Los LOS Neisseria síndromes mielodisplásicos son un grupo de neoplasias clonales con defectos de maduración caracterizados por displasia, citopenia y precursores de médula ósea inmaduros. Pueden ser idiopáticos o secundarios a diversas exposiciones dañinas, como quimioterapia citotóxica, radiación ionizante o toxinas ambientales. La mediana de edad de los LOS Neisseria pacientes es de 70 años. La presentación incluye síntomas de anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types (fatiga), neutropenia Neutropenia Neutrophils are an important component of the immune system and play a significant role in the eradication of infections. Low numbers of circulating neutrophils, referred to as neutropenia, predispose the body to recurrent infections or sepsis, though patients can also be asymptomatic. Neutropenia (infección) o trombocitopenia (sangrado). El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la evaluación de la médula ósea, que revela citopenia, displasia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum al AL Amyloidosis menos 1 linaje y células blásticas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum < 20% de la celularidad de la médula ósea. Se requieren estudios citogenéticos y moleculares para la clasificación, el pronóstico y las decisiones relacionadas con el tratamiento. Existe un mayor riesgo acumulativo de transformación a leucemia mieloide aguda y varía según el subtipo de síndrome mielodisplásico. El tratamiento incluye medidas de soporte, uso de factores de crecimiento hematopoyéticos, terapia inmunosupresora y trasplante alogénico de células hematopoyéticas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los síndromes mielodisplásicos son enfermedades clonales de la médula ósea caracterizadas por la presencia de precursores displásicos, inmaduros de la médula ósea y citopenias periféricas. La Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS) publicó una actualización en 2022 en la que renombró los síndromes mielodisplásicos como “Neoplasias mielodisplásicas”.
La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria síndromes mielodisplásicos se atribuyen a deleciones y translocaciones cromosómicas o mutaciones genéticas.
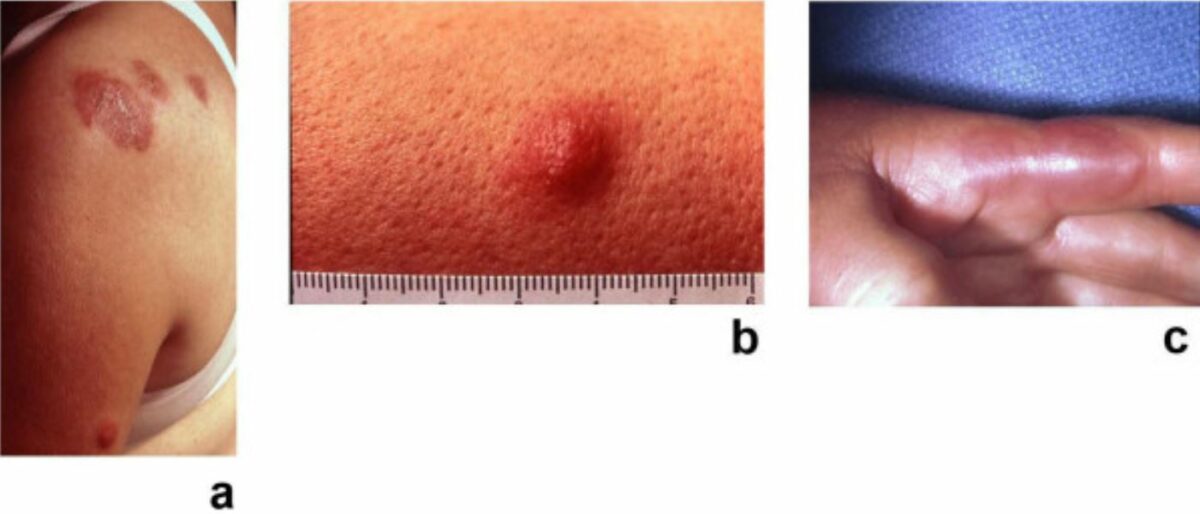
Síndrome de Sweet: placas dolorosas, eritematosas, seudovasculares de dermatosis neutrofílica febril aguda
Imagen: “Sweet’s syndrome–a comprehensive review of an acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis” por Cohen PR. Licencia: CC BY 2.0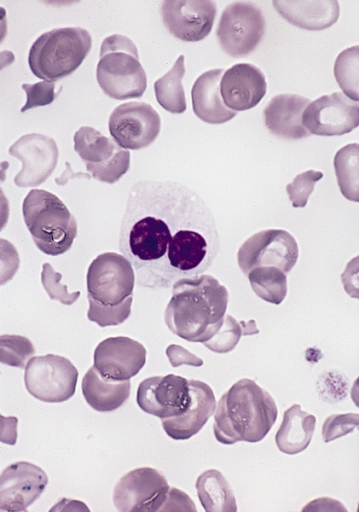
Frotis periférico en síndrome mielodisplásico que muestra un neutrófilo displásico con núcleo bilobulado y granulación alterada (pseudo–anomalía de Pelger-Huët)
Imagen: “Hypogranular neutrophil with a pseudo-Pelger-Huet nucleus in MDS” por The Armed Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP) Licencia: Dominio Público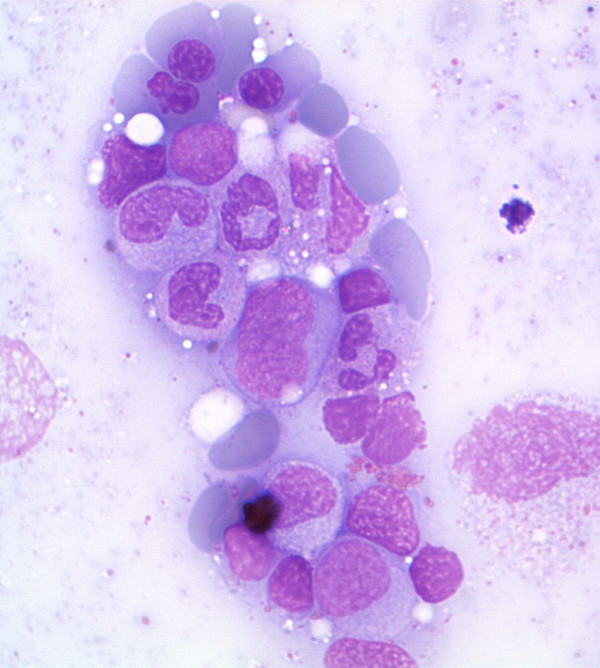
Aspirado de médula ósea en síndrome mielodisplásico que muestra células eritroides displásicas y precursores mieloides
Imagen: “Antiretroviral activity of 5-azacytidine during treatment of a HTLV-1 positive myelodysplastic syndrome with autoimmune manifestations” por Diamantopoulos, P.T. et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Después de confirmar el diagnóstico de neoplasia mielodisplásica, los LOS Neisseria pacientes se clasifican según la quinta edición de la clasificación de tumores hematolinfoides de la Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS), publicada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 2022.
La clasificación se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum:
Tipos: