Los LOS Neisseria virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology BK (BKV, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) y JC (JCV, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) son pequeños virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de ácido desoxirribonucleico (ADN) de doble cadena sin envoltura, pertenecientes a la familia Polyomaviridae Polyomaviridae A family of small, non-enveloped DNA viruses, infecting mainly mammals. JC Virus and BK Virus, que son ubicuos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la población humana. Mientras que la infección primaria suele ser asintomática, la infección se mantiene latente de por vida en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria riñones y órganos linfoides. Las infecciones latentes pueden activarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes inmunodeprimidos. La reactivación del BKV se observa con mayor frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes trasplantados y puede provocar nefropatía, pérdida de aloinjertos, cistitis hemorrágica y estenosis uretral. La reactivación del JCV causa la leucoencefalopatía multifocal Multifocal Retinoblastoma progresiva, que se considera una enfermedad definitoria del síndrome de inmunodeficiencia adquirida (SIDA). El diagnóstico puede confirmarse mediante reacción en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cadena de polimerasa ( PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) o biopsia de tejido. No hay disponible una terapia específica. El objetivo del tratamiento es reducir la inmunosupresión.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
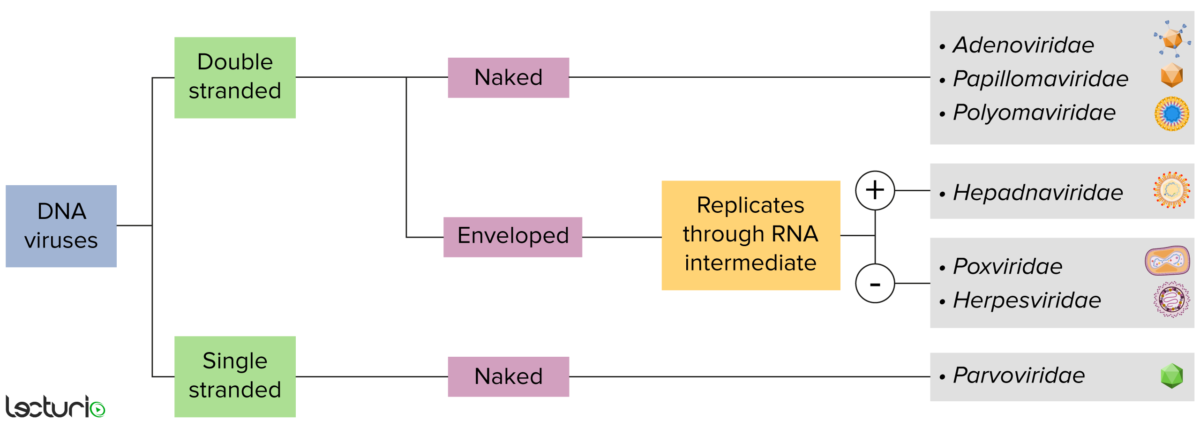
Identificación de virus de ADN:
Los virus pueden clasificarse de muchas maneras. Sin embargo, la mayoría de los virus tienen un genoma formado por ADN o ácido ribonucleico (ARN). Los virus con un genoma de ADN pueden caracterizarse además como de cadena simple o doble. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular, que suele tomarse de la célula huésped. Sin embargo, si la capa está ausente, los virus se denominan “desnudos”. Algunos virus con envoltura traducen el ADN en ARN antes de incorporarse al genoma de la célula huésped.
El BKV y el JCV comparten características similares:
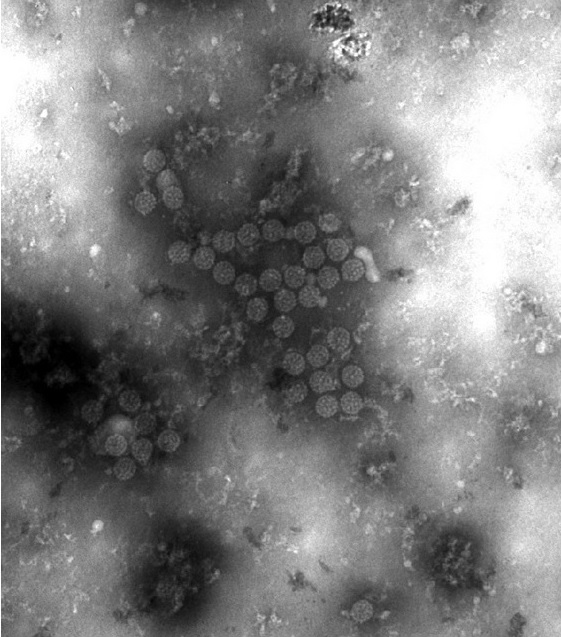
Micrografía electrónica que muestra los viriones del virus BK (BKV):
Obsérvese el pequeño tamaño y la simetría icosaédrica.
El ser humano es el huésped natural del JCV y del BKV (no reservorios animales)
La enfermedad clínica suele surgir por la reactivación del virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes inmunodeprimidos:
Infección primaria:
Infección secundaria:
La leucoencefalopatía multifocal Multifocal Retinoblastoma progresiva es una enfermedad progresiva (y a menudo mortal) que se observa con mayor frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes con SIDA (considerada una condición definidora de SIDA) con un recuento de CD4 < 200 células/µl.
BKV:
JCV:
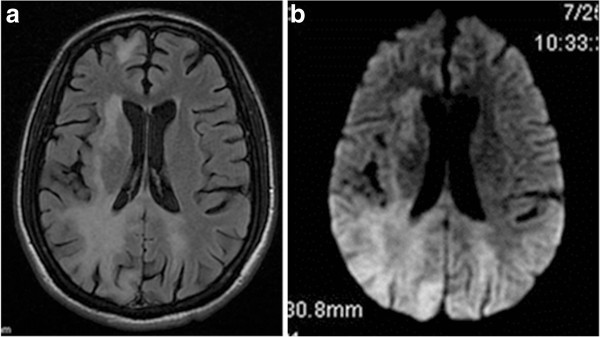
Resonancia magnética (RM) de un paciente con leucoencefalopatía multifocal progresiva:
a: RM axial en T2-flair del cerebro que muestra una hiperintensidad de señal bilateral en la sustancia blanca parietooccipital
b: imagen axial ponderada en T2-flair de las mismas lesiones
No hay disponible terapias específicas para el BKV o el JCV. El tratamiento suele estar dirigido a reducir la inmunosupresión.