Os agentes antimicobacterianos representam um grupo diverso de compostos que têm atividade contra infeções por micobactérias, incluindo tuberculose, hanseníase (lepra) e doença do complexo Mycobacterium avium Mycobacterium avium A bacterium causing tuberculosis in domestic fowl and other birds. In pigs, it may cause localized and sometimes disseminated disease. The organism occurs occasionally in sheep and cattle. It should be distinguished from the m. avium complex, which infects primarily humans. Mycobacterium (MAC). Os agentes de 1ª linha para a tuberculose são a rifampicina, a isoniazida, a pirazinamida e o etambutol. Os fármacos variam nos seus mecanismos de ação: a rifampicina inibe a síntese de RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure, a isoniazida inibe a síntese de ácido micólico, a pirazinamida atua no transporte pela membrana e na síntese de proteínas e o etambutol impede a síntese da parede celular. A monoterapia não está recomendada devido ao risco aumentado de resistência aos fármacos. O tratamento com múltiplos fármacos demora vários meses e requer monitorização da espectoração. Já na hanseníase, infeção causada pelo Mycobacterium leprae Mycobacterium leprae A species of gram-positive, aerobic bacteria that causes leprosy in man. Its organisms are generally arranged in clumps, rounded masses, or in groups of bacilli side by side. Mycobacterium, também se usa a rifampicina, com a dapsona. A forma lepromatosa requer um terceiro agente (clofazimina). As infeções pulmonares com MAC são tratadas com macrólidos (azitromicina), rifampicina e etambutol.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Os agentes antimicobacterianos representam um grupo diverso de compostos usados contra infeções por micobactérias (por exemplo, TB TB Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis, lepra, complexo Mycobacterium avium Mycobacterium avium A bacterium causing tuberculosis in domestic fowl and other birds. In pigs, it may cause localized and sometimes disseminated disease. The organism occurs occasionally in sheep and cattle. It should be distinguished from the m. avium complex, which infects primarily humans. Mycobacterium).
| Bactérias | Regime de tratamento * | Profilaxia |
|---|---|---|
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mycobacterium tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis |
|
Isoniazida |
| M. leprae |
|
Nenhuma |
As espécies predominantes do complexo M. avium (MAC) dentro do complexo incluem:
|
|
Azitromicina ou rifabutina |
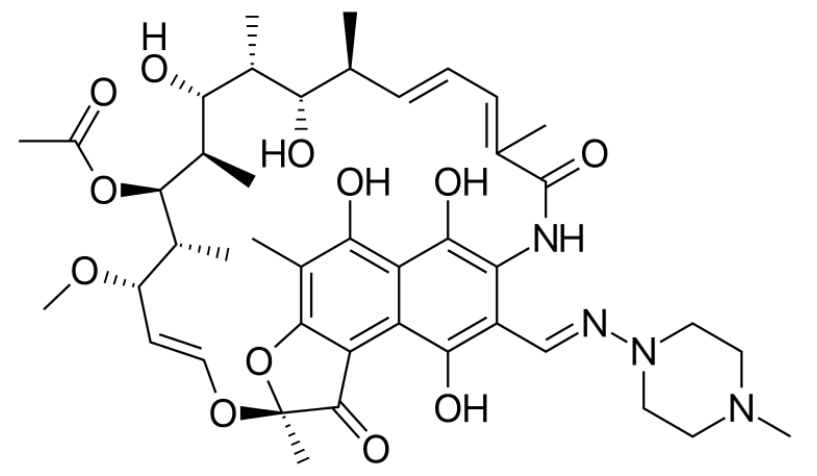
Fórmula esquelética da rifampicina
Imagem: “Skeletal formula of rifampin” por Vaccinationist. Licença: Public Domain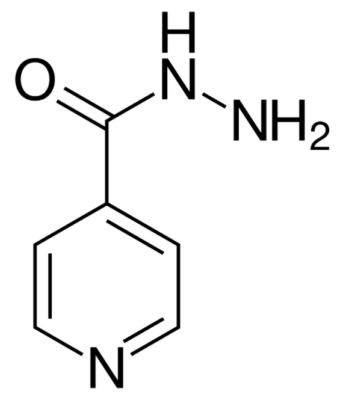
Fórmula esquelética de isoniazida (hidrazida de ácido isonicotínico (INH))
Imagem: “Skeletal formula of isoniazid” por Fvasconcellos. Licença: Public Domain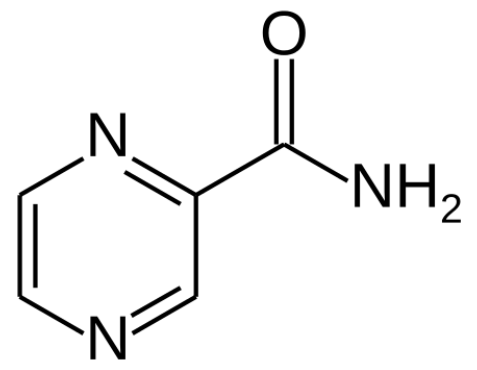
Estrutura da pirazinamida
Imagem: “Structure of pyrazinamide” por Fvasconcellos. Licença: Public Domain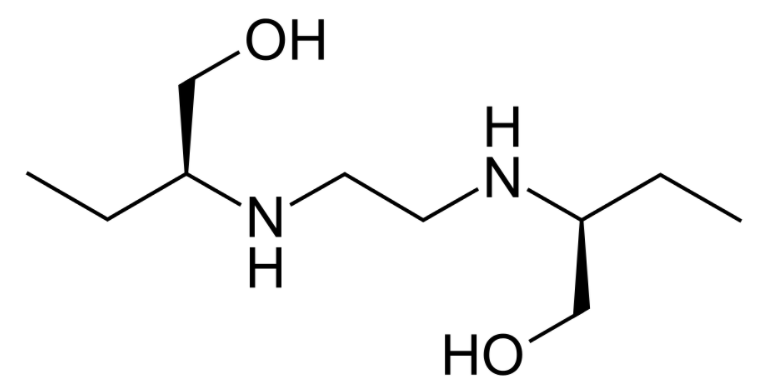
Estrutura do etambutol
Imagem: “Structure of ethambutol” por Fvasconcellos. Licença: Public DomainHidróxido de alumínio ↓ absorção de fármacos
São usados outros agentes dependendo das condições subjacentes e da presença de Mycobacterium Mycobacterium Mycobacterium is a genus of the family Mycobacteriaceae in the phylum Actinobacteria. Mycobacteria comprise more than 150 species of facultative intracellular bacilli that are mostly obligate aerobes. Mycobacteria are responsible for multiple human infections including serious diseases, such as tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis), leprosy (M. leprae), and M. avium complex infections. Mycobacterium multirresistente.
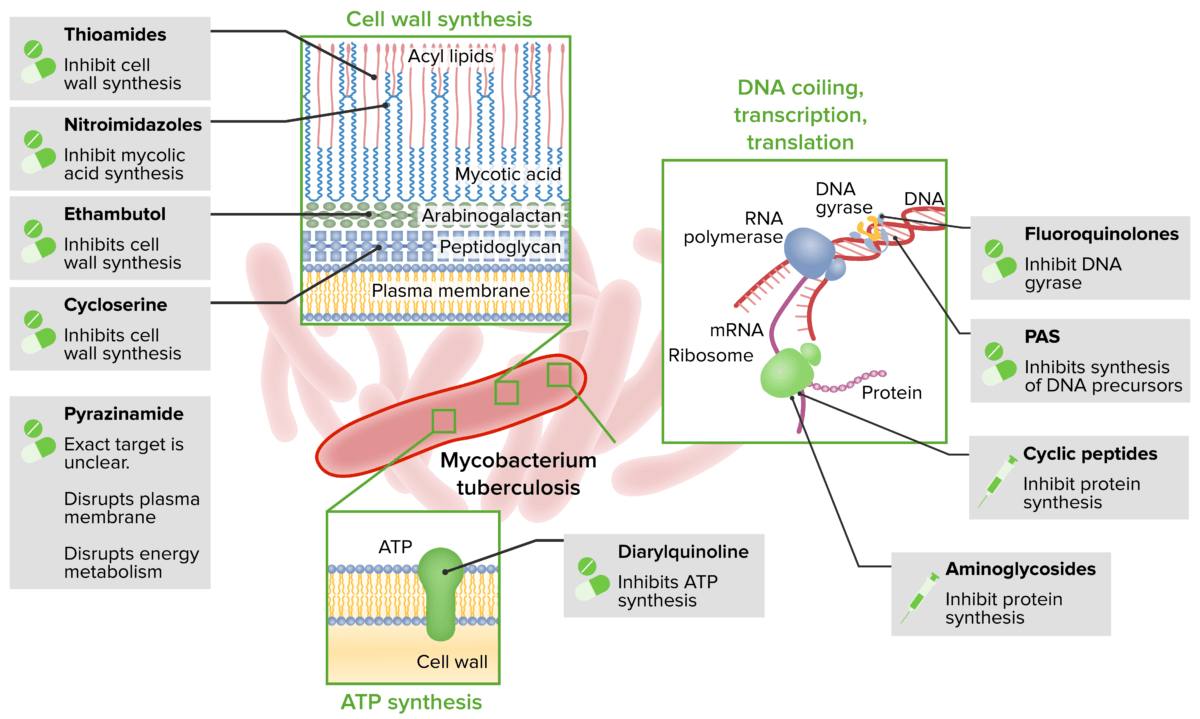
Agentes e mecanismos anti-tuberculose
PAS: Ácido para-aminosalicílico