El síndrome del túnel carpiano es un complejo de signos y síntomas causados por la compresión del nervio mediano cuando cruza el túnel carpiano. La presentación clínica es dolor Dolor Inflammation y parestesia de los LOS Neisseria dermatomas inervados por el nervio mediano, así como debilidad y atrofia de los LOS Neisseria miotomas del nervio. Los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo que causan una predisposición al AL Amyloidosis síndrome del túnel carpiano incluyen la obesidad, el sexo femenino, el embarazo, la diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus, las afecciones inflamatorias, la predisposición genética y los LOS Neisseria factores ocupacionales. Se puede hacer un diagnóstico clínico con base en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria antecedentes y el examen físico y confirmarlo mediante pruebas de electrodiagnóstico. El tratamiento conservador incluye entablillado y fisioterapia de la muñeca; los LOS Neisseria casos más severos pueden requerir de corrección quirúrgica.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Mnemotécnia:
Los músculos de la mano inervados por el nervio mediano, usando el acrónimo “Meat-LOAF” ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés,) son:
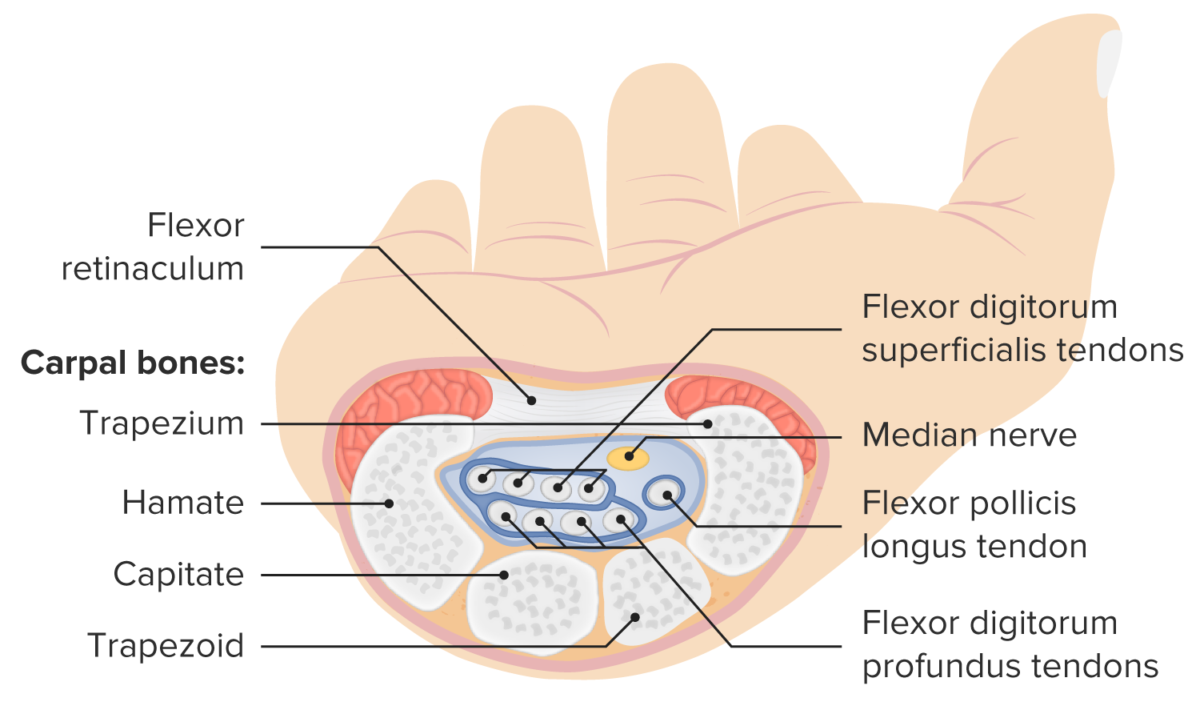
Estructura y contenido del túnel carpiano
Imagen por Lecturio.
Músculos tenares de la mano
Imagen por Lecturio.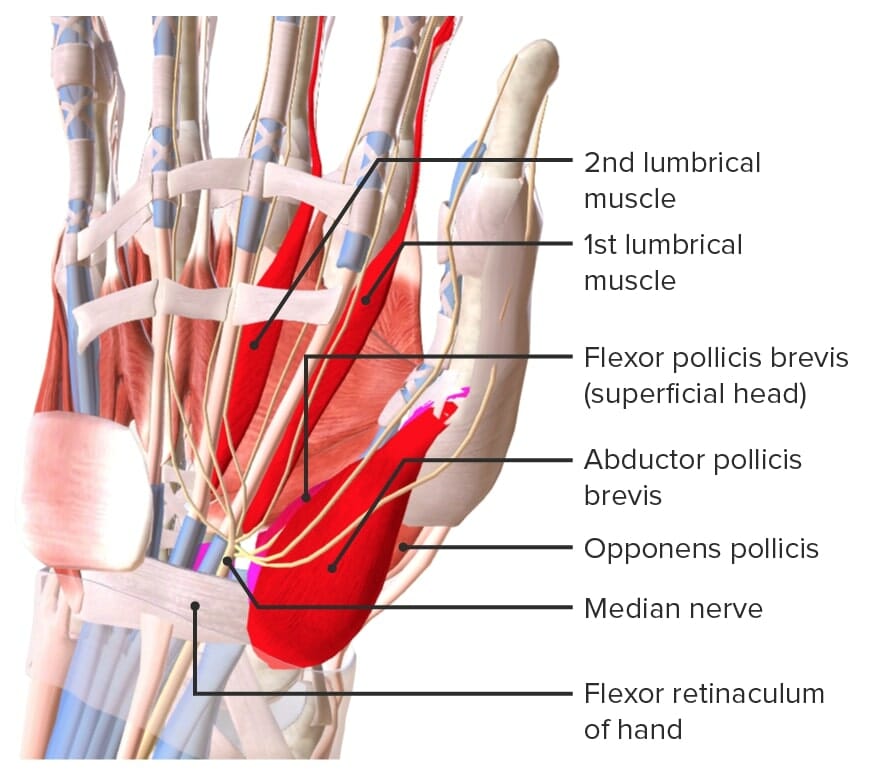
Músculos de la mano inervados por el nervio mediano (Meat-LOAF):
MEAT: median nerve (nervio mediano)
L: 1st and 2nd lumbricals (1er y 2do lumbrical)
O: Opponens pollicis (oponente del pulgar)
A: Abductor pollicis brevis (abductor corto del pulgar)
F: Flexor pollicis brevis (flexor corto del pulgar)
Inervación sensitiva del nervio mediano
Imagen por Lecturio.La fisiopatología del estrechamiento del túnel carpiano y la disfunción del nervio mediano son multifactoriales.
El síndrome del túnel carpiano es un diagnóstico clínico. Una combinación de hallazgos clínicos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum combinación con pruebas de electrodiagnóstico confirmatorias para mayor precisión en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el diagnóstico.
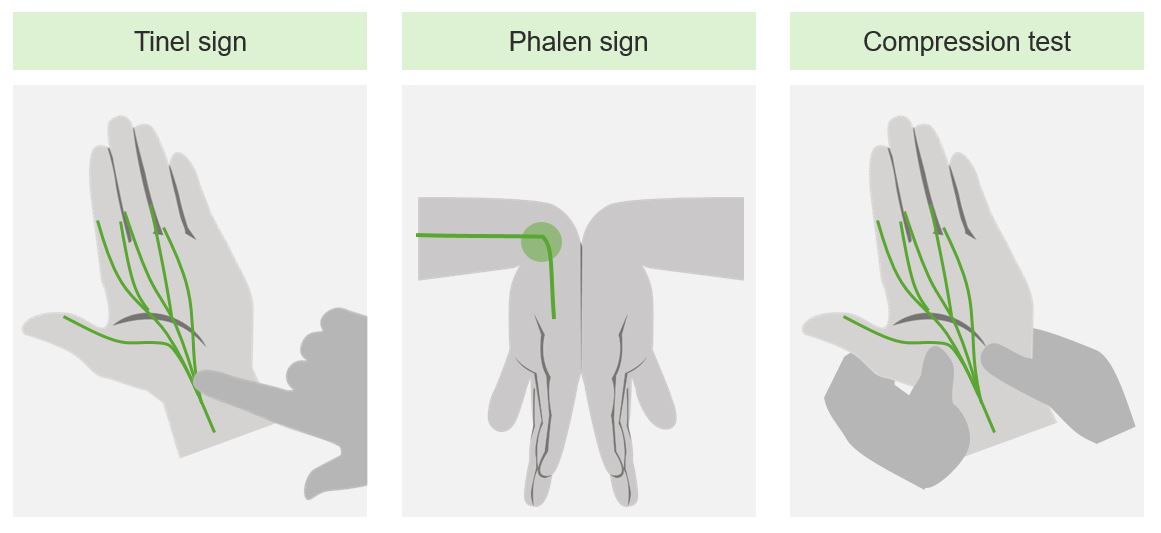
Maniobras de provocación para la evaluación clínica del síndrome del túnel carpiano
Imagen por Lecturio.
La imagenología es útil si se sospecha una anomalía estructural.
Clasificación clínica de la gravedad del síndrome del túnel carpiano:
Clasificación electrodiagnóstica de la gravedad del síndrome del túnel carpiano:
El tratamiento se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la agudeza y la gravedad de los LOS Neisseria síntomas clínicos y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el grado de lesión neurogénica evaluada mediante los LOS Neisseria estudios de electrodiagnóstico.
Para los LOS Neisseria pacientes con síndrome del túnel carpiano de leve a moderado, la tasa de resultados exitosos es del 20%–93%. Las opciones terapéuticas incluyen: