El adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus (member of the family Adenoviridae) is a nonenveloped, double-stranded DNA virus. Adenovirus is transmitted in a variety of ways, and it can have various presentations based on the site of entry. Presentation can include febrile pharyngitis, conjunctivitis, acute respiratory disease, atypical pneumonia, and gastroenteritis. Adenovirus (miembro de la familia Adenoviridae Adenoviridae A family of non-enveloped viruses infecting mammals (mastadenovirus) and birds (aviadenovirus) or both (atadenovirus). Infections may be asymptomatic or result in a variety of diseases. Adenovirus) es un virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de ácido desoxirribonucleico (ADN) de doble cadena no envuelto. El adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus (member of the family Adenoviridae) is a nonenveloped, double-stranded DNA virus. Adenovirus is transmitted in a variety of ways, and it can have various presentations based on the site of entry. Presentation can include febrile pharyngitis, conjunctivitis, acute respiratory disease, atypical pneumonia, and gastroenteritis. Adenovirus se transmite de diversas formas y puede tener varias presentaciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función del lugar de entrada. La presentación puede incluir faringitis febril, conjuntivitis, enfermedad respiratoria aguda, neumonía atípica y gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis is inflammation of the stomach and intestines, commonly caused by infections from bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Transmission may be foodborne, fecal-oral, or through animal contact. Common clinical features include abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and dehydration. Gastroenteritis. Las manifestaciones graves incluyen cistitis hemorrágica aguda, hepatitis, miocarditis e infección diseminada. El diagnóstico se confirma con reacción en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cadena de polimerasa ( PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) y pruebas de antígenos. La mayoría de las infecciones son autolimitadas, por lo que el tratamiento suele ser de soporte. El tratamiento antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B se reserva para los LOS Neisseria pacientes inmunocomprometidos e infecciones graves.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
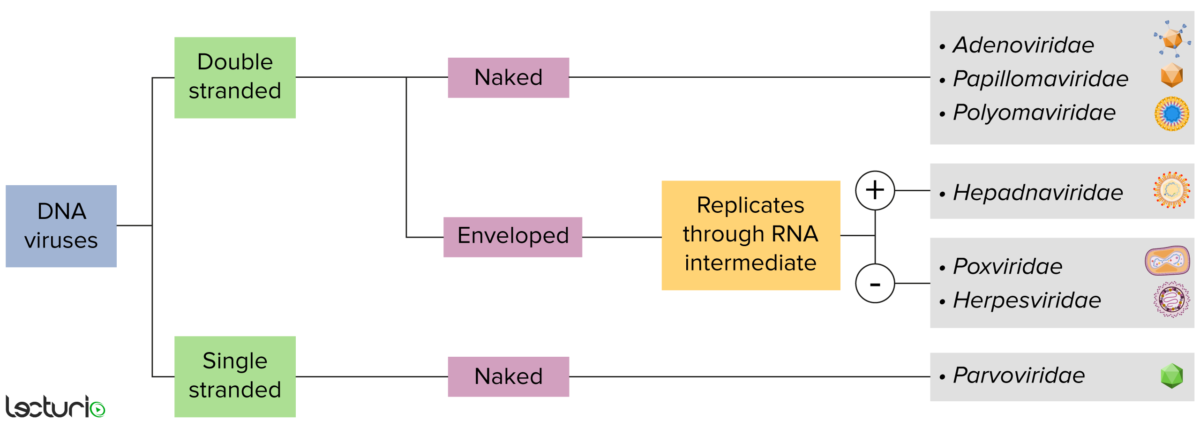
Identificación de virus de ADN:
Los virus pueden clasificarse de muchas maneras. Sin embargo, la mayoría de los virus tienen un genoma formado por ADN o ácido ribonucleico (ARN). Los virus con un genoma de ADN pueden caracterizarse además como de cadena simple o doble. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular, que suele tomarse de la célula huésped. Sin embargo, si la capa está ausente, los virus se denominan “desnudos”. Algunos virus con envoltura traducen el ADN en ARN antes de incorporarse al genoma de la célula huésped.
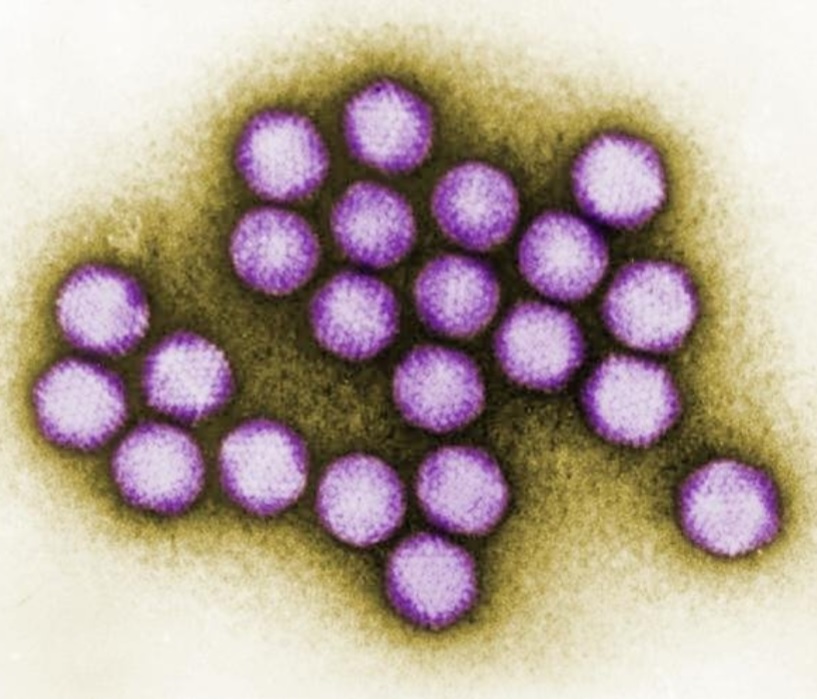
Imagen que muestra algunos detalles ultraestructurales exhibidos por un pequeño grupo de viriones de adenovirus
Imagen: “Image demonstrating some ultrastructural details exhibited by a small cluster of adenovirus virions” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público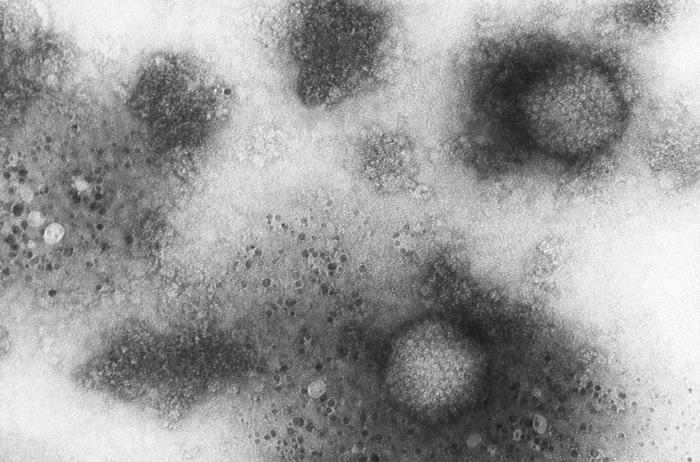
Imagen de microscopía electrónica de transmisión que muestra la morfología ultraestructural de 2 viriones de adenovirus
Imagen: “Transmission electron microscopic image showing the ultrastructural morphology of 2 adenovirus virions.” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoEl virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology tiene mayor prevalencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum:
El sitio de entrada generalmente dicta el tipo de infección; pueden ocurrir 2 procesos:
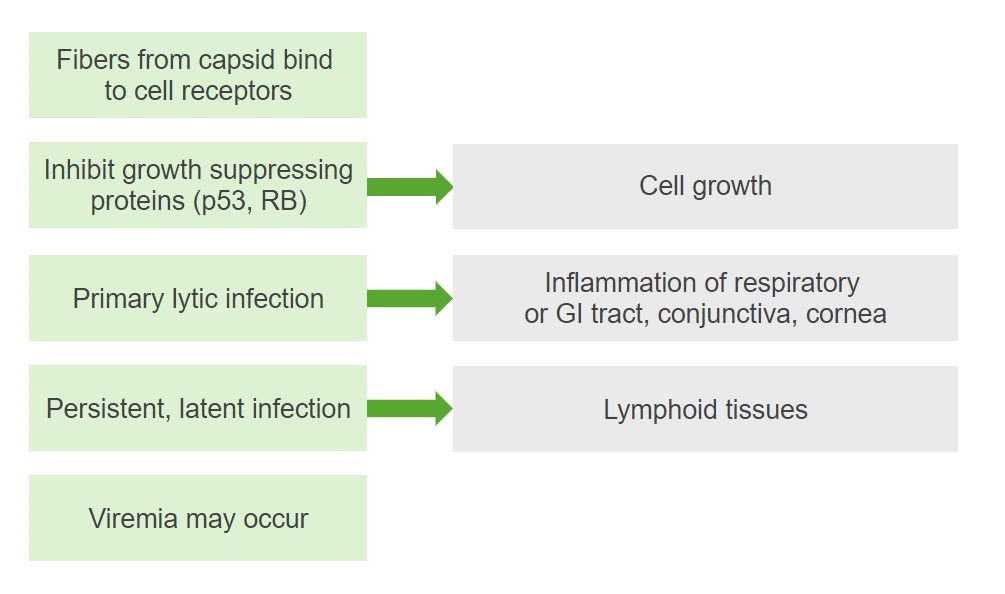
Diagrama que resume la patogénesis de la infección por adenovirus
RB: retinoblastoma
La mayoría de las infecciones por adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus (member of the family Adenoviridae) is a nonenveloped, double-stranded DNA virus. Adenovirus is transmitted in a variety of ways, and it can have various presentations based on the site of entry. Presentation can include febrile pharyngitis, conjunctivitis, acute respiratory disease, atypical pneumonia, and gastroenteritis. Adenovirus son asintomáticas. Las infecciones con enfermedad clínicamente aparente pueden presentarse con las siguientes afecciones:
| Enfermedad | Incubación | Población de riesgo | Presentación Clínica |
|---|---|---|---|
| Faringitis febril | 4–9 días | Niños (< 3 años) |
|
| Enfermedad respiratoria aguda | Reclutas militares |
|
|
| Conjuntivitis | Niños mayores y adultos (especialmente la exposición a piscinas y lagos) |
|
|
| Neumonía atípica | 10–14 días | Niños y adultos |
|
| Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis is inflammation of the stomach and intestines, commonly caused by infections from bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Transmission may be foodborne, fecal-oral, or through animal contact. Common clinical features include abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and dehydration. Gastroenteritis | 3–10 días | Lactantes y niños pequeños |
|
| Apendicitis | < 10 días | Niños | La hiperplasia linfoide compromete el suministro de sangre → inflamación |
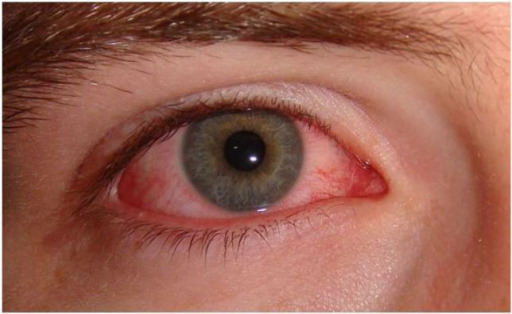
Presentación de la amigdalitis viral:
Conjuntivitis, que se observa típicamente con la infección viral de la faringe
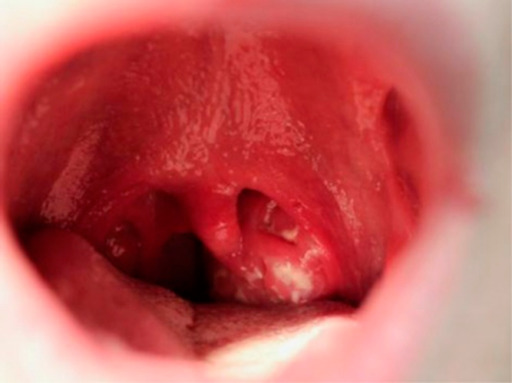
Faringitis que demuestra amigdalitis exudativa y úvula agrandada en un paciente adolescente 5 días después del inicio de la mononucleosis infecciosa.
Imagen: “Infectious mononucleosis” por University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis, MN, USA. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Para confirmar el diagnóstico se puede utilizar lo siguiente:
Las infecciones por adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus (member of the family Adenoviridae) is a nonenveloped, double-stranded DNA virus. Adenovirus is transmitted in a variety of ways, and it can have various presentations based on the site of entry. Presentation can include febrile pharyngitis, conjunctivitis, acute respiratory disease, atypical pneumonia, and gastroenteritis. Adenovirus suelen ser autolimitadas, por lo que en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos el tratamiento es de soporte.
La siguiente tabla compara y contrasta los LOS Neisseria virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology con presentaciones clínicas similares:
| Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology | Adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus (member of the family Adenoviridae) is a nonenveloped, double-stranded DNA virus. Adenovirus is transmitted in a variety of ways, and it can have various presentations based on the site of entry. Presentation can include febrile pharyngitis, conjunctivitis, acute respiratory disease, atypical pneumonia, and gastroenteritis. Adenovirus | Rinovirus | Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology sincitial respiratorio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Familia | Adenoviridae Adenoviridae A family of non-enveloped viruses infecting mammals (mastadenovirus) and birds (aviadenovirus) or both (atadenovirus). Infections may be asymptomatic or result in a variety of diseases. Adenovirus | Picornaviridae Picornaviridae A family of small RNA viruses comprising some important pathogens of humans and animals. Transmission usually occurs mechanically. There are nine genera: aphthovirus; cardiovirus; enterovirus; erbovirus; hepatovirus; kobuvirus; parechovirus; rhinovirus; and teschovirus. Coxsackievirus | Paramyxoviridae Paramyxoviridae A family of spherical viruses, of the order mononegavirales, somewhat larger than the orthomyxoviruses, and containing single-stranded RNA. Subfamilies include paramyxoviridae and pneumovirinae. Respiratory Syncytial Virus |
| Características |
|
|
|
| Transmisión |
|
|
|
| Cuadro clínico |
|
|
|
| Diagnóstico |
|
|
|
| Tratamiento | De soporte | ||
| Prevención |
|
|
|