La genética es el estudio de los LOS Neisseria genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure y sus funciones y comportamientos. La genética es un tema importante para los LOS Neisseria exámenes, y una comprensión profunda de los LOS Neisseria diferentes términos utilizados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el estudio de la genética es un conocimiento importante. Los LOS Neisseria términos cruciales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el estudio de la genética se enumeran y definen, a continuación, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum orden alfabético.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
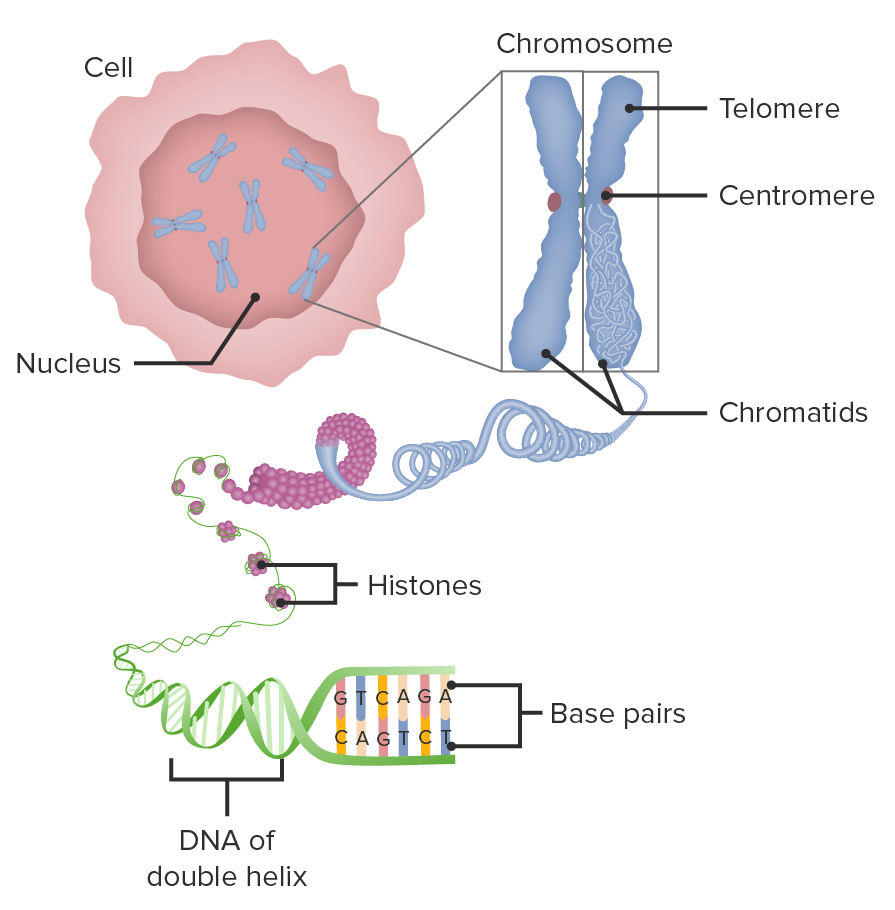
Estructura de un cromosoma
Imagen por Lecturio.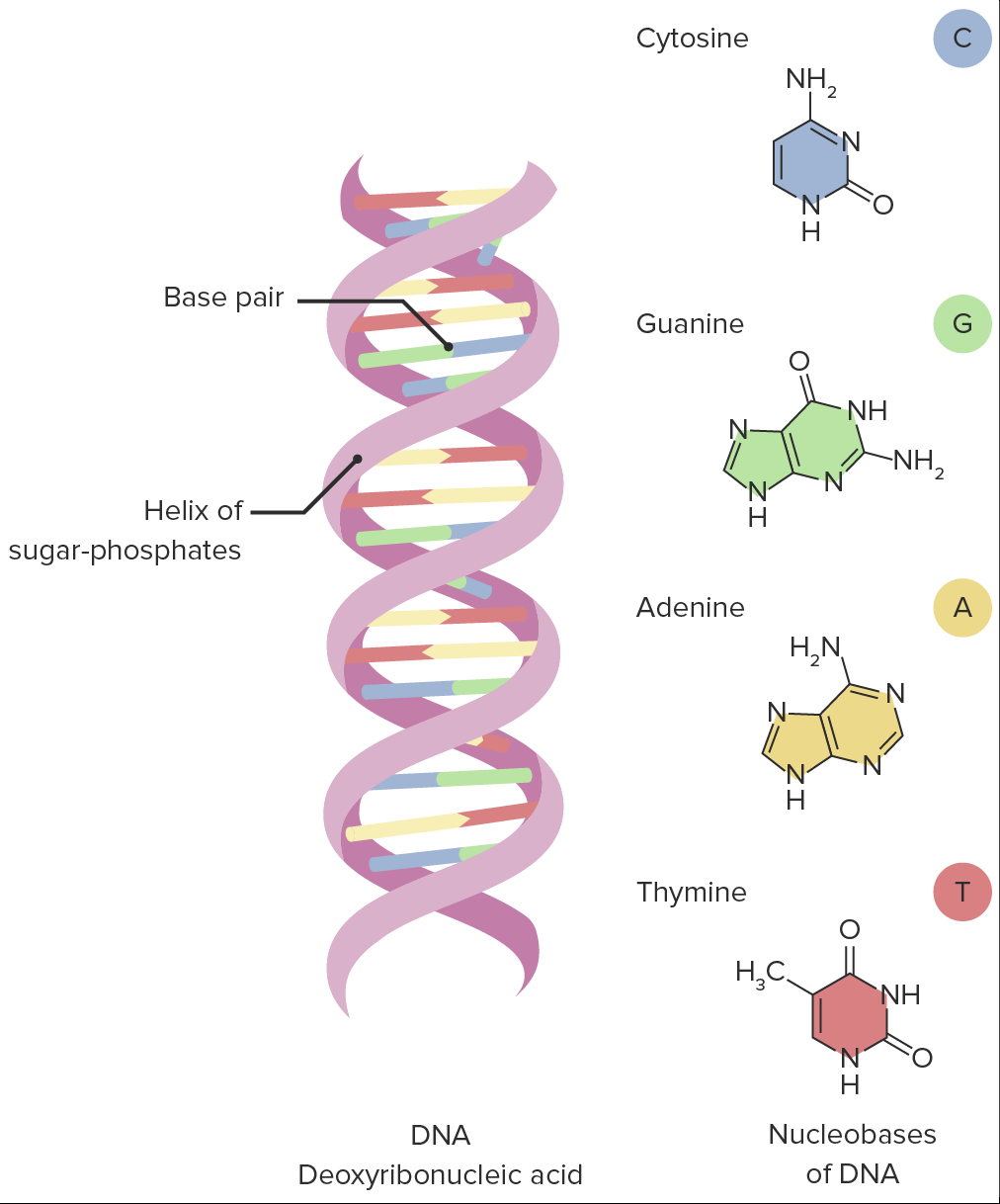
Molécula de ADN
Imagen por Lecturio.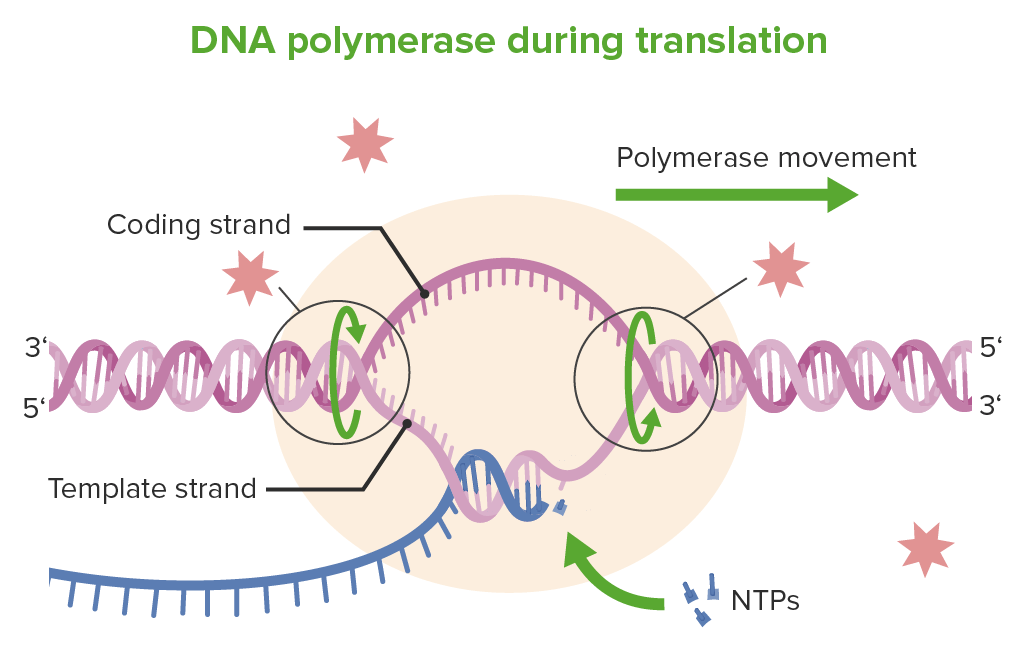
La ADN polimerasa durante la traducción:
Se puede ver la cadena de codificación y la cadena molde. La cadena de codificación también se conoce como cadena “codificante” y la cadena molde actúa como “plantilla” para la ARN polimerasa.
NTP: nucleósidos trifosfatos
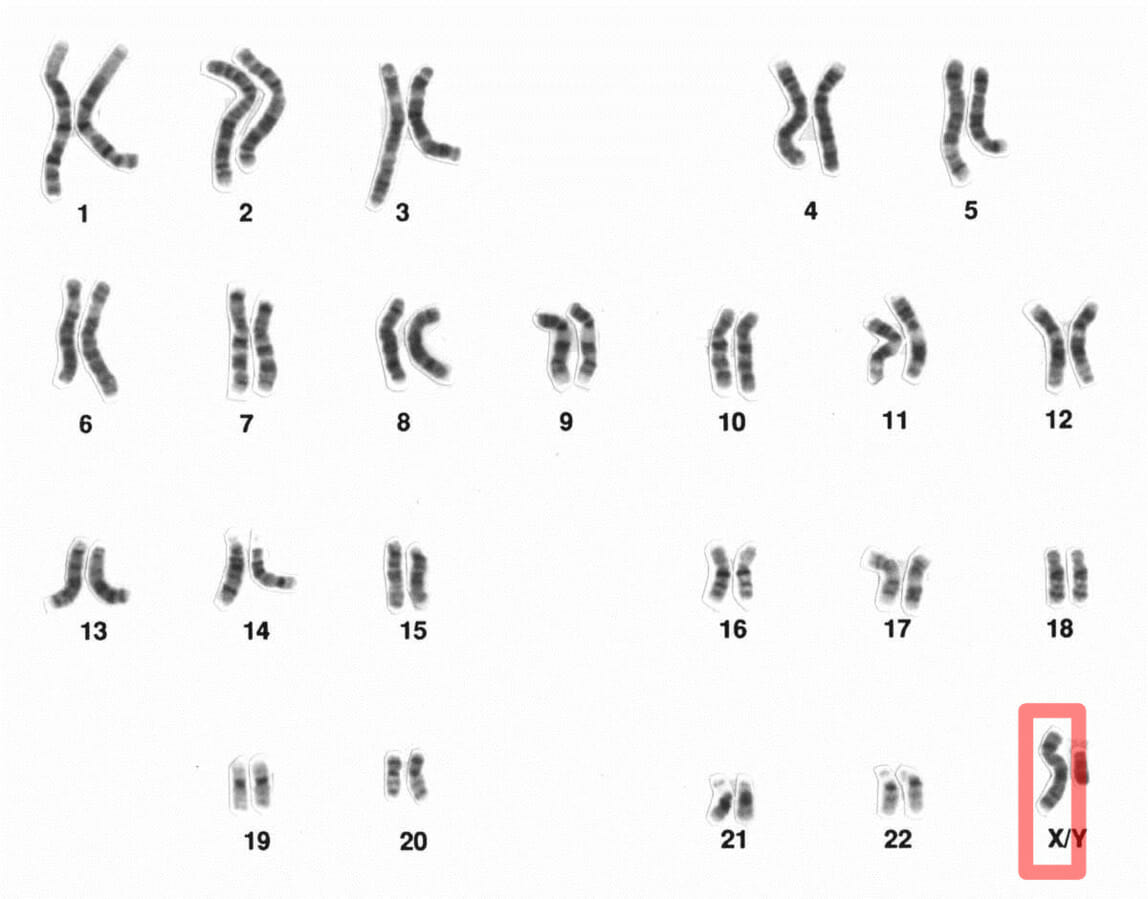
Cariotipo humano masculino:
Un cariotipo es un conjunto completo de cromosomas homólogos emparejados (el cromosoma X está resaltado).
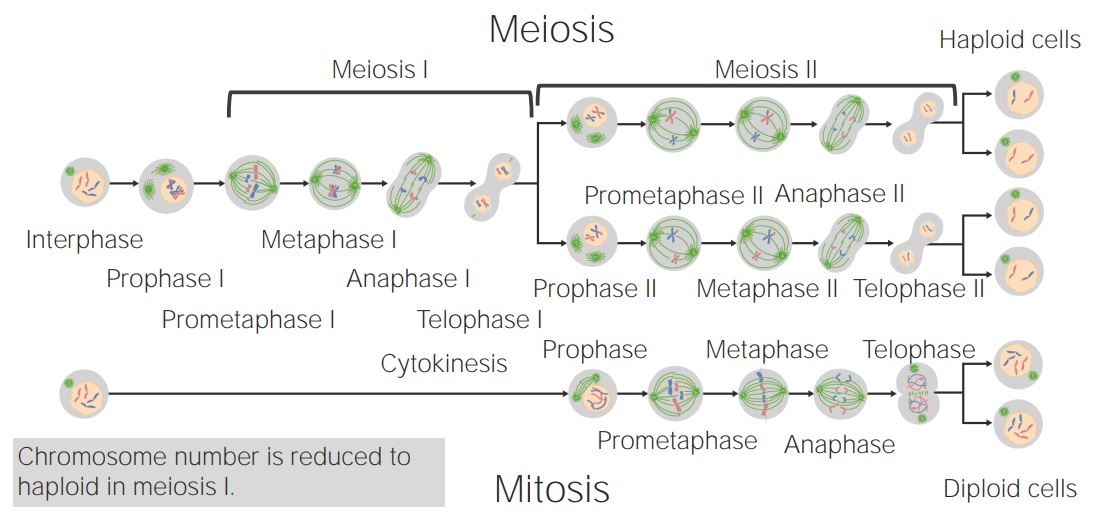
Comparación de la mitosis y la meioisis
Imagen por Lecturio.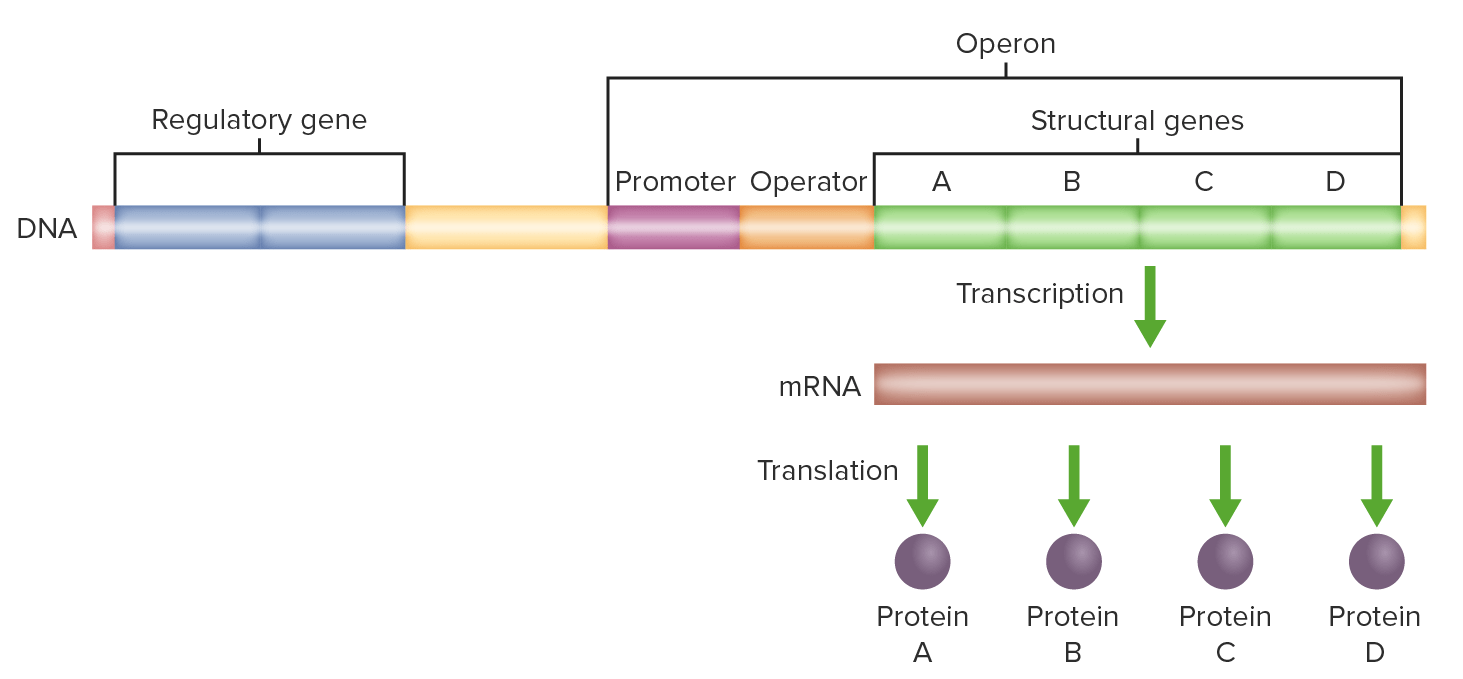
Diagrama que muestra un modelo de operón con regulador, promotor, operador y genes estructurales:
El operón contiene los genes de interés. El promotor es el sitio de unión de ciertas proteínas para permitir el inicio de la transcripción. El operador contiene el código necesario para iniciar el proceso de transcripción del ADN.
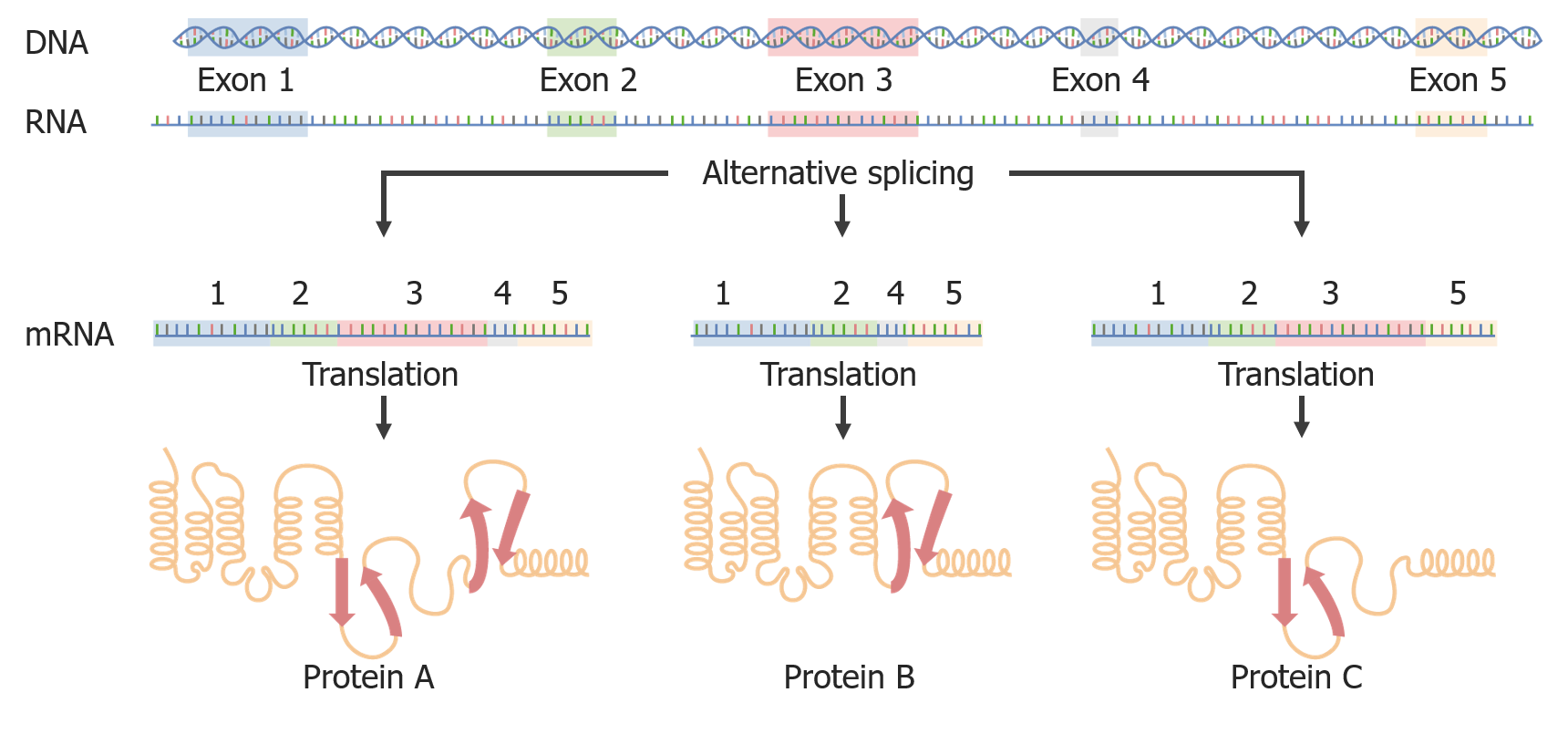
Empalme alternativo:
Al empalmar el ARNm de diferentes maneras, se pueden crear diferentes proteínas a partir del mismo ARNm.
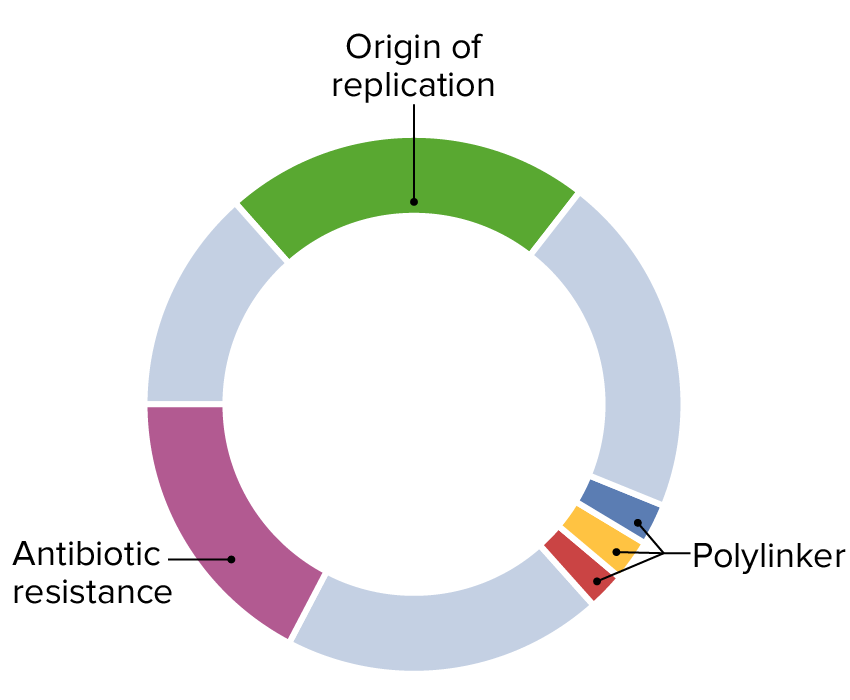
Imagen de un plásmido: ADN circular extracromosómico
Imagen por Lecturio.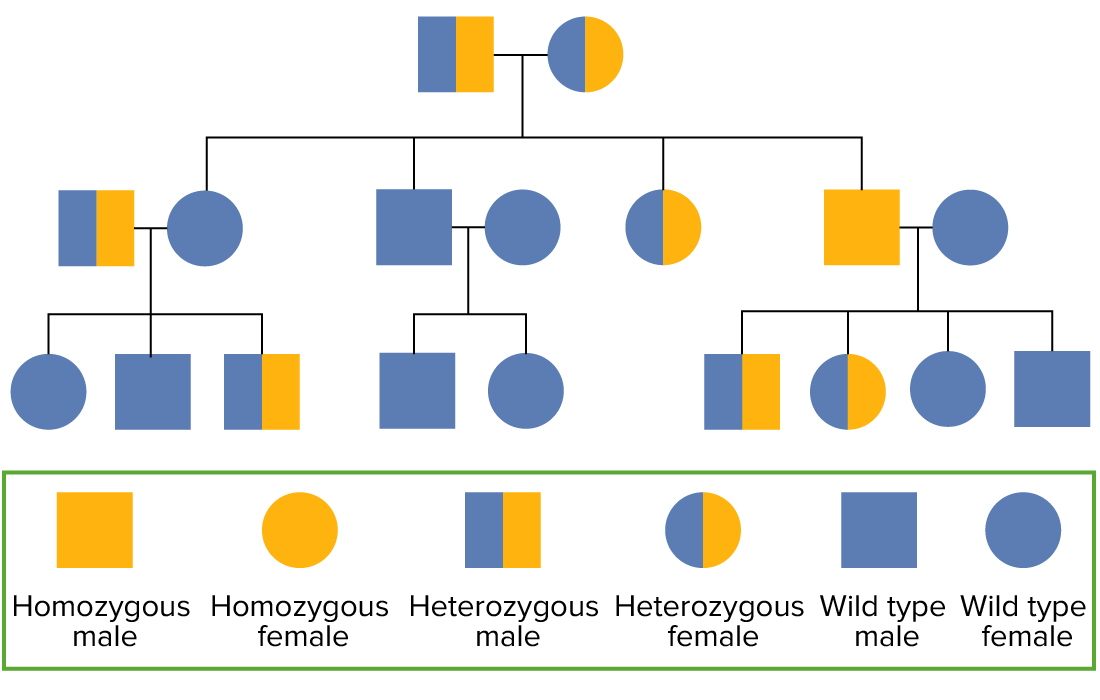
Cuadro de pedigrí autosómico recesivo
Imagen por Lecturio.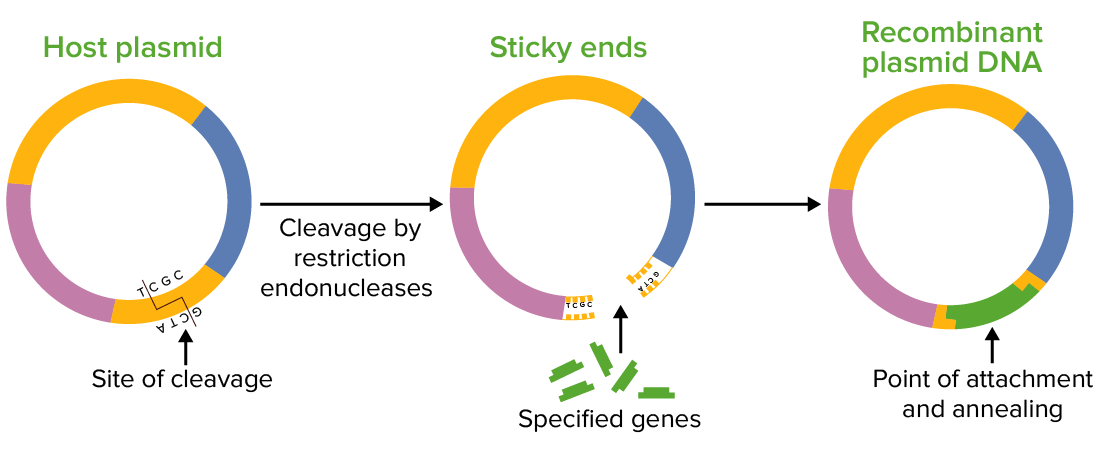
Construcción de ADN recombinante en la que se inserta un fragmento de ADN extraño en un vector plasmídico:
El gen indicado por el color blanco se inactiva al insertar el fragmento de ADN extraño.
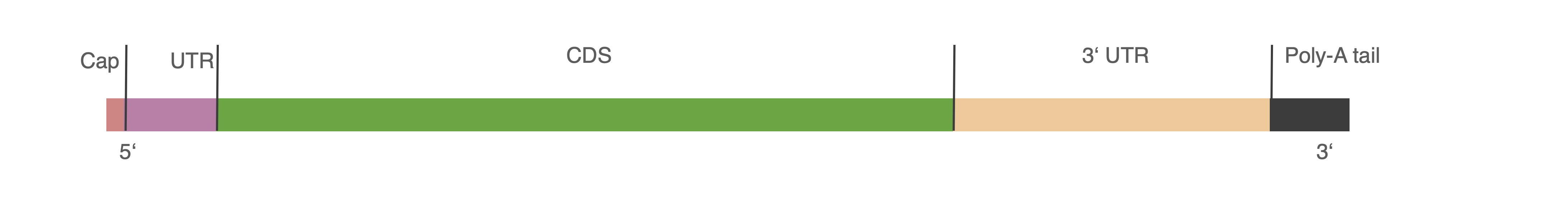

La estructura de un ARNm eucariótico maduro incluye
Caperuza 5′: La unión de la 7-metilguanosina ayuda al reconocimiento por parte de la maquinaria de síntesis de proteínas y protege de la degradación por parte de las exonucleasas.
UTR: regiones no traducidas
CDS: secuencia codificante, que consiste en codones correspondientes a aminoácidos específicos
Cola 3′ de poli-A: cadena de moléculas de adenilato que mantiene la estabilidad del ARNm al salir del núcleo hacia el citosol
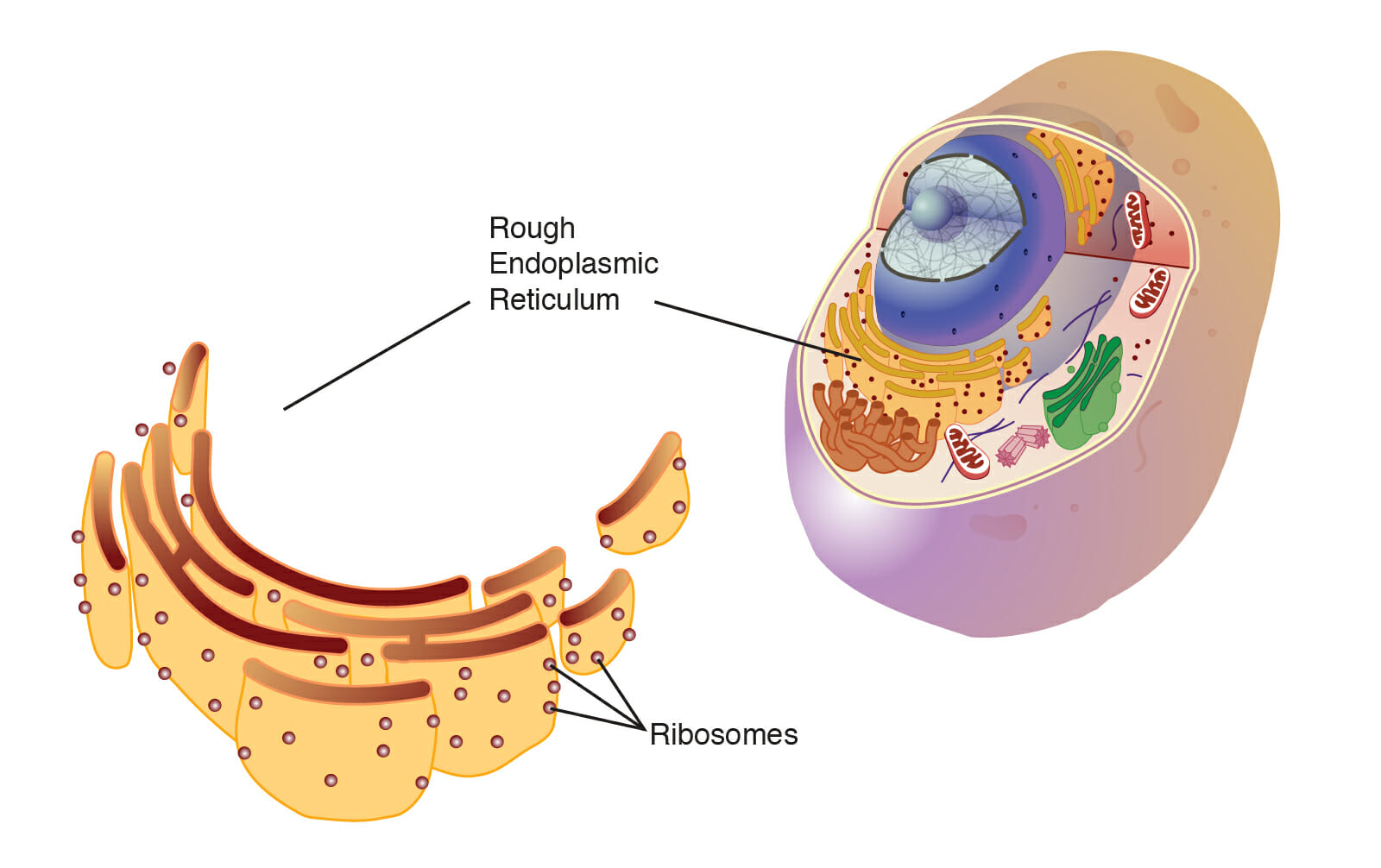
Un ribosoma es una partícula celular formada por ARN y proteínas que sirve de lugar para la síntesis de proteínas en la célula. El ribosoma lee la secuencia del ARN mensajero (ARNm) y, utilizando el código genético, traduce la secuencia de bases de ARN en una secuencia de aminoácidos.
Imagen: “endoplasmic_reticulum_rough” por National Human Genome Research Institute. Licencia: Dominio Público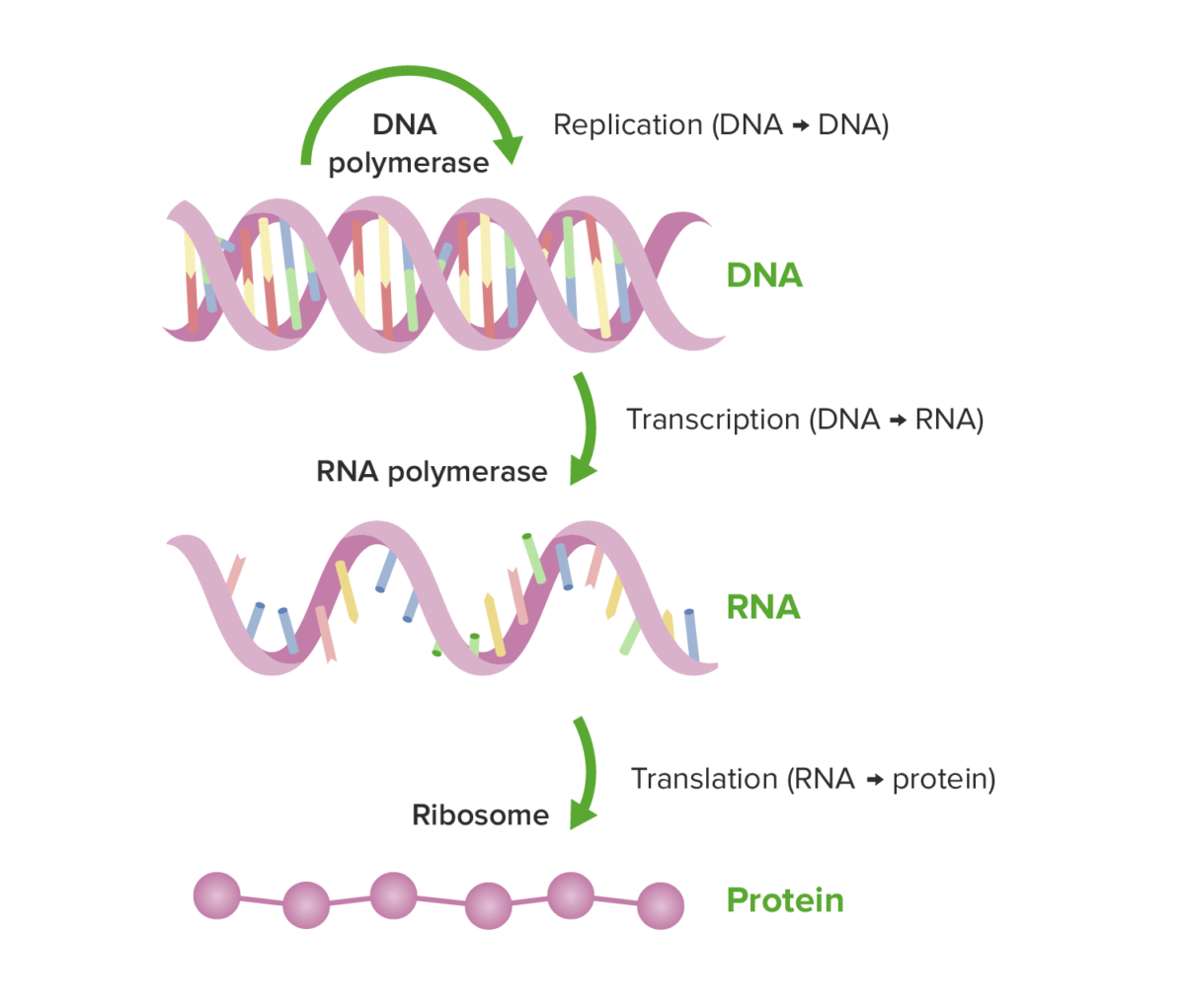
Dogma central de la biología molecular:
Ilustración de la diferencia entre transcripción y traducción junto con las enzimas necesarias.
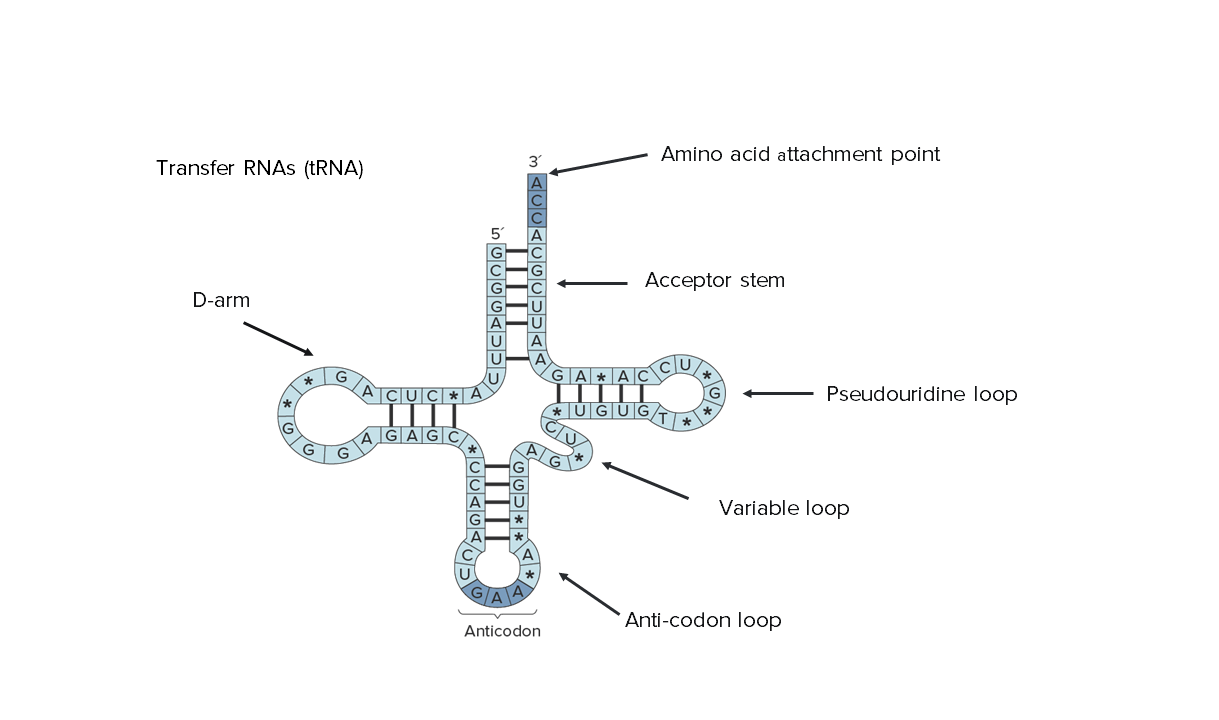
Estructura secundaria del ARN de transferencia (ARNt), junto con varios sitios funcionales del ARNt.
Imagen por Lecturio.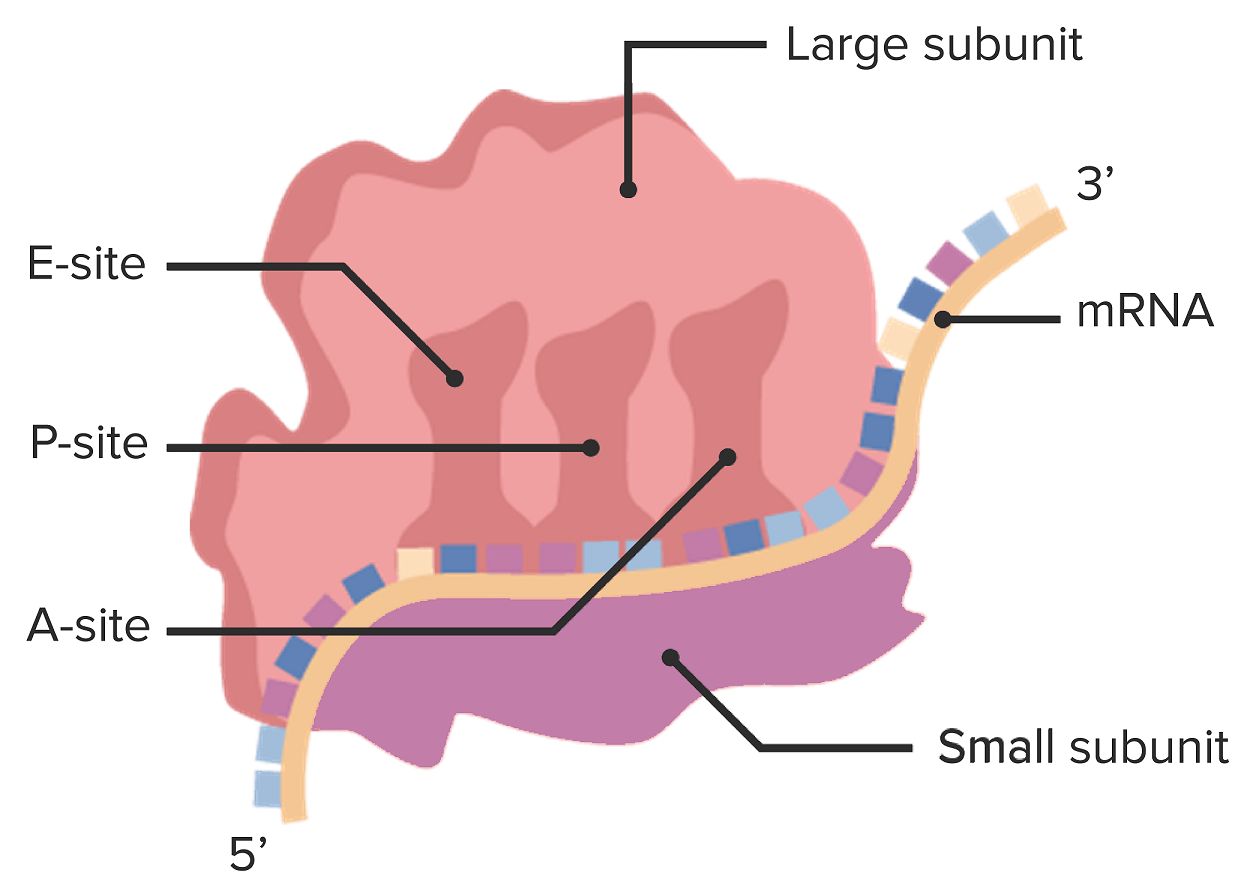
Estructura de un ribosoma:
La subunidad grande se muestra en la parte superior con los sitios de unión A, P y E para los ARN de transferencia cargados; la subunidad pequeña está debajo del ARN mensajero (ARNm).