A talassemia é uma causa hereditária de anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types microcítica hipocrómica e resulta de uma deficiência nas cadeias de globina α ou β, resultando numa hemoglobinopatia. A apresentação clínica da talassemia depende do número de cadeias de globina afetadas e pode variar desde assintomática até transfusão-dependente. O diagnóstico pode ser confirmado por eletroforese da hemoglobina, que irá mostrar a presença de cadeias anormais de α- ou β-globina.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
| Número de genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure afetados/genótipo | Doença | Apresentação |
|---|---|---|
| 1 (αα/α-) |
α-talassemia mínima | Portador silencioso |
| 2 (α-/α-; trans) (αα/–; cis CIS Multiple Sclerosis) |
α-talassemia minor |
|
| 3 (α-/–) |
HbH HbH An abnormal hemoglobin composed of four beta chains. It is caused by the reduced synthesis of the alpha chain. This abnormality results in alpha-thalassemia. Thalassemia (4 cadeias β) | Anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types moderada a grave |
| 4 (–/–) |
Hb Barts Hb Barts Thalassemia (4 cadeias γ) | Hidropsia fetal (incompatível com a vida) |
| Número de genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure afetados/genótipo | Doença | Apresentação |
|---|---|---|
| β0/β ou β+/β | Talassemia minor | Assintomático (leve) |
| β0/β0 ou β+/β+ | Talassemia major ( anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types de Cooley) | Dependente de transfusão |
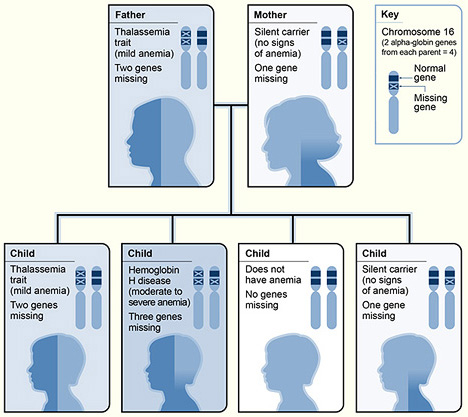
Um exemplo da hereditariedade da α-talassemia
Imagem : “The picture shows one example of how alpha thalassemia is inherited” por National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NIH). Licença: Public Domain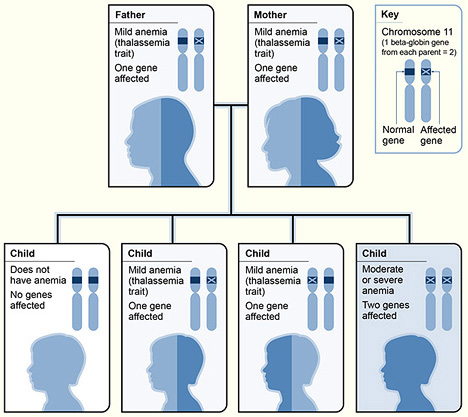
Um exemplo da hereditariedade β-talassemia
Imagem : “The picture shows one example of how beta thalassemia is inherited” por National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NIH). Licença: Public Domain| Doença | Apresentação clínica |
|---|---|
| α-talassemia mínima | Fase assintomática |
| α-talassemia minor |
|
| Doença HbH HbH An abnormal hemoglobin composed of four beta chains. It is caused by the reduced synthesis of the alpha chain. This abnormality results in alpha-thalassemia. Thalassemia |
|
| Hb Barts Hb Barts Thalassemia |
|
| β-talassemia minor |
|
| β-talassemia major ( anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types de Cooley) |
|
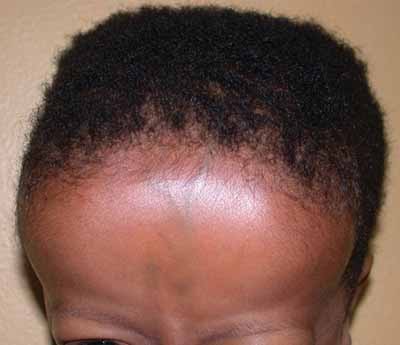
Protuberância frontal devido à necessidade excessiva de hematopoiese
Imagem : “Frontal bossing (abnormally enlarged forehead) in a child” por National Human Genome Research Institute (NIH). Licença: Public Domain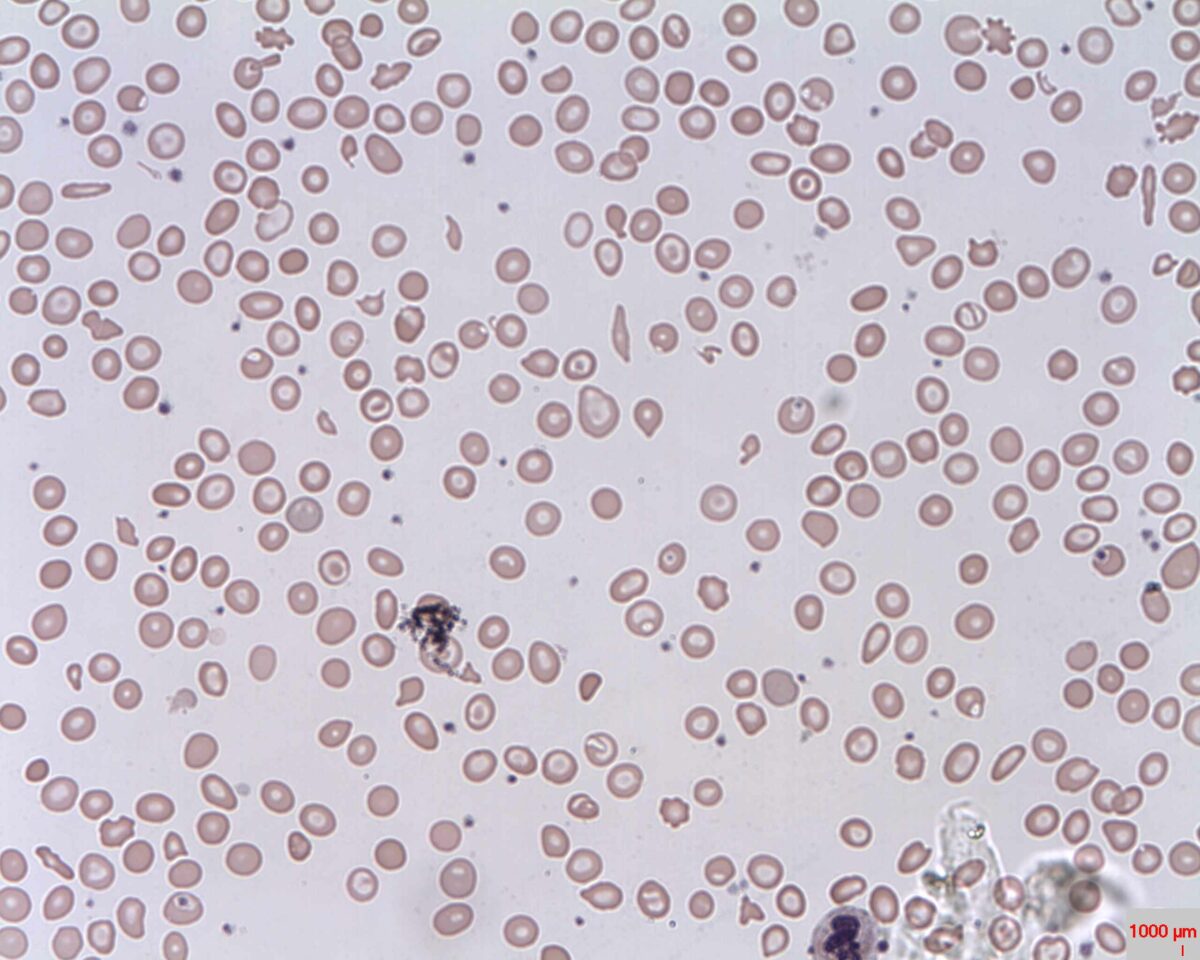
Esfregaço Periférico: anemia microcítica hipocrómica com células em alvo (olho de boi); anisocitose (hemácias com tamanhos diferentes).
Imagem: “Target cells (Codocytes, Leptocytes or Mexican hat cells)” pelo Prof. Osaro Erhabor. Licença: CC0 1.0O diagnóstico diferencial inclui outras doenças associadas à anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types microcítica ou com células em alvo.