O adenovírus (membro da família Adenoviridae Adenoviridae A family of non-enveloped viruses infecting mammals (mastadenovirus) and birds (aviadenovirus) or both (atadenovirus). Infections may be asymptomatic or result in a variety of diseases. Adenovirus) é um vírus de DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure de cadeia dupla não envelopado. O adenovírus pode ser transmitido de várias maneiras e manifesta-se clinicamente dependendo do local de entrada. A apresentação pode incluir faringite febril, conjuntivite, doença respiratória aguda, pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia atípica e gastroenterite. As manifestações mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome graves são cistite hemorrágica aguda, hepatite, miocardite e infeção disseminada. O diagnóstico é confirmado por PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) e teste de antigénio. A maioria das infeções é autolimitada, sendo o tratamento de suporte. A terapêutica antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B está reservada para pacientes imunodeprimidos e infeções graves.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
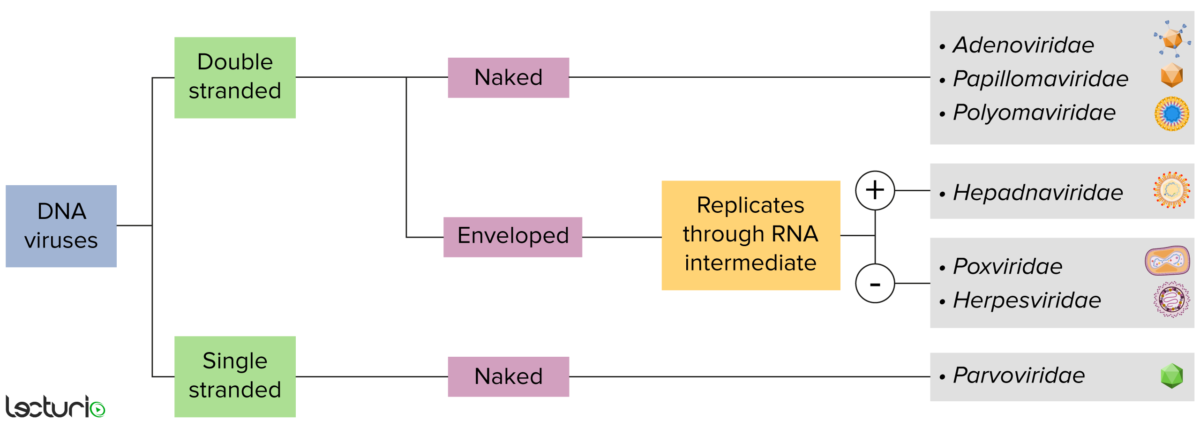
Identificação de vírus de DNA:
Os vírus podem ser classificados de várias formas. Contudo, a maioria dos vírus possui um genoma formado por DNA ou RNA. Os vírus com genoma de DNA podem ainda ser caracterizados como de cadeia simples ou dupla. Os vírus com envelope são revestidos por uma camada fina de membrana celular, que geralmente é retirada da célula hospedeira. Os vírus sem envelope são apelidados de vírus “nus”. Alguns vírus com envelope traduzem DNA em RNA antes de serem incorporados no genoma da célula hospedeira.
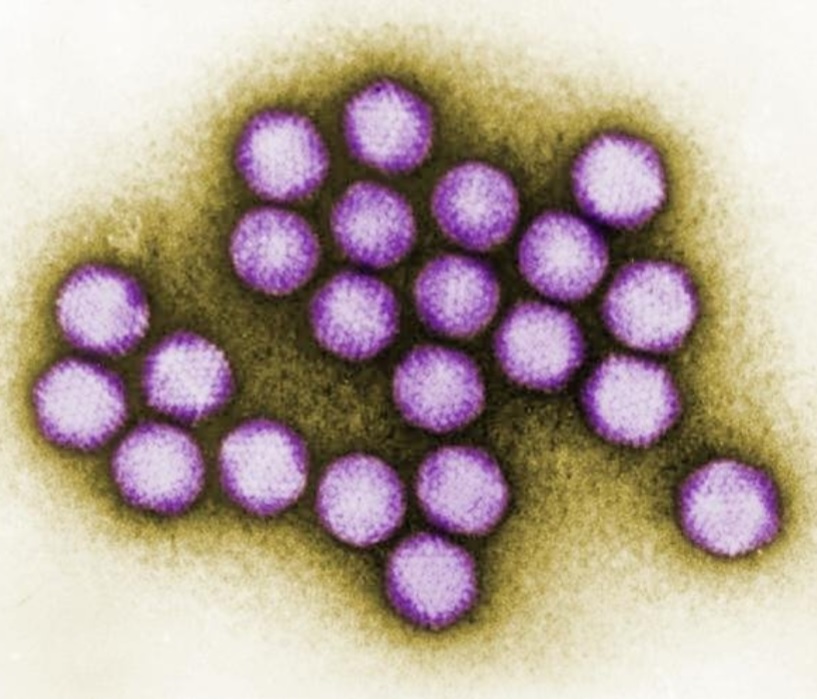
Imagem com alguns detalhes ultraestruturais exibidos por um pequeno aglomerado de viriões de adenovírus
Imagem: “Image demonstrating some ultrastructural details exhibited by a small cluster of adenovirus virions” por CDC. Licença: Domínio Público
Imagem de microscopia eletrónica de transmissão a revelar a morfologia ultraestrutural de 2 viriões de adenovírus
Imagem: “Transmission electron microscopic image showing the ultrastructural morphology of 2 adenovirus virions.” pelo CDC. Licença: Domínio PúblicoO vírus é mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome prevalente em:
O local de entrada por norma determina o tipo de infeção; podem ocorrer 2 processos:
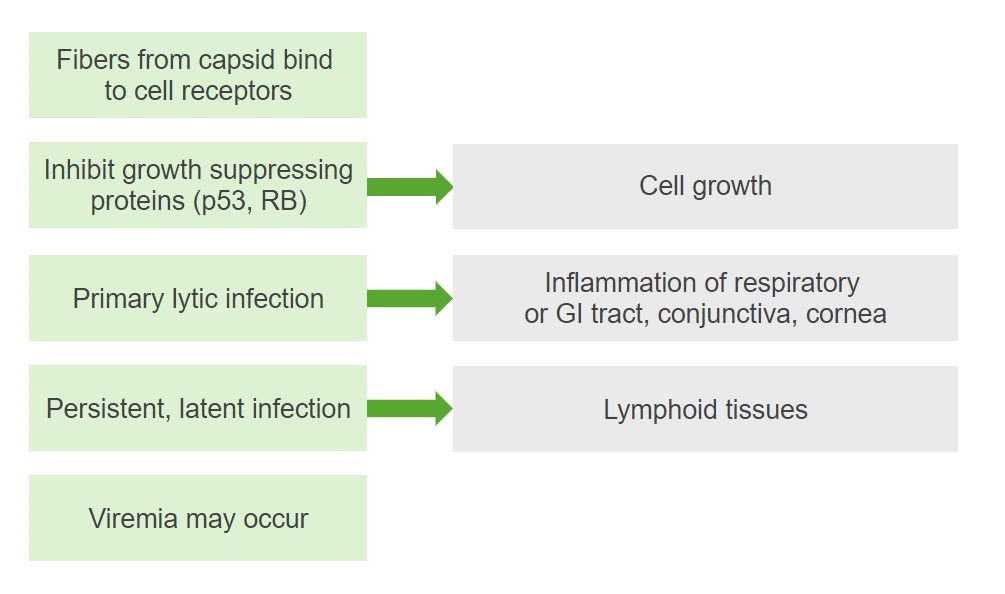
Diagrama resumido da patogénese da infeção por adenovírus
RB: retinoblastoma
A maioria das infeções por adenovírus é assintomática. As infeções com doença clinicamente aparente podem apresentar as seguintes condições:
| Doença | Incubação | População de risco | Apresentação Clínica |
|---|---|---|---|
| Faringite febril | 4-9 dias | Crianças (<< 3 anos) |
|
| Doença respiratória aguda | Militares |
|
|
| Conjuntivite | Crianças mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome velhas e adultos (especialmente exposição em piscinas e lagos) |
|
|
| Pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia atípica | 10-14 dias | Crianças e adultos |
|
| Gastroenterite | 3-10 dias | Bebés e crianças pequenas |
|
| Apendicite | <10 dias | Crianças | A hiperplasia linfóide compromete o aporte sanguíneo → inflamação |
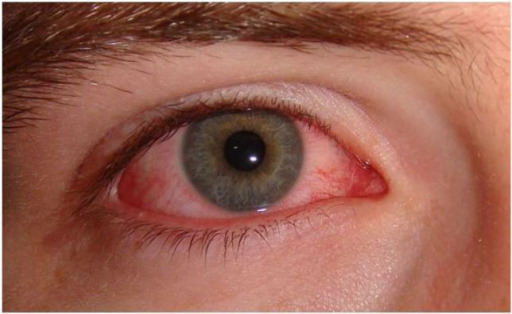
Apresentação de amigdalite viral:
Conjuntivite, tipicamente concomitante a uma faringite.
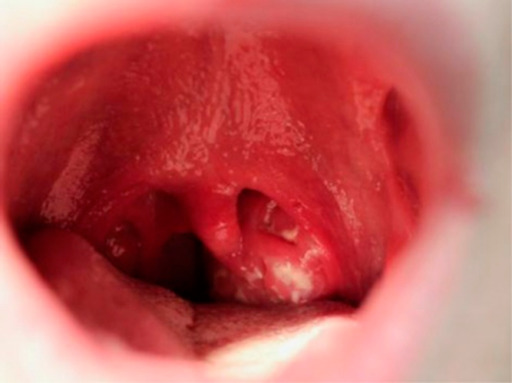
Faringite com amigdalite exsudativa e aumento da úvula, em paciente adolescente 5 dias após início de mononucleose infeciosa.
Imagem: “Infectious mononucleosis” por University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis, MN, USA. Licença: CC BY 4.0Os seguintes exames podem ser utilizados para confirmar o diagnóstico:
As infeções por adenovírus são habitualmente autolimitadas, portanto, na maioria dos casos, o tratamento é de suporte.
A tabela abaixo compara vírus com apresentações clínicas semelhantes:
| Vírus | Adenovírus | Rinovírus | Vírus sincicial respiratório |
|---|---|---|---|
| Família | Adenoviridae Adenoviridae A family of non-enveloped viruses infecting mammals (mastadenovirus) and birds (aviadenovirus) or both (atadenovirus). Infections may be asymptomatic or result in a variety of diseases. Adenovirus | Picornaviridae Picornaviridae A family of small RNA viruses comprising some important pathogens of humans and animals. Transmission usually occurs mechanically. There are nine genera: aphthovirus; cardiovirus; enterovirus; erbovirus; hepatovirus; kobuvirus; parechovirus; rhinovirus; and teschovirus. Coxsackievirus | Paramyxoviridae Paramyxoviridae A family of spherical viruses, of the order mononegavirales, somewhat larger than the orthomyxoviruses, and containing single-stranded RNA. Subfamilies include paramyxoviridae and pneumovirinae. Respiratory Syncytial Virus |
| Características |
|
|
|
| Transmissão |
|
|
|
| Clínica |
|
|
|
| Diagnóstico |
|
|
|
| Tratamento | De suporte | ||
| Prevenção |
|
|
|