somnoliento o confundido |
| Frecuencia respiratoria (respiraciones/minuto) | Aumentada | Aumentada | > 30 | Movimiento toracoabdominal paradójico o frecuencia respiratoria normal-baja |
| Pulso (latidos/minuto) | < 100 | 100–120 | > 120 | Bradicardia |
| Sibilancias | Solo al AL Amyloidosis final de la espiración | A lo largo de la espiración | Durante la inhalación y la espiración | Ausentes |
| Relación inspiración/espiración (normalmente 2:1) | Relación inspiratoria/espiratoria de 1:1 | Relación inspiratoria/espiratoria de 1:2 | < 1:2 | N/A |
| Uso de musculatura accesoria | Ninguno | Común | Presente | Presente, pero en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum disminución |
| Saturación de O2 | > 95% | 90%–95% | < 90% ± cianosis | < 90% ± cianosis |
| PCO2 (mm Hg) | < 42 | < 42 | < 42 | < 42 |
| Flujo espiratorio máximo | ≥ 70% | 40%–69% | 25%–39% | ≤ 25% |