Los LOS Neisseria agentes antivirales contra los LOS Neisseria herpesvirus humanos (HHVs, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) incluyen aciclovir, cidofovir Cidofovir An acyclic nucleoside phosphonate that acts as a competitive inhibitor of viral DNA polymerases. It is used in the treatment of retinitis caused by cytomegalovirus infections and may also be useful for treating herpesvirus infections. Antivirals for Herpes Virus y foscarnet Foscarnet An antiviral agent used in the treatment of cytomegalovirus retinitis. Foscarnet also shows activity against human herpesviruses and HIV. Antivirals for Herpes Virus. Los LOS Neisseria herpesvirus humanos son virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de ADN de la familia Herpesviridae Herpesviridae A family of enveloped, linear, double-stranded DNA viruses infecting a wide variety of animals. Subfamilies, based on biological characteristics, include: alphaherpesvirinae; betaherpesvirinae; and gammaherpesvirinae. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2 . El virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology del herpes simple ( HSV HSV Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is a double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the family Herpesviridae. Herpes simplex virus commonly causes recurrent infections involving the skin and mucosal surfaces, including the mouth, lips, eyes, and genitals. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés), el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la varicela-zoster (VZV, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés), el citomegalovirus (CMV), el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de Epstein-Barr ( EBV EBV Epstein-barr virus (EBV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the herpesviridae family. This highly prevalent virus is mostly transmitted through contact with oropharyngeal secretions from an infected individual. The virus can infect epithelial cells and B lymphocytes, where it can undergo lytic replication or latency. Epstein-Barr Virus, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) y el herpesvirus humano tipo 8 (HHV-8, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) pertenecen a la familia Herpesviridae Herpesviridae A family of enveloped, linear, double-stranded DNA viruses infecting a wide variety of animals. Subfamilies, based on biological characteristics, include: alphaherpesvirinae; betaherpesvirinae; and gammaherpesvirinae. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2. Los LOS Neisseria antivirales contra esta familia generalmente actúan mediante la inhibición de la ADN polimerasa. El aciclovir (el análogo de nucleósido prototípico) requiere quinasa viral para la fosforilación a fin de convertirse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un trifosfato, que se incorpora en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ADN viral. El cidofovir Cidofovir An acyclic nucleoside phosphonate that acts as a competitive inhibitor of viral DNA polymerases. It is used in the treatment of retinitis caused by cytomegalovirus infections and may also be useful for treating herpesvirus infections. Antivirals for Herpes Virus requiere la fosforilación por parte de la cinasa celular del huésped, lo que permite que el cidofovir Cidofovir An acyclic nucleoside phosphonate that acts as a competitive inhibitor of viral DNA polymerases. It is used in the treatment of retinitis caused by cytomegalovirus infections and may also be useful for treating herpesvirus infections. Antivirals for Herpes Virus tenga actividad contra los LOS Neisseria virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology mutados y se vuelva deficiente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la cinasa viral. Foscarnet Foscarnet An antiviral agent used in the treatment of cytomegalovirus retinitis. Foscarnet also shows activity against human herpesviruses and HIV. Antivirals for Herpes Virus (un análogo de pirofosfato) no requiere fosforilación. La nefrotoxicidad es un efecto secundario compartido entre los LOS Neisseria medicamentos. El aciclovir también puede causar nefropatía cristalina obstructiva y el foscarnet Foscarnet An antiviral agent used in the treatment of cytomegalovirus retinitis. Foscarnet also shows activity against human herpesviruses and HIV. Antivirals for Herpes Virus conlleva un riesgo de anomalías electrolíticas y convulsiones. El efecto nefrotóxico del cidofovir Cidofovir An acyclic nucleoside phosphonate that acts as a competitive inhibitor of viral DNA polymerases. It is used in the treatment of retinitis caused by cytomegalovirus infections and may also be useful for treating herpesvirus infections. Antivirals for Herpes Virus puede reducirse con solución salina intravenosa y probenecid Probenecid The prototypical uricosuric agent. It inhibits the renal excretion of organic anions and reduces tubular reabsorption of urate. Probenecid has also been used to treat patients with renal impairment, and, because it reduces the renal tubular excretion of other drugs, has been used as an adjunct to antibacterial therapy. Gout Drugs.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
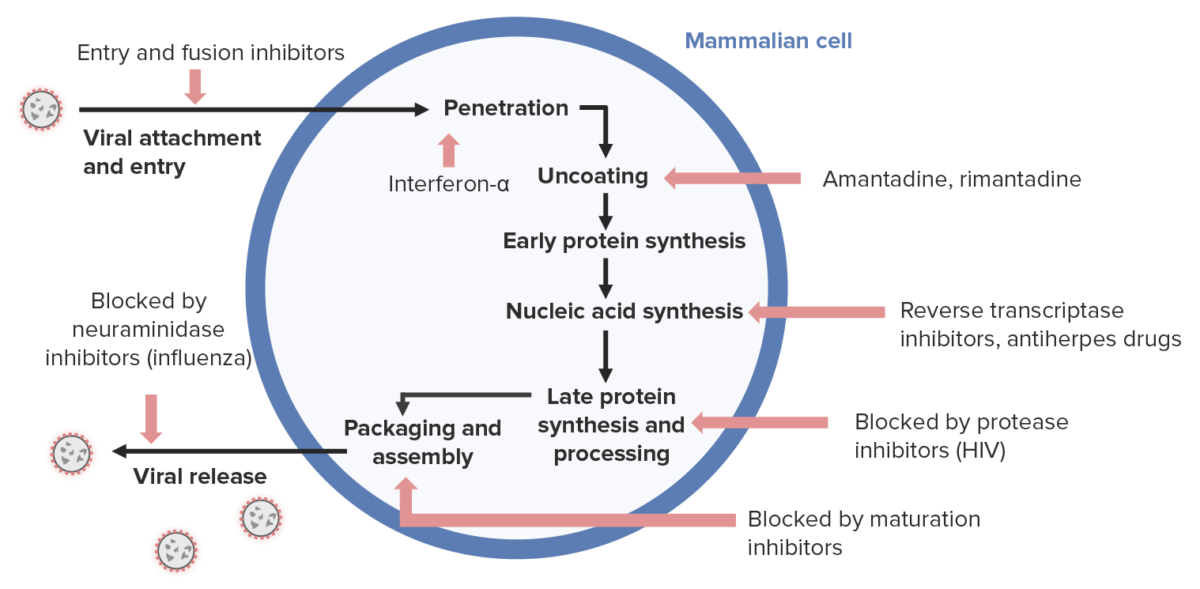
Mecanismo de acción de medicamentos antivirales:
Los antivirales para los herpesvirus (lado derecho) generalmente inhiben la síntesis de ácidos nucleicos.
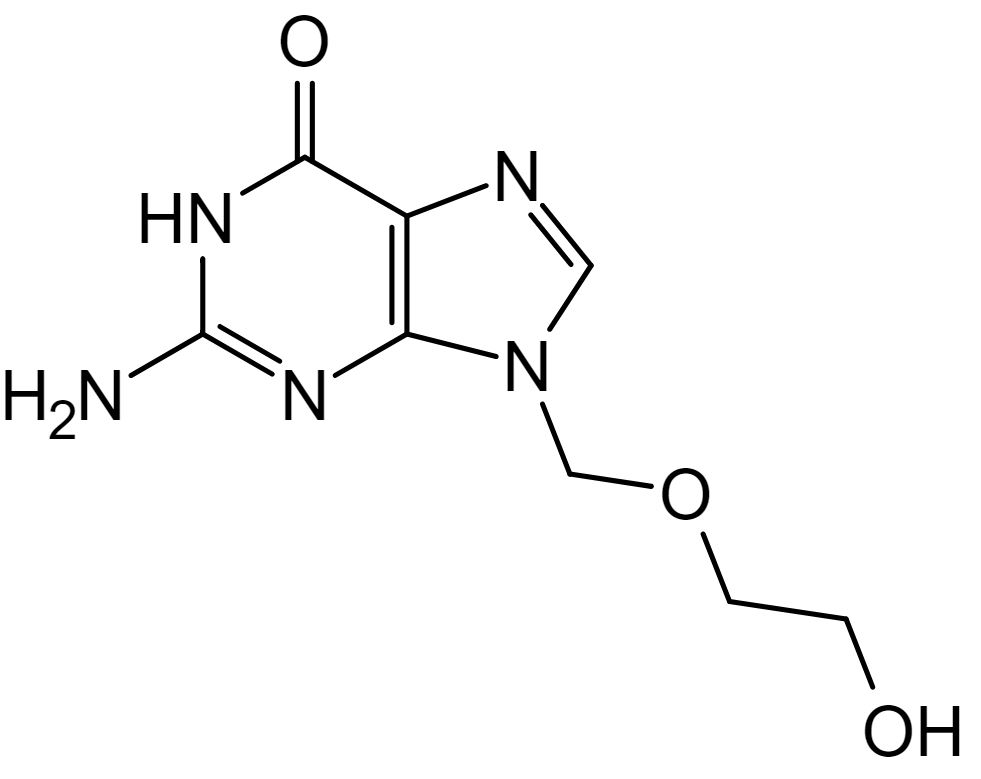
Estructura química del aciclovir
Imagen : “Aciclovir structure” por Steffen 962. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoAciclovir:
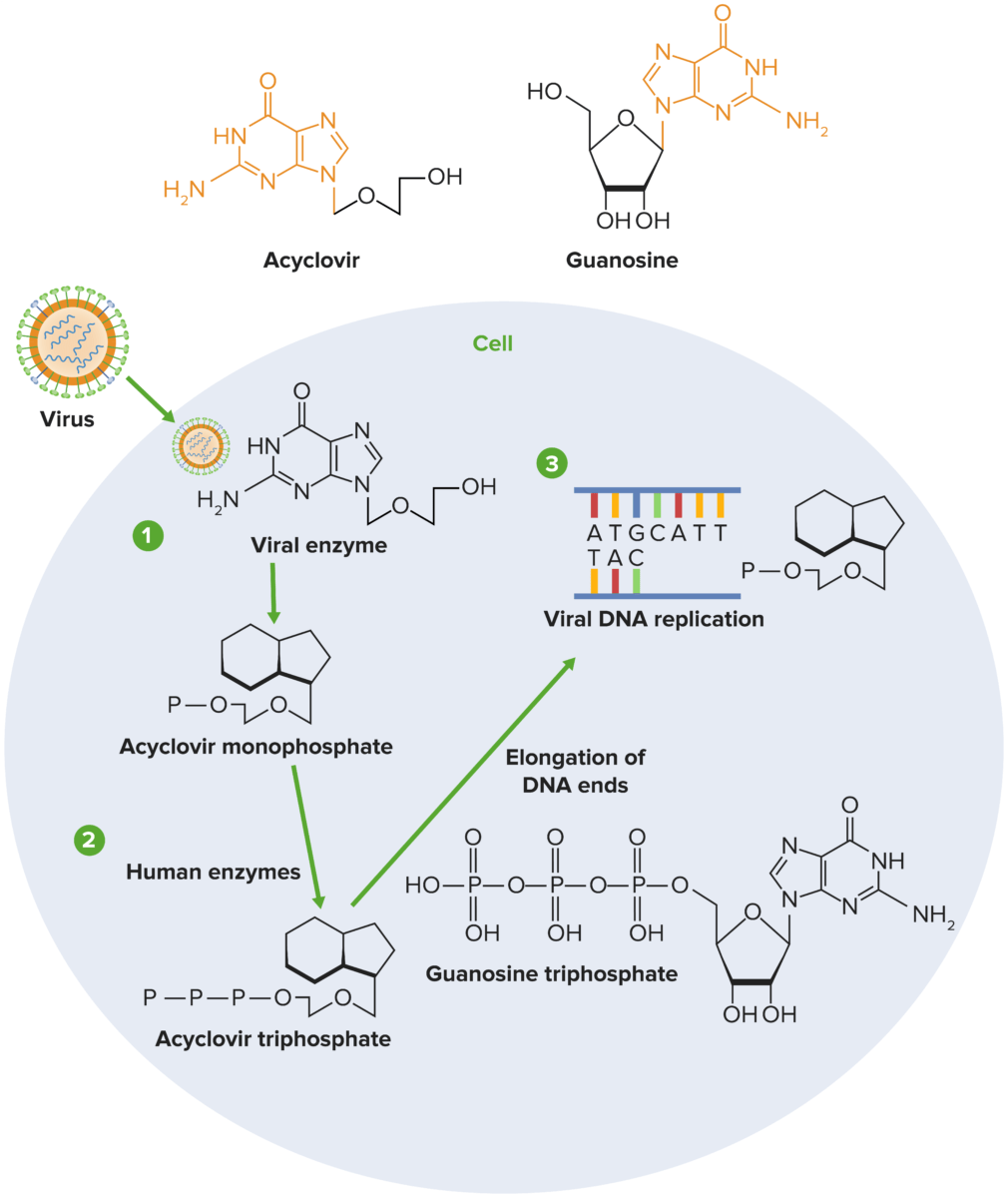
Mecanismo de acción del aciclovir:
1) El aciclovir sufre una fosforilación secuencial, facilitada por la timidina quinasa del herpesvirus y las quinasas del huésped. Dado que la timidina quinasa viral es necesaria para la fosforilación del aciclovir, solo las células infectadas por el virus se ven afectadas por el medicamento.
2) Las enzimas del huésped convierten el monofosfato en trifosfato de aciclovir, que posteriormente compite con el trifosfato de desguanosina (dGTP) por la ADN polimerasa viral.
3) El aciclovir se añade a la hebra en crecimiento durante la replicación viral en lugar del guanosintrifosfato (GTP), lo que detiene la replicación viral al detener la elongación de la molécula de ADN.
Aciclovir (y otros medicamentos relacionados):
Aciclovir:
| Medicamento | Características y mecanismo de acción | Farmacocinética | Indicación aprobada | Efectos secundarios de los LOS Neisseria medicamentos |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aciclovir |
|
Mala biodisponibilidad oral |
|
|
| Valaciclovir |
|
Buena biodisponibilidad oral | ||
| Penciclovir Penciclovir Antivirals for Herpes Virus |
|
Tópica | HSV HSV Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is a double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the family Herpesviridae. Herpes simplex virus commonly causes recurrent infections involving the skin and mucosal surfaces, including the mouth, lips, eyes, and genitals. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2 (herpes labial) | Efectos secundarios leves |
| Famciclovir Famciclovir An aminopurine derivative and prodrug of penciclovir which is a competitive inhibitor of herpes simplex 2 DNA polymerase. It is used to treat herpes simplex virus infection. Antivirals for Herpes Virus |
|
Mejor biodisponibilidad oral que penciclovir Penciclovir Antivirals for Herpes Virus |
|
|
| Ganciclovir Ganciclovir An acyclovir analog that is a potent inhibitor of the herpesvirus family including cytomegalovirus. Ganciclovir is used to treat complications from aids-associated cytomegalovirus infections. Antivirals for Herpes Virus |
|
|
Infecciones por citomegalovirus (CMV) |
|
| Valganciclovir |
|
Mejor biodisponibilidad oral que ganciclovir Ganciclovir An acyclovir analog that is a potent inhibitor of the herpesvirus family including cytomegalovirus. Ganciclovir is used to treat complications from aids-associated cytomegalovirus infections. Antivirals for Herpes Virus |
El cidofovir Cidofovir An acyclic nucleoside phosphonate that acts as a competitive inhibitor of viral DNA polymerases. It is used in the treatment of retinitis caused by cytomegalovirus infections and may also be useful for treating herpesvirus infections. Antivirals for Herpes Virus es un análogo de nucleótido de citidina.
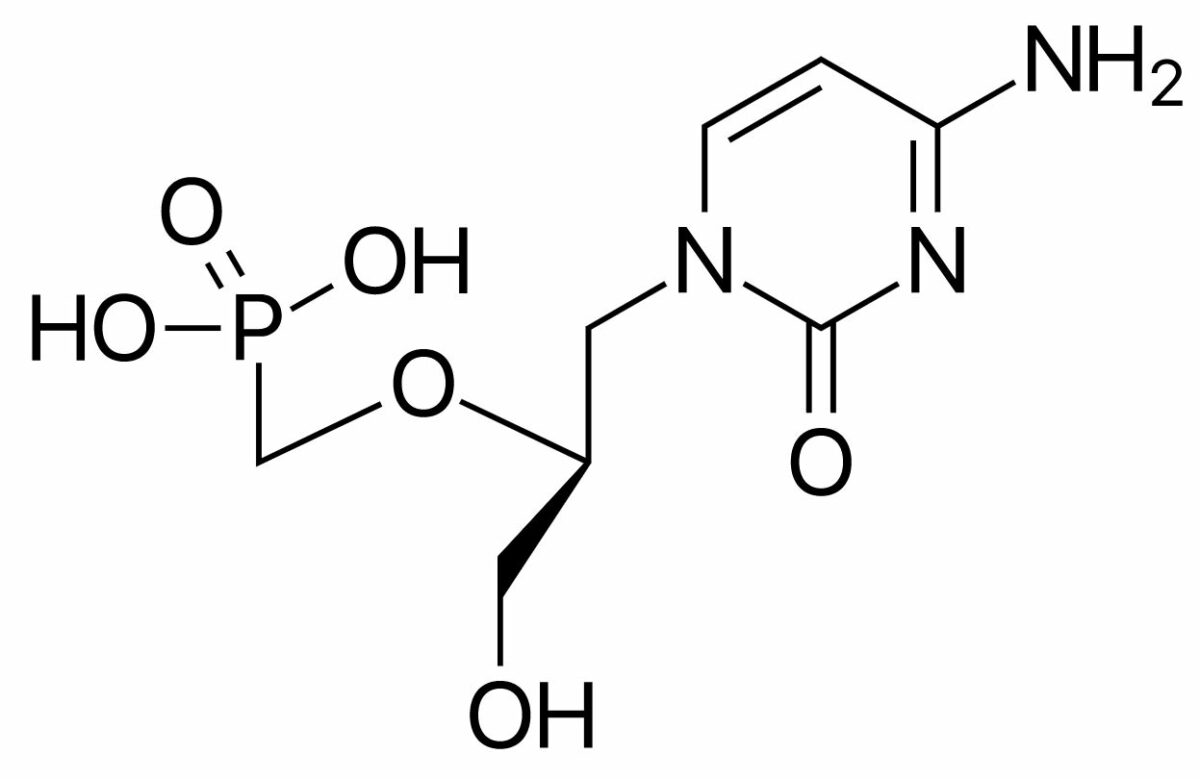
Estructura química del cidofovir
Imagen : “Cidofovir” por ljfa-ag. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoFoscarnet Foscarnet An antiviral agent used in the treatment of cytomegalovirus retinitis. Foscarnet also shows activity against human herpesviruses and HIV. Antivirals for Herpes Virus es un análogo de pirofosfato.
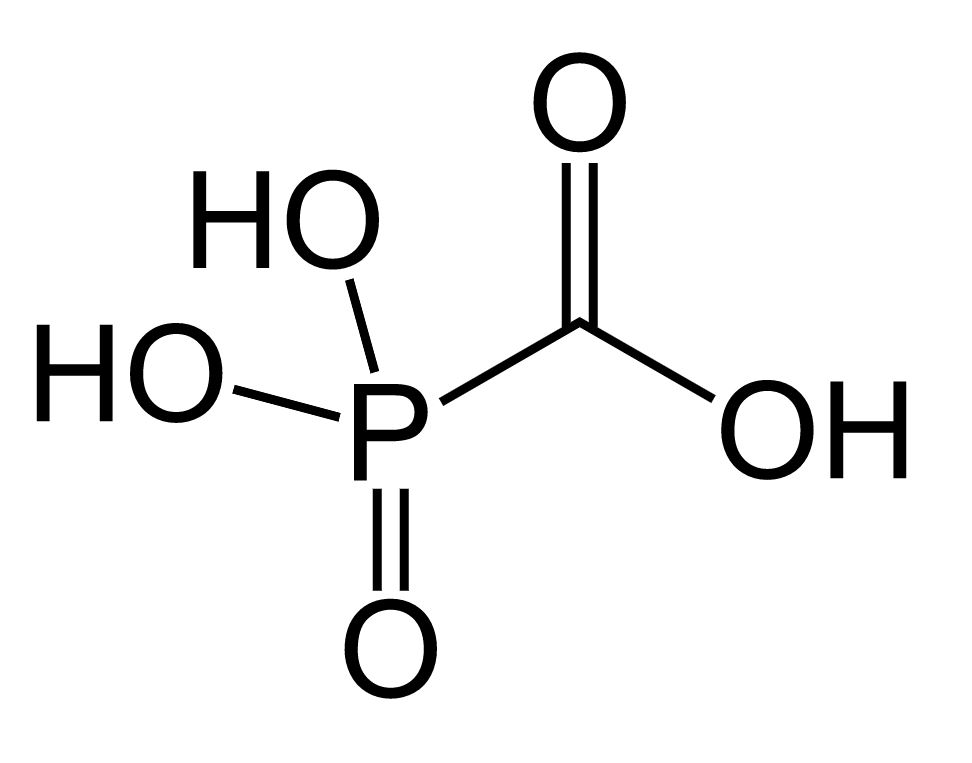
Estructura química de foscarnet
Imagen : “Foscarnet” por Fvasconcellos. Licencia: Dominio Público| Medicamento antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B | Mecanismo de acción | Indicaciones | Principales efectos secundarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aciclovir (análogo de nucleósido) | Inhibidor de la polimerasa que requiere fosforilación por cinasa viral |
|
Lesión renal aguda (nefropatía obstructiva) |
| Cidofovir Cidofovir An acyclic nucleoside phosphonate that acts as a competitive inhibitor of viral DNA polymerases. It is used in the treatment of retinitis caused by cytomegalovirus infections and may also be useful for treating herpesvirus infections. Antivirals for Herpes Virus (análogo de nucleótido) | Inhibidor de la polimerasa que requiere fosforilación por la cinasa del huésped (no la cinasa viral) | Aprobado para retinitis por CMV con actividad contra otros virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology* | Nefrotoxicidad (riesgo disminuido por solución salina IV y probenecid Probenecid The prototypical uricosuric agent. It inhibits the renal excretion of organic anions and reduces tubular reabsorption of urate. Probenecid has also been used to treat patients with renal impairment, and, because it reduces the renal tubular excretion of other drugs, has been used as an adjunct to antibacterial therapy. Gout Drugs) |
| Foscarnet Foscarnet An antiviral agent used in the treatment of cytomegalovirus retinitis. Foscarnet also shows activity against human herpesviruses and HIV. Antivirals for Herpes Virus (análogo de pirofosfato) | Inhibidor de la polimerasa que no requiere fosforilación | Resistente a CMV y HSV HSV Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is a double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the family Herpesviridae. Herpes simplex virus commonly causes recurrent infections involving the skin and mucosal surfaces, including the mouth, lips, eyes, and genitals. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2 |
|