Los LOS Neisseria pólipos colorrectales son crecimientos de tejido mucoso en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy, el lugar más común de los LOS Neisseria pólipos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tracto gastrointestinal. Los LOS Neisseria pólipos pueden clasificarse como neoplásicos o no neoplásicos y pueden estar asociados a síndromes genéticos. Los LOS Neisseria pólipos hiperplásicos no son neoplásicos y son el tipo más común en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum general, mientras que los LOS Neisseria adenomas son el tipo más común de pólipo neoplásico y tienen el potencial de progresar a cáncer. Para la mayoría de las personas sin síndromes hereditarios, el tamizaje del cáncer de colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy debe comenzar a los LOS Neisseria 45 años y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la adolescencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el caso de las personas con el raro síndrome de poliposis adenomatosa familiar. El diagnóstico se realiza mediante biopsia y el tratamiento incluye la vigilancia frecuente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum personas con pólipos adenomatosos o el tamizaje cada 10 años en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la población general hasta los LOS Neisseria 75 años.
Last updated: Jan 15, 2026
Cada síndrome se presenta en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum <1% de la población y representa el 5%–10% de los LOS Neisseria cánceres colorrectales.
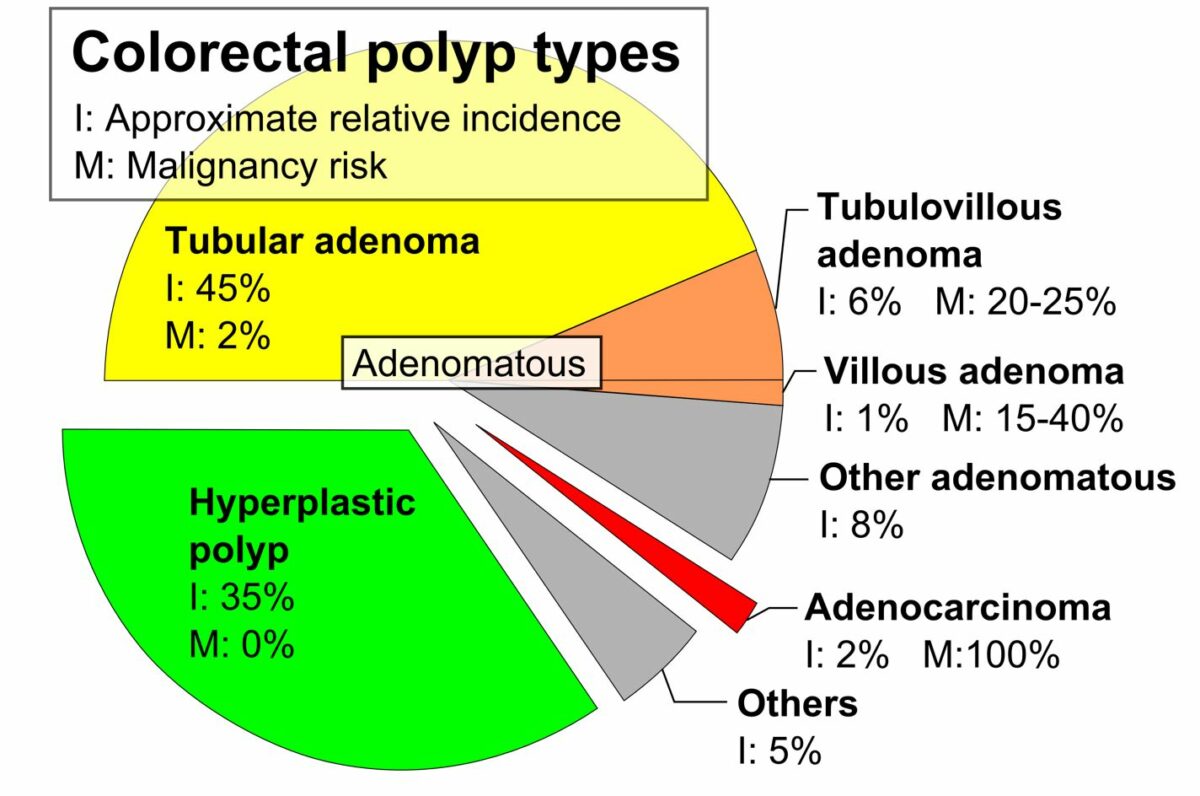
Tipos de pólipos colorrectales, incidencia relativa aproximada (I) y riesgo de malignidad (M) (2019)
Imagen: “Pie chart of colorectal polyp etiologies” por Mikael Häggström. Licencia: CC0 1.0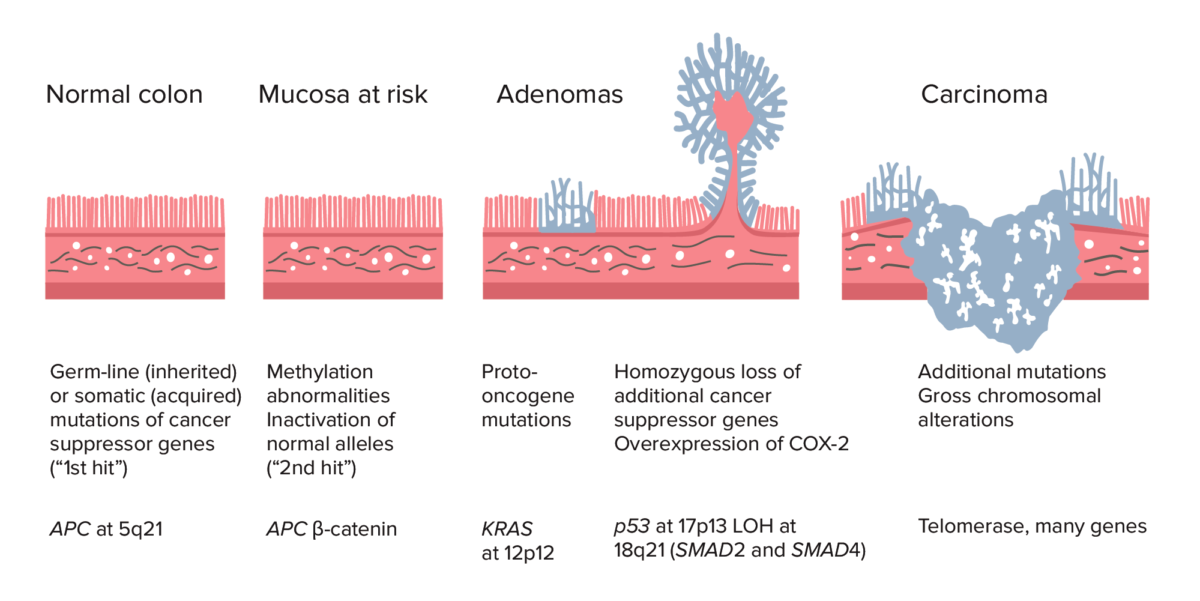
Secuencia adenoma–carcinoma de colon normal a carcinoma:
La formación del cáncer colorrectal comienza con la mutación del gen APC (heredada o adquirida) y las anomalías de metilación. Otros cambios pueden incluir la mutación del gen KRAS. En una fase avanzada del proceso, la deleción de p53, la pérdida de heterocigosidad (LOH) en 18q21 (que implica a SMAD2 y SMAD4), con la sobreexpresión de COX-2 pueden contribuir a un mayor crecimiento y a la progresión del cáncer. La acumulación de mutaciones, más que el momento en que se producen, es lo más crucial en la carcinogénesis.
La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria pólipos colorrectales son asintomáticos y se descubren en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tamizaje rutinario para cáncer de colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy.
El diagnóstico y el tratamiento definitivo de los LOS Neisseria pólipos colorrectales se consiguen mediante la extirpación endoscópica de todo el pólipo.
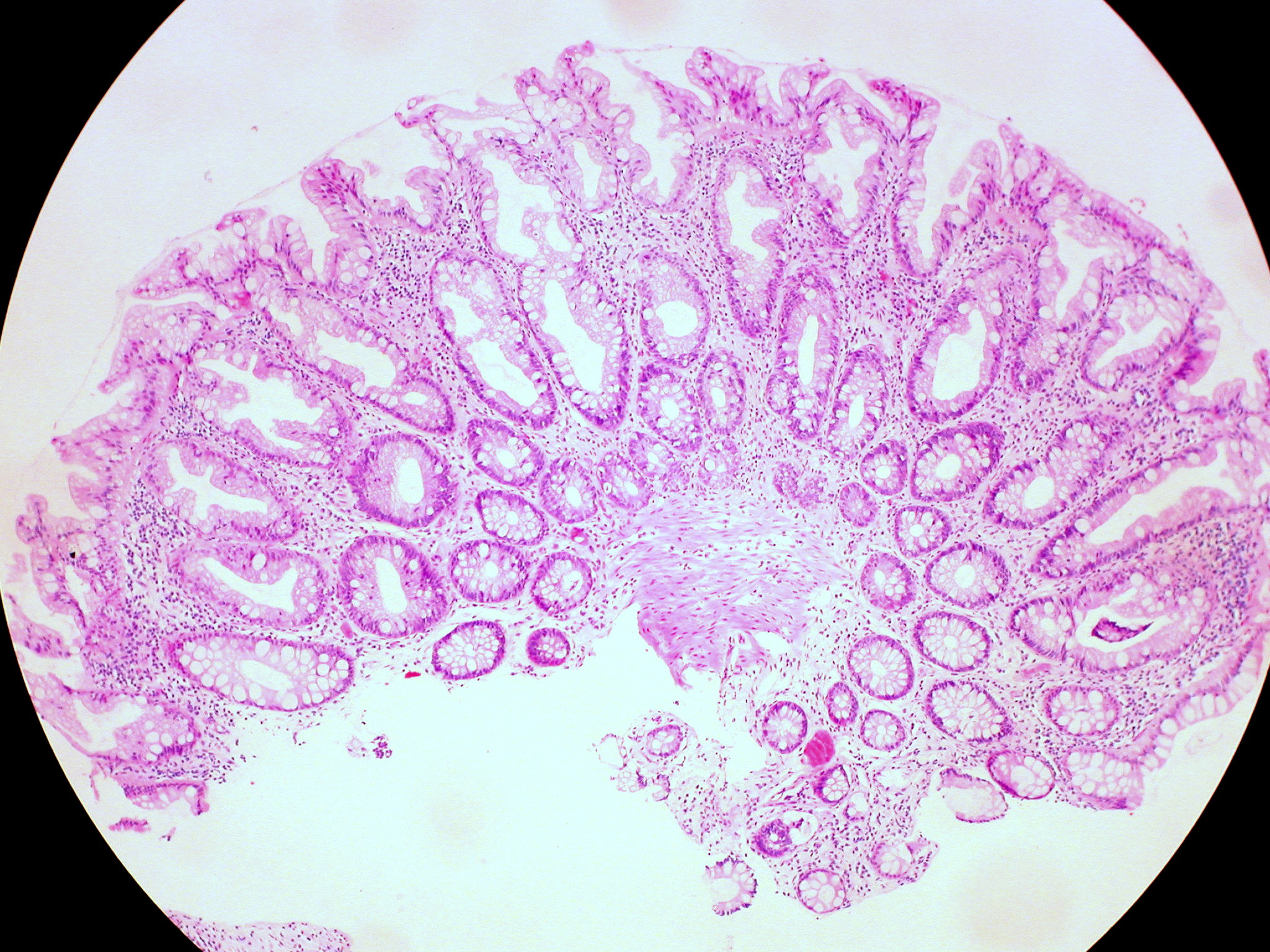
Pólipo hiperplásico del recto
Imagen: “Hyperplastic Polyp of the Rectum (14060044206)” por Ed Uthman. Licencia: CC BY 2.0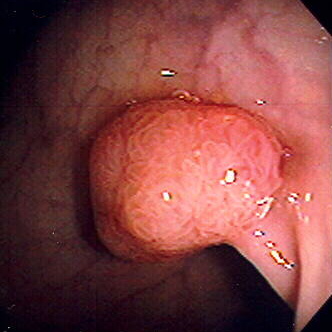
Pólipo de colon con un tallo (pedunculado)
Imagen: “Polyp” por Stephen Holland. Licencia: CC BY 2.5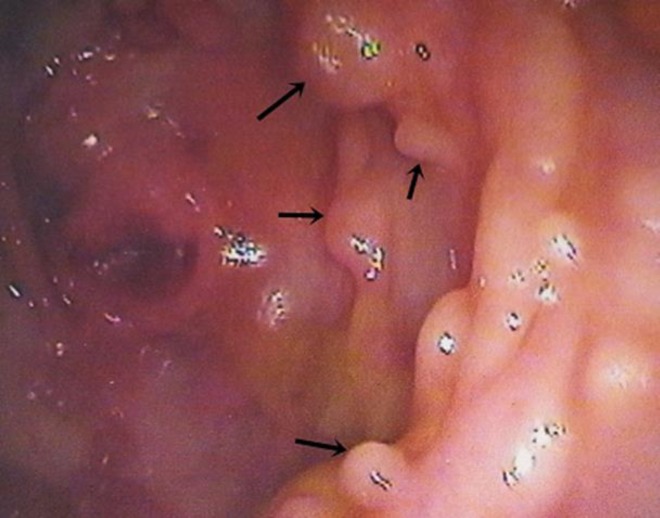
Múltiples pólipos en el colon, de 0,5 a 1 cm de diámetro
Imagen: “Multiple polyps in colon” por Agrawal N, Santra T, Kar A, Guha P, Bar M, Adhikary A, Datta S. Licencia: CC BY 3.0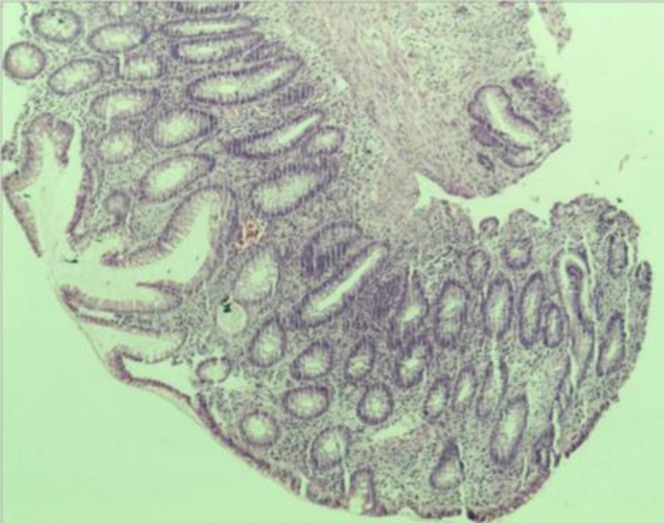
Biopsia del pólipo sigmoideo que revela un pólipo adenomatoso sin evidencia de malignidad
Imagen: “Biopsy from sigmoid polyp revealing adenomatous polyp without any evidence of malignancy” por Agrawal N, Santra T, Kar A, Guha P, Bar M, Adhikary A, Datta S. Licencia: CC BY 3.0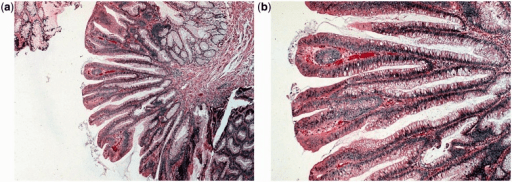
Adenoma velloso: El aspecto histológico es de proyecciones largas en forma de dedo.
a: vista de bajo aumento (tinción de H&E, 400x)
b: vista a gran aumento (tinción H&E, 2000x)
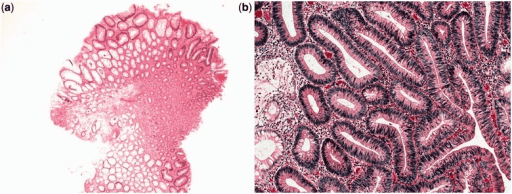
Adenoma tubular: El aspecto histológico es de glándulas tubulares ramificadas.
a: vista de bajo aumento (tinción H&E, 400x)
b: vista a gran aumento (tinción H&E, 2000x)
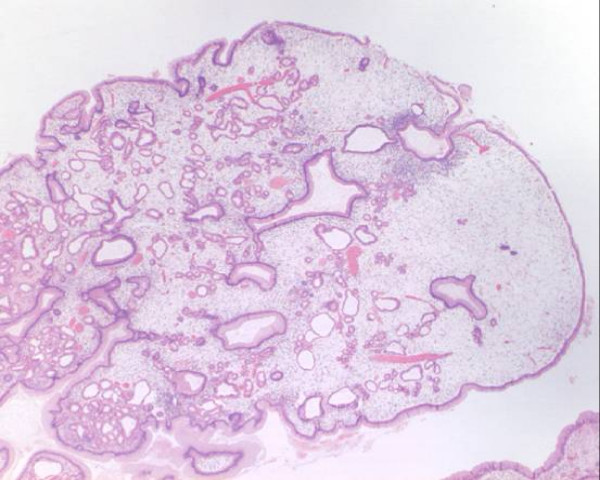
Histología del pólipo juvenil que muestra las glándulas dilatadas quísticas características:
Incluso a bajo poder, la naturaleza benigna y no neoplásica se ve apoyada por la observación de solo una capa de células epiteliales en la superficie y el revestimiento de los espacios glandulares.
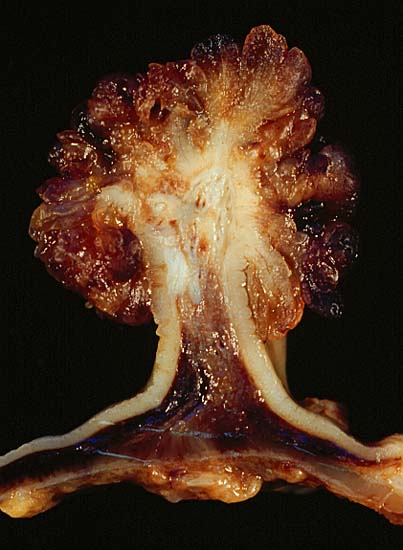
Pólipo tubulovelloso
Imagen: “Tubulovillous Polyp of the Colon 2” por Ed Uthman. Licencia: Dominio Público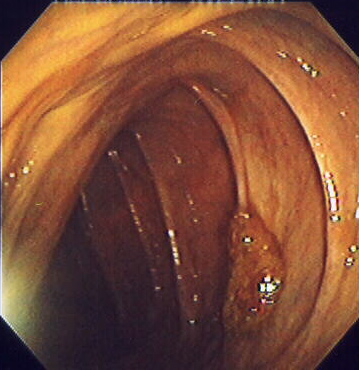
Pólipo colorrectal sésil visto en la colonoscopia
Imagen: “Endomucosal resection 1” por Stephen Holland. Licencia: CC BY 2.5Pautas de seguimiento después de la colonoscopia y la polipectomía (basadas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la Actualización del Consenso 2020 por la U.S. Multi-Society Task Force sobre el Cáncer Colorrectal):
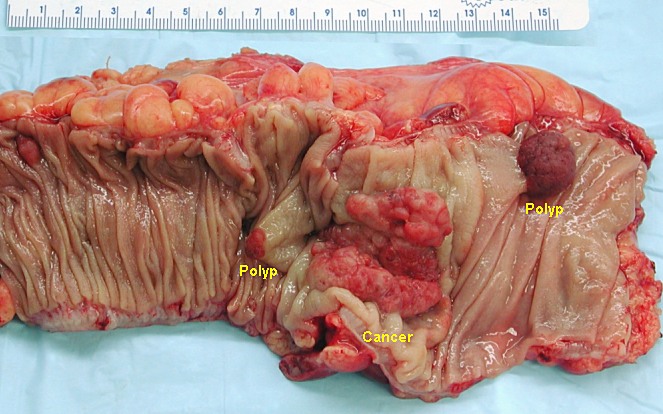
Segmento de colon resecado en estado no fijado que contiene un carcinoma colorrectal invasivo y 2 pólipos adenomatosos
Imagen: “Colon cancer” por Emmanuelm. Licencia: CC BY 3.0