O herpesvírus humano 8, também conhecido como herpesvírus associado ao sarcoma de Kaposi Kaposi A multicentric, malignant neoplastic vascular proliferation characterized by the development of bluish-red cutaneous nodules, usually on the lower extremities, most often on the toes or feet, and slowly increasing in size and number and spreading to more proximal areas. The tumors have endothelium-lined channels and vascular spaces admixed with variably sized aggregates of spindle-shaped cells, and often remain confined to the skin and subcutaneous tissue, but widespread visceral involvement may occur. Hhv-8 is the suspected cause. There is also a high incidence in AIDS patients. AIDS-defining Conditions, é um vírus de DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure de cadeia dupla, pertencente à família Herpesviridae Herpesviridae A family of enveloped, linear, double-stranded DNA viruses infecting a wide variety of animals. Subfamilies, based on biological characteristics, include: alphaherpesvirinae; betaherpesvirinae; and gammaherpesvirinae. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2. Este vírus oncogénico é raro e causa sarcoma de Kaposi Kaposi A multicentric, malignant neoplastic vascular proliferation characterized by the development of bluish-red cutaneous nodules, usually on the lower extremities, most often on the toes or feet, and slowly increasing in size and number and spreading to more proximal areas. The tumors have endothelium-lined channels and vascular spaces admixed with variably sized aggregates of spindle-shaped cells, and often remain confined to the skin and subcutaneous tissue, but widespread visceral involvement may occur. Hhv-8 is the suspected cause. There is also a high incidence in AIDS patients. AIDS-defining Conditions (uma condição definidora de SIDA), linfomas de efusão primária e doença de Castleman multicêntrica, sobretudo em pacientes imunodeprimidos. O processo ocorre através da indução da atividade de crescimento celular e da inibição da apoptose nas células infetadas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
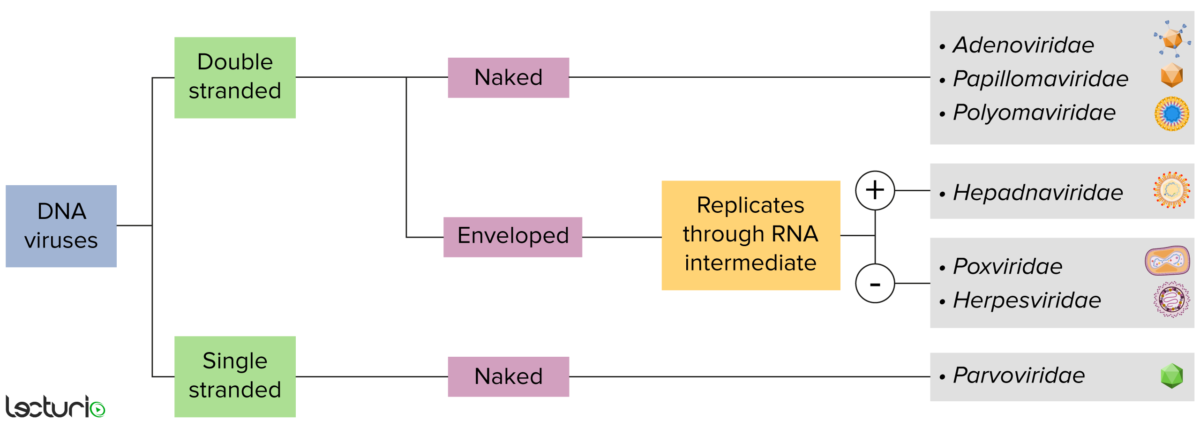
Identificação de vírus de DNA:
Os vírus podem ser classificados de várias formas. Contudo, a maioria dos vírus possui um genoma formado por DNA ou RNA. Os vírus com genoma de DNA podem ainda ser caracterizados como de cadeia simples ou dupla. Os vírus com envelope são revestidos por uma camada fina de membrana celular, que geralmente é retirada da célula hospedeira. Os vírus sem envelope são apelidados de vírus “nus”. Alguns vírus com envelope traduzem DNA em RNA antes de serem incorporados no genoma da célula hospedeira.
Os humanos são o único reservatório conhecido.
O mecanismo de transmissão do vírus ainda não está totalmente esclarecido.
A infeção pelo herpesvírus humano 8 é maioritariamente assintomática. As manifestações clínicas podem ocorrer em pacientes imunodeprimidos:
| Doença | Apresentação clínica | Diagnóstico | Tratamento |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sarcoma de Kaposi Kaposi A multicentric, malignant neoplastic vascular proliferation characterized by the development of bluish-red cutaneous nodules, usually on the lower extremities, most often on the toes or feet, and slowly increasing in size and number and spreading to more proximal areas. The tumors have endothelium-lined channels and vascular spaces admixed with variably sized aggregates of spindle-shaped cells, and often remain confined to the skin and subcutaneous tissue, but widespread visceral involvement may occur. Hhv-8 is the suspected cause. There is also a high incidence in AIDS patients. AIDS-defining Conditions | Lesões vasculares malignas da/o:
|
Biópsia das lesões |
|
| Doença multicêntrica de Castleman |
|
|
|
| Linfomas primários de efusão | As manifestações dependem do local de acumulação de líquido:
|
|
|
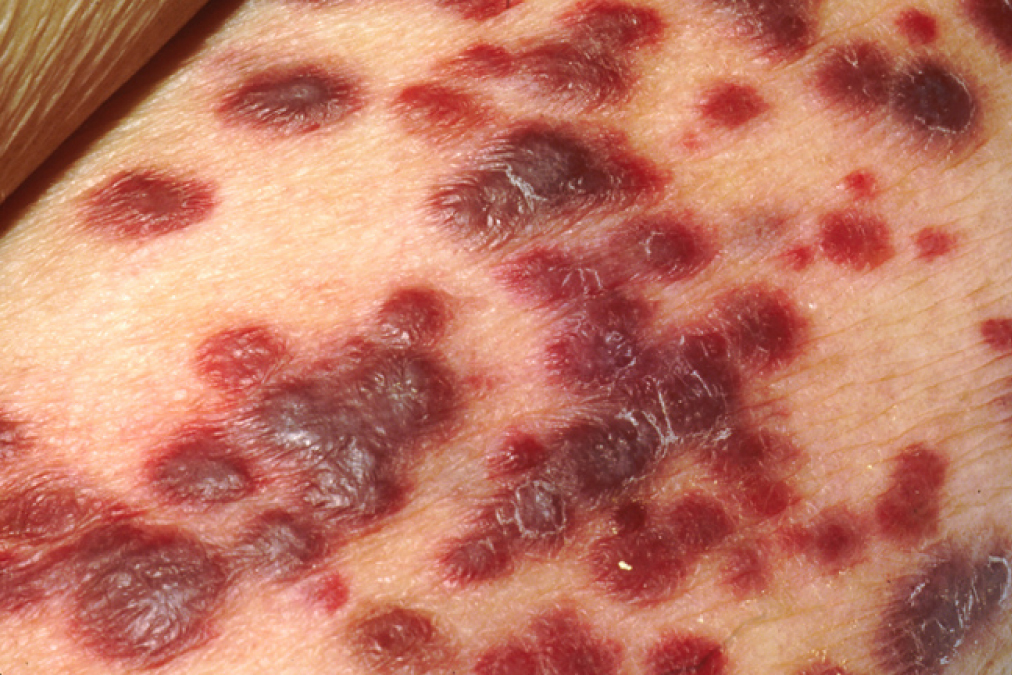
Lesões cutâneas do sarcoma de Kaposi
Imagem: “Kaposi’s sarcoma” por OpenStax College. Licença: CC BY 3.0A tabela abaixo compara os 9 herpesvírus considerados endémicos em humanos; existem 115 espécies diferentes de herpesvírus no total, agrupadas em 3 famílias:
| HHV | Nome comum | Principais células-alvo | Local de latência | Apresentação clínica* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 (grupo alfa) |
HSV-1 | Células mucoepiteliais | Gânglios da raiz dorsal |
|
|
2 (grupo alfa) |
HSV-2 |
|
||
|
3 (grupo alfa) |
VZV |
|
||
|
4 (grupo gama) |
EBV EBV Epstein-barr virus (EBV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the herpesviridae family. This highly prevalent virus is mostly transmitted through contact with oropharyngeal secretions from an infected individual. The virus can infect epithelial cells and B lymphocytes, where it can undergo lytic replication or latency. Epstein-Barr Virus |
|
Células B de memória |
|
|
5 (grupo beta) |
CMV |
|
Células progenitoras hematopoiéticas da medula óssea |
|
|
6A, 6B (grupo beta) |
HHV-6 HHV-6 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 | células T | Monócitos | Roséola |
|
7 (grupo beta) |
HHV-7 HHV-7 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 | células T | ||
|
8 (grupo gama) |
Herpesvírus associado ao sarcoma de Kaposi Kaposi A multicentric, malignant neoplastic vascular proliferation characterized by the development of bluish-red cutaneous nodules, usually on the lower extremities, most often on the toes or feet, and slowly increasing in size and number and spreading to more proximal areas. The tumors have endothelium-lined channels and vascular spaces admixed with variably sized aggregates of spindle-shaped cells, and often remain confined to the skin and subcutaneous tissue, but widespread visceral involvement may occur. Hhv-8 is the suspected cause. There is also a high incidence in AIDS patients. AIDS-defining Conditions |
|
células B | Sarcoma de Kaposi Kaposi A multicentric, malignant neoplastic vascular proliferation characterized by the development of bluish-red cutaneous nodules, usually on the lower extremities, most often on the toes or feet, and slowly increasing in size and number and spreading to more proximal areas. The tumors have endothelium-lined channels and vascular spaces admixed with variably sized aggregates of spindle-shaped cells, and often remain confined to the skin and subcutaneous tissue, but widespread visceral involvement may occur. Hhv-8 is the suspected cause. There is also a high incidence in AIDS patients. AIDS-defining Conditions |