La regulación renal del sodio (Na+) y del agua funcionan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum conjunto para controlar la distribución del líquido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria compartimentos del organismo. El sodio es el soluto extracelular dominante en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el organismo y es responsable de la fuerza osmótica que mantiene diferentes cantidades de agua en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cada compartimento. Los LOS Neisseria cambios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el equilibrio del Na+ son percibidos por el cuerpo a través de los LOS Neisseria cambios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el volumen sanguíneo. Los LOS Neisseria cambios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el equilibrio hídrico son percibidos por el cuerpo a través de los LOS Neisseria cambios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la osmolalidad del plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products. Ambos envían, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum última instancia, señales de retroalimentación a los LOS Neisseria riñones para garantizar el mantenimiento de la homeostasis Homeostasis The processes whereby the internal environment of an organism tends to remain balanced and stable. Cell Injury and Death. Las anomalías en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum estos procesos pueden provocar problemas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la volemia (e.g., hipertensión, edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema pulmonar, edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema con fóvea) y disnatremias (hiponatremia e hipernatremia).
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Para entender la regulación renal del sodio y del agua, es importante comprender cómo se distribuye normalmente el agua en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el organismo.
Agua corporal total:
Líquido intracelular:
Líquido extracelular:
Compartimentos de fluidos corporales
Imagen por Lecturio.La osmolalidad del plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products se refiere a la concentración combinada de todos los LOS Neisseria solutos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sangre.
La tonicidad plasmática se refiere a la concentración de solo los LOS Neisseria solutos osmóticamente activos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sangre y suele denominarse osmolalidad efectiva.
La nefrona es la unidad funcional del riñón a través de la cual se filtran, reabsorben y secretan fluidos y solutos, incluido el Na+.
Reabsorción en el túbulo proximal:
Los números sobre los túbulos representan la osmolalidad del tejido circundante.
Reabsorción en la porción gruesa ascendente:
El sodio, potasio y cloruro se reabsorben a través del cotransportador NKCC2, pero la porción gruesa ascendente no es permeable al agua. La porción gruesa ascendente es un segmento diluyente de la nefrona.
Reabsorción en el túbulo contorneado distal:
El sodio y cloruro se reabsorben en el túbulo contorneado distal, pero el túbulo contorneado distal no es permeable al agua. El túbulo contorneado distal es otro segmento diluyente.
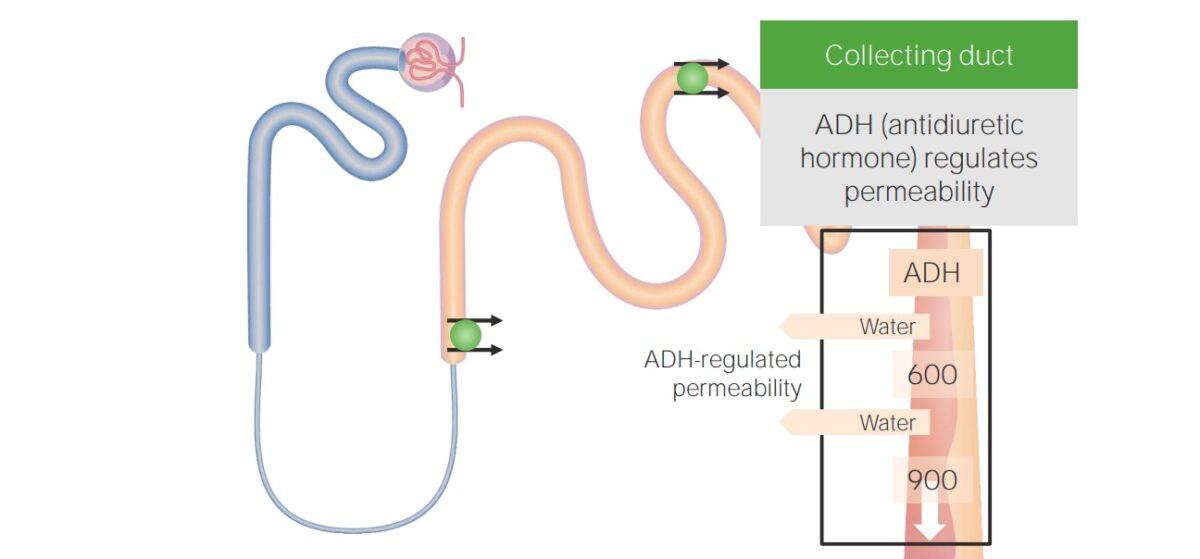
Reabsorción de agua en el conducto colector
Imagen por Lecturio.El organismo regula el equilibrio del Na+ detectando los LOS Neisseria cambios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el volumen circulante efectivo, también conocido como volumen sanguíneo arterial efectivo.
El sistema renina-angiotensina-aldosterona es estimulado por un volumen circulante efectivo bajo:
Sistema renina-angiotensina-aldosterona
Imagen por Lecturio.Efectos de la aldosterona:
Efectos de la aldosterona sobre las proteínas reguladoras del transporte de sodio y potasio en las células principales de los conductos colectores
Imagen por Lecturio.Los LOS Neisseria cambios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el volumen circulante efectivo son percibidos por el aparato yuxtaglomerular, los LOS Neisseria barorreceptores del arco carotídeo y aórtico y los LOS Neisseria barorreceptores cardíacos.
La regulación del agua está controlada principalmente por los LOS Neisseria osmorreceptores del hipotálamo, que mantienen la osmolalidad del plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products de forma muy estricta. Cambios muy pequeños en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la osmolalidad del plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products provocan cambios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la liberación de hormona antidiurética y la sensación de sed.
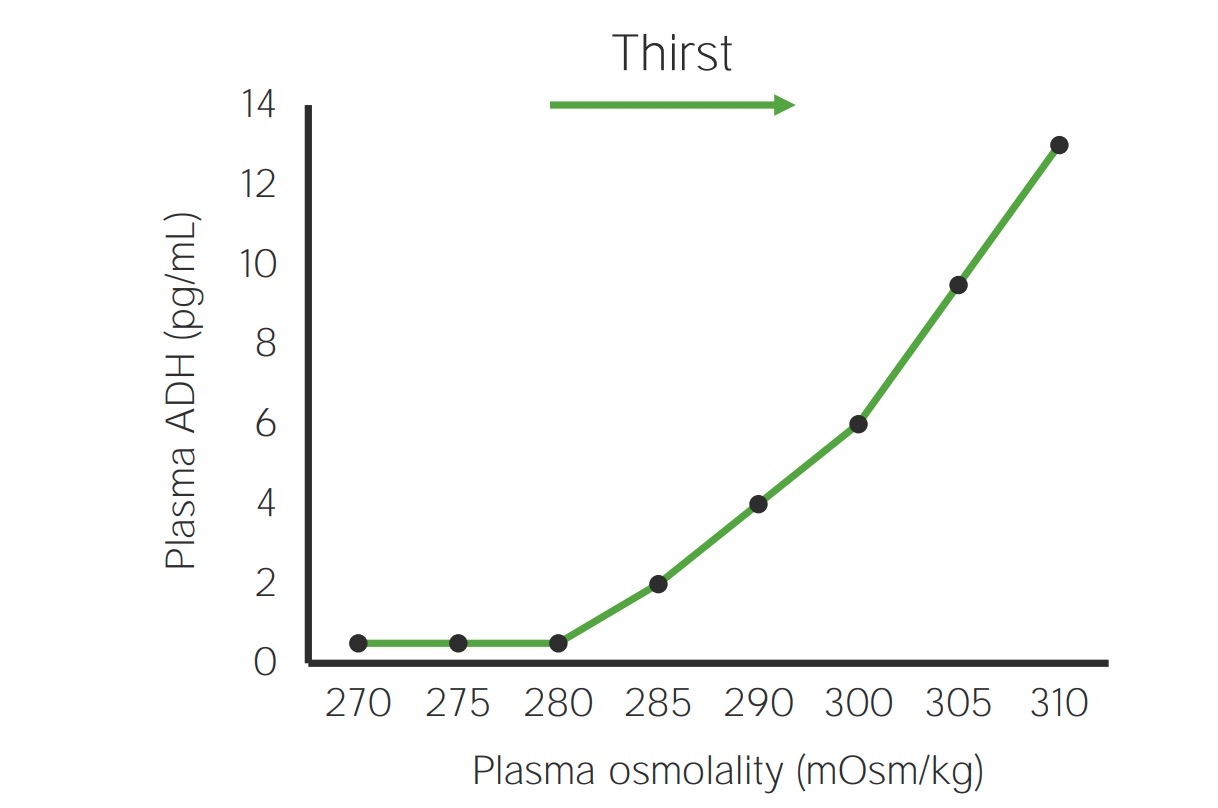
Regulación de la hormona antidiurética (ADH, por sus siglas en inglés) osmótica:
Ligeros aumentos de la osmolalidad plasmática estimulan la liberación de hormona antidiurética de forma lineal.
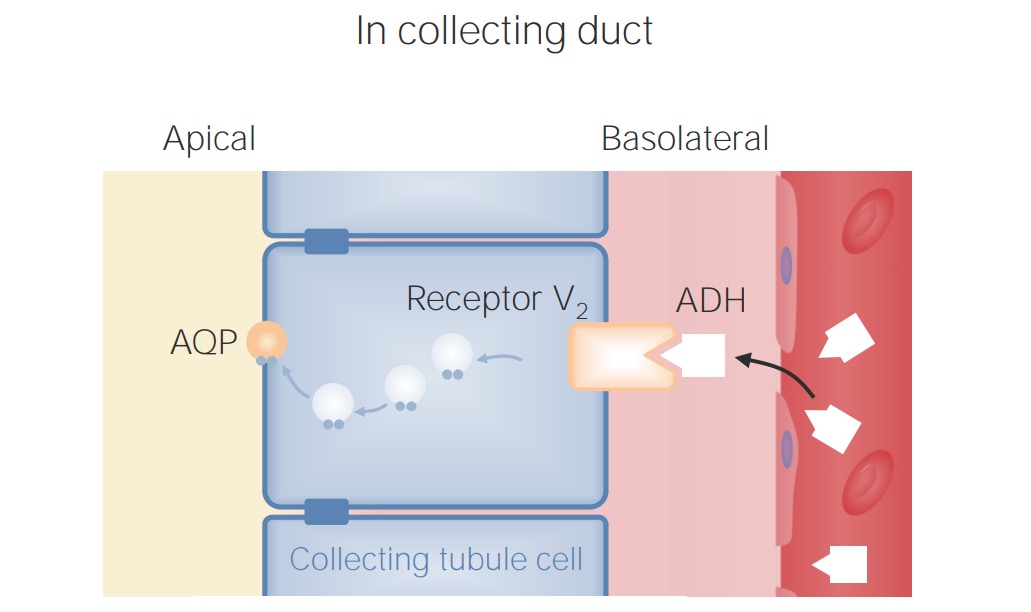
Localización y función del receptor V2 de la hormona antidiurética (ADH) en los conductos colectores
AQP: acuaporinaLas disminuciones grandes del volumen circulante efectivo pueden provocar independientemente la liberación de hormona antidiurética en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un intento de preservar el volumen.
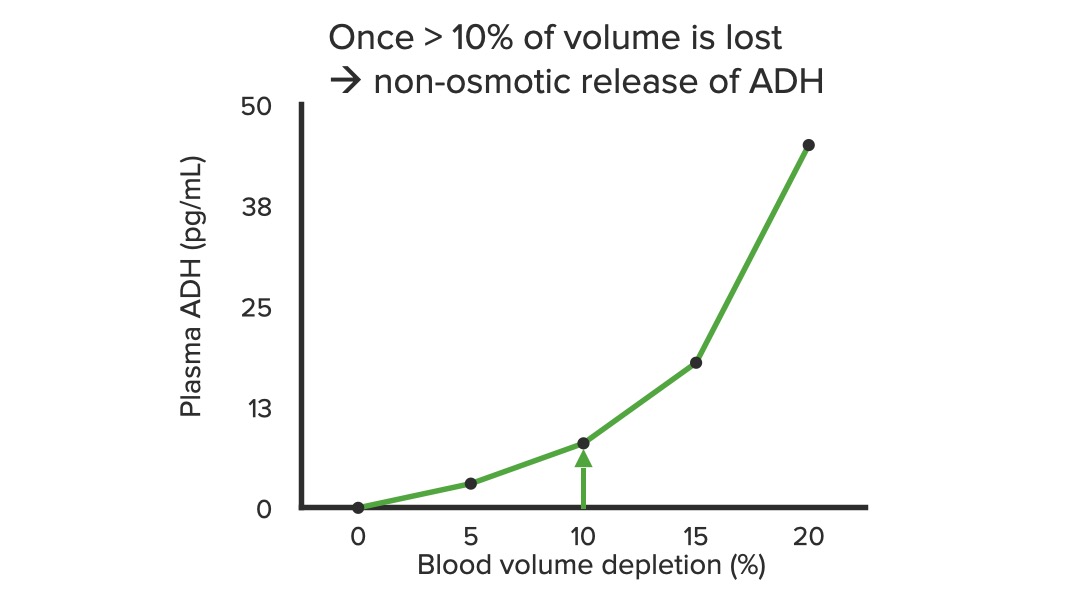
Las disminuciones severas del volumen sanguíneo estimulan la liberación de ADH.
ADH: hormona antidiurética
Regulación osmótica y no osmótica de la hormona antidiurética (ADH)
ANP: Péptido natriurético auricular
Regulación de la hormona antidiurética
Imagen por Lecturio.