Os testes Testes Gonadal Hormones de função hepática, também conhecidos como painéis de função hepática, são uma das análises sanguíneas de rastreio mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome frequentemente realizadas. Estes testes Testes Gonadal Hormones também são usados para detetar, avaliar e monitorizar doenças hepáticas agudas e crónicas. Os testes Testes Gonadal Hormones de função hepática avaliam os níveis de várias proteínas e enzimas hepáticas para determinar o estado da atividade metabólica do fígado, homeostase, metabolismo da bílis e capacidade de síntese de proteínas. O painel hepático standard inclui os níveis de proteínas totais, bilirrubina, albumina, ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests, AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests, rácio AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests/ ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests e fosfatase alcalina ( ALP ALP An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of an orthophosphoric monoester and water to an alcohol and orthophosphate. Osteosarcoma, pela sigla em inglês). Nota: Os valores laboratoriais apresentados nesta página devem ser vistos como um exemplo. Os intervalos podem variar consoante as unidades de medida, reagentes, técnicas ou instrumentos utilizados.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
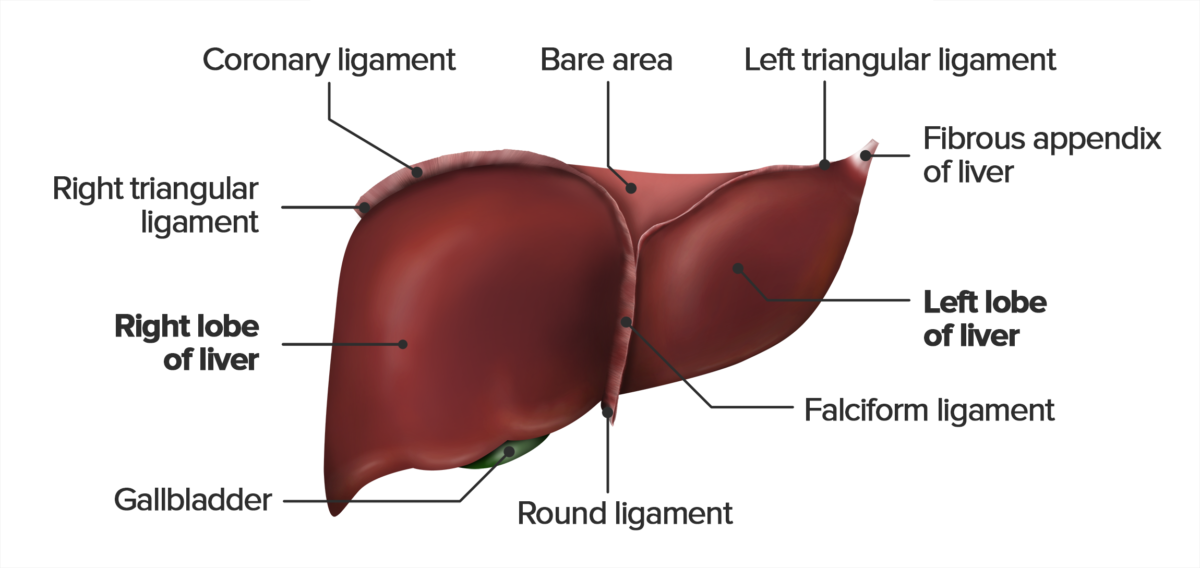
Vista da superfície diafragmática do fígado.
Imagem por Lecturio. Licença: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0| Doença hepática | ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests e AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests | ALP ALP An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of an orthophosphoric monoester and water to an alcohol and orthophosphate. Osteosarcoma | Bilirrubina | GGTP GGTP An enzyme, sometimes called ggt, with a key role in the synthesis and degradation of glutathione; (GSH, a tripeptide that protects cells from many toxins). It catalyzes the transfer of the gamma-glutamyl moiety to an acceptor amino acid. Liver Function Tests | TP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lesão hepática aguda (por exemplo, hepatite viral) | ↑↑↑
> 10 vezes o valor normal Geralmente ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests > AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests |
Normal ou ↑ | Normal ou ↑ | ↑ | Normal |
| Lesão hepática crónica (por exemplo, esteatose hepática) | ↑↑ | Normal ou ↑ | Normal ou ↑ | ↑ | Normal |
| Doença hepática alcoólica (ALD, pela sigla em inglês) | ↑
AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests/ ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests > 2 |
Normal ou ↑ | Normal ou ↑ | ↑↑ | Normal |
| Colestase | ↑ | ↑↑
> 4 vezes |
↑↑ | ↑↑ | Normal |
| Cirrose | ↑
AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests > ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests |
Normal ou ↑ | ↑ Em estadios avançados | ↑ | Prolongado |
| Cancro de fígado | Normal ou ↑ | ↑↑ | Normal ou ↑ | Normal ou ↑ | Prolongado |
| Hepatite autoimune | ↑↑
ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests > AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests |
↑ | Normal ou ↑ | ↑ | Normal |
| Lesão isquémica/choque hepático | ↑↑↑ | ↑ | Normal ou ↑ | ↑ | Prolongado |
Quando os hepatócitos estão danificados, libertam as suas enzimas na circulação. A magnitude da disfunção dos níveis enzimáticos reflete a gravidade do dano hepático.
| Parâmetro | Intervalo normal | Função | Causas de elevação |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests | 8–20 U/L |
|
> 1000 U/L:
|
| AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests | 8–20 U/L |
|
|
| GLDH GLDH An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-glutamate and water to 2-oxoglutarate and NH3 in the presence of NAD+. Liver Function Tests | 1–10 U/L |
|
|
| Rácio AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests/ ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests | Aproximadamente 0.8 | Usado para diferenciar as causas de lesão hepatocelular |
|
| Parâmetro | Intervalo normal | Função | Causas de elevação | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GGTP GGTP An enzyme, sometimes called ggt, with a key role in the synthesis and degradation of glutathione; (GSH, a tripeptide that protects cells from many toxins). It catalyzes the transfer of the gamma-glutamyl moiety to an acceptor amino acid. Liver Function Tests | 9–48 U/L |
|
|
|
| ALP ALP An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of an orthophosphoric monoester and water to an alcohol and orthophosphate. Osteosarcoma | 44–147 UI/L | Responsável pela desfosforilação de vários compostos |
|
|
| Bilirrubina | Total | 0.1–1 mg/dL | Pigmento amarelo produzido durante a destruição das hemácias via catabolismo do grupo heme | Elevada em várias doenças do fígado, vesícula biliar, árvore biliar ou hemácias (por exemplo, hemólise) |
| Direto | 0.0–0.3 mg/dL | Conjugada com ácido glucurónico, solúvel em água | Geralmente associada a causas de colestase obstrutiva | |
| Indireto | Geralmente medida como a diferença entre a bilirrubina total e direta | Não conjugada com ácido glucurónico, lipossolúvel |
|
|
| Parâmetro | Intervalo normal | Função | Causas de elevação |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albumina | 3.5–5.5 g/dL |
|
|
| Colinesterase | 8–18 U/mL |
|
|
| TP | 9.5–13.5 segundos |
|
|