A presença de uma quantidade anormal de lípidos no sangue é denominada dislipidemia, a qual inclui níveis anormais de colesterol, triglicerídeos e/ou lipoproteínas. A dislipidemia pode ser primária (familiar) ou secundária (adquirida). Tanto as causas primárias como as secundárias podem levar ao desenvolvimento de doença cardiovascular prematura (aterosclerose). As causas familiares são classificadas de acordo com o sistema de Fredrickson, o qual considera a patologia e a elevação dos lípidos. Certos tipos de dislipidemia não cursam com aumento do risco de doença aterosclerótica prematura, mas afetam o risco cardíaco geral e a probabilidade de eventos cardiovasculares no futuro. O rastreio, o diagnóstico precoce e o rigor no controlo e no tratamento são a chave para a prevenção de eventos cardiovasculares.
Last updated: Apr 25, 2025
Dislipidemia: quantidades anormais de lípidos no sangue
As causas da dislipidemia podem ser divididas em causas primárias (familiares) e secundárias (adquiridas).
Causas primárias:
Causas secundárias (adquiridas):
| Tipo | Condição, modo de hereditariedade (autossómico dominante ( AD AD The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment. Advance Directives), autossómico recessivo ( AR AR Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders. Aortic Regurgitation)), alteração lipídica | Patologia | Notas |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Hiperquilomicronemia familiar (
AR
AR
Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders.
Aortic Regurgitation) Elevação dos quilomícrons |
Deficiência de LPL ou apolipoproteína C-II (ApoC-II) |
|
| IIa | Hipercolesterolemia familiar (HF) (
AD
AD
The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment.
Advance Directives) LDL elevado |
Mutação na PCSK-9, defeitos nos recetores de LDL ou na apolipoproteína B-100 (ApoB-100) |
|
| IIb | Hipercolesterolemia familiar combinada (
AD
AD
The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment.
Advance Directives) VLDL e LDL elevados |
|
|
| III | Hiperlipoproteinemia familiar (
AR
AR
Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders.
Aortic Regurgitation) Remanescentes de VLDL e quilomícrons |
Defeitos na ApoE |
|
| IV | Hipertrigliceridemia familiar (
AD
AD
The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment.
Advance Directives) VLDL elevado |
Produção excessiva de VLDL pelo fígado |
|
| V | HLD Mista (
AR
AR
Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders.
Aortic Regurgitation) Quilomícrons e VLDL elevados |
Defeito na apolipoproteína A5 (ApoA5) |
|
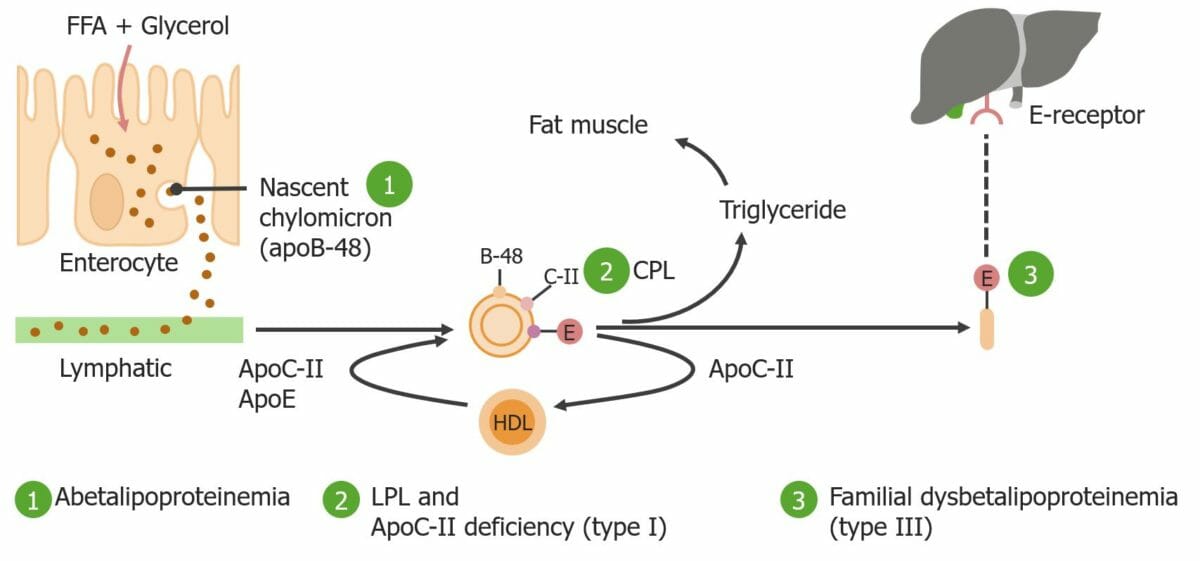
Representação esquemática dos tipos de classificação de Fredrickson I e III
AGL: ácido gordo livre
ApoB-48: apolipoproteína-B-48
ApoC-II: apolipoproteína C-II
ApoE: apolipoproteína E
LPL: lipoproteína lipase
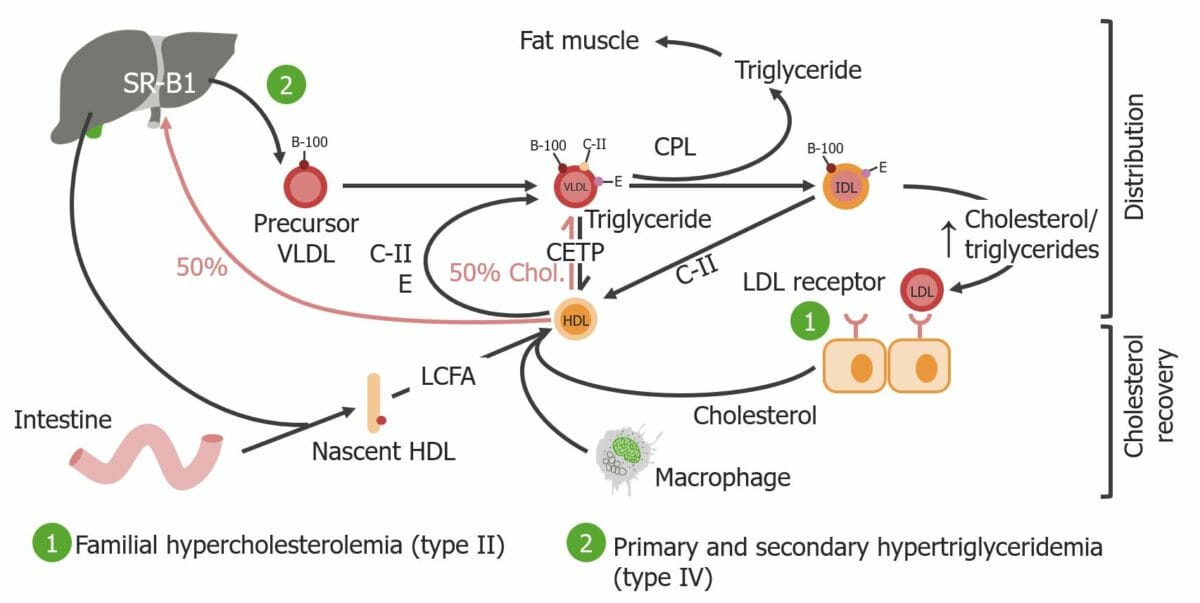
Representação esquemática dos tipos de classificação de Fredrickson II e IV
Imagem por Lecturio.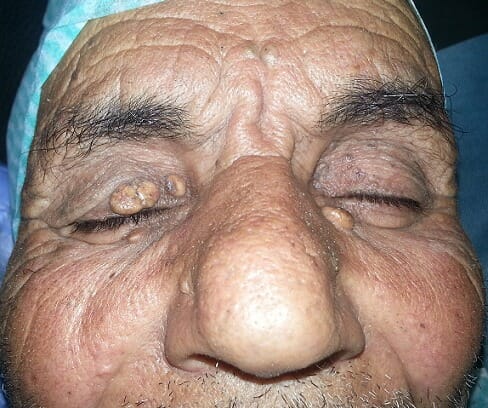
Um doente idoso com depósitos amarelados em redor das pálpebras, provavelmente indicativos de xantelasma
Imagem: “Les différentes lésions jaunâtres au niveau des deux paupières en rapport avec le xanthélasma” por Elghazi, T. and Hafidi, Z. Licença: CC BY 2.0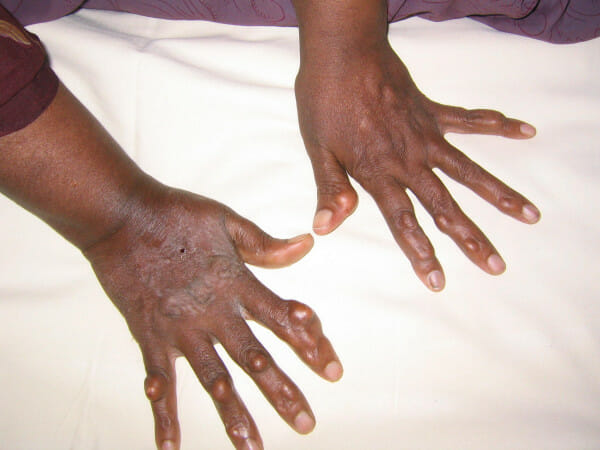
Xantomas múltiplos nas mãos
Imagem: “Xanthomas” por Kumar, A.A. et al. Licença: CC BY 2.0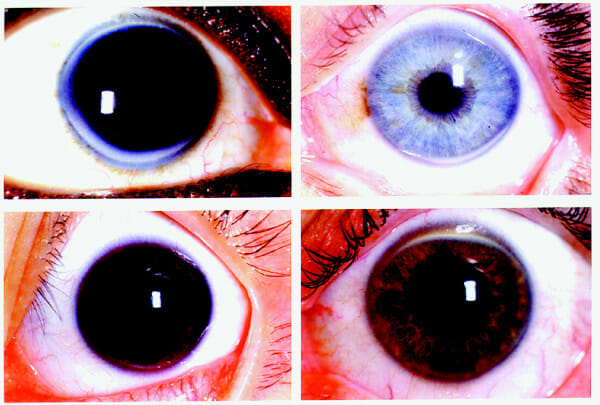
Quatro lâminas representativas do arco corneano:
Os depósitos no arco corneano tendem a surgir às 6 e 12 horas e acumulam-se até se tornarem completamente circunferenciais.
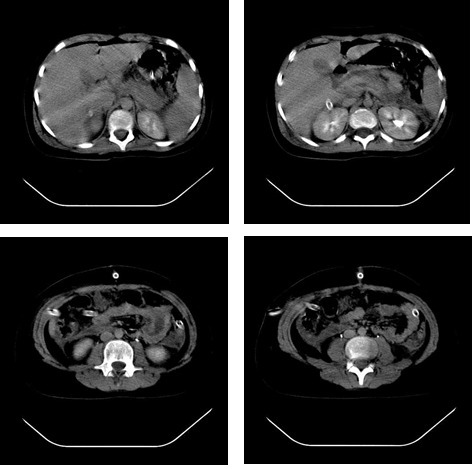
T de uma pancreatite aguda secundária a hiperlipidemia numa menina de 11 anos: A imagem mostra um pâncreas de grande dimensão, particularmente a cabeça, com estrutura heterogénea e coleções peripancreáticas.
Imagem: “Acute pancreatitis secondary to hyperlipidemia in an 11-year-old girl” por Department of Pediatric Surgery, “Grigore Alexandrescu” Clinical Emergency Hospital for Children, Bucharest. Licença: CC BY 2.0.| Lípido | Valor normal |
|---|---|
| Colesterol total | < 200 mg/dL |
| Colesterol HDL | > 60 mg/dL |
| Colesterol LDL | < 100 mg/dL |
| Triglicerídeos | < 150 mg/dL |
| Fórmula de Friedewald: LDL= colesterol total – HDL – (triglicerídeos/5) | |
O objetivo do tratamento é reduzir o risco de doenças cardiovasculares.