El polihidramnios es un exceso patológico de líquido amniótico. Las causas más comunes de polihidramnios son las anomalías fetales, la diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus gestacional, las gestaciones múltiples y las infecciones congénitas. Las pacientes suelen ser asintomáticas, pero pueden presentar un tamaño uterino aumentado para la edad gestacional, disnea, edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema de las extremidades o contracciones uterinas. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria hallazgos por ultrasonido que muestran un índice de líquido amniótico excesivo ≥24 cm o una bolsa única más profunda ≥8 cm. Se asocia a una importante morbilidad y mortalidad neonatal y materna. Los LOS Neisseria casos leves pueden resolverse espontáneamente. El manejo de los LOS Neisseria casos moderados a graves puede incluir la monitorización fetal, la amniorreducción, la administración de medicamentos como los LOS Neisseria AINE (e.g., indometacina) y la inducción del parto.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El polihidramnios es un nivel anormalmente alto de líquido amniótico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el saco amniótico.
Condiciones fisiológicas normales:
Dos causas principales de polihidramnios:
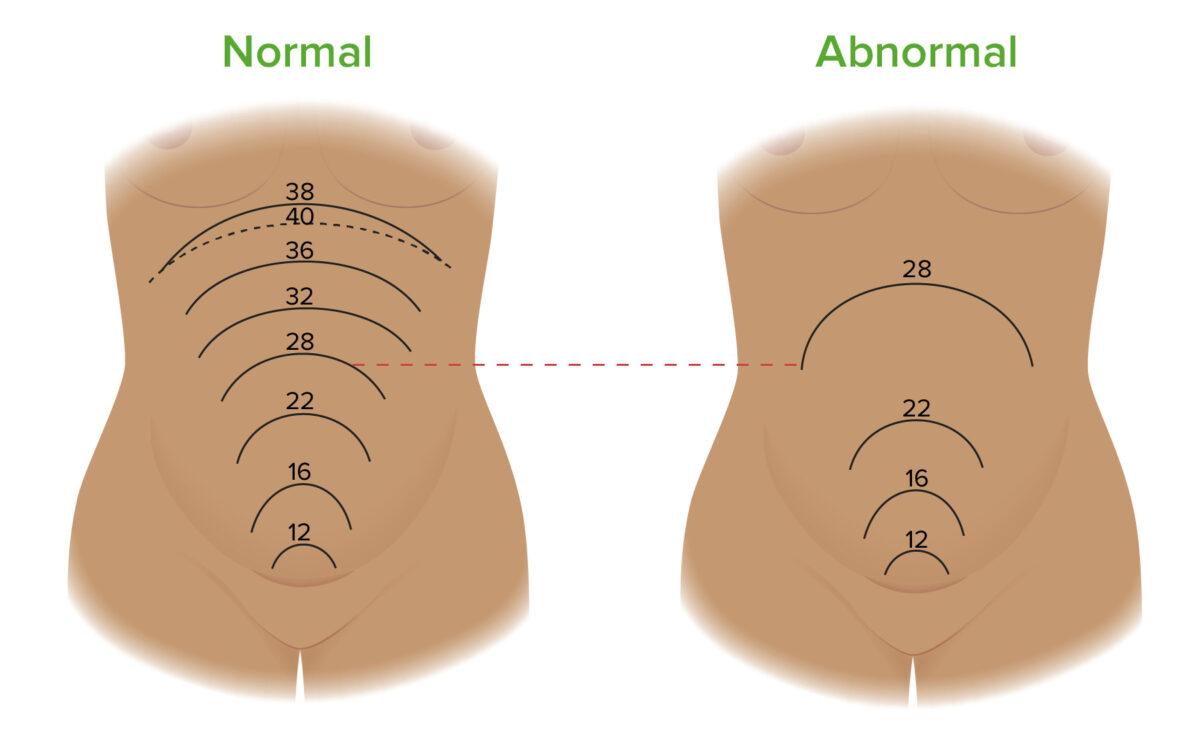
Alturas del fondo uterino a lo largo del embarazo en casos normales (izquierda) y en embarazos complicados por polihidramnios (derecha). La altura uterina es la longitud entre la sínfisis del pubis y la parte superior del fondo uterino. La altura uterina medida en centímetros debe ser aproximadamente igual a la edad gestacional del feto en semanas. Por ejemplo, a las 28 semanas, la altura uterina debe medir ~ 28 cm. Una discrepancia de > 3 cm es sospechosa de polihidramnios. La imagen de la izquierda muestra dónde se encuentra el fondo del útero a diferentes edades gestacionales a lo largo de un embarazo normal. La imagen de la derecha muestra la posible progresión del crecimiento del fondo uterino en un embarazo complicado por polihidramnios. Obsérvese cómo la altura uterina a las 28 semanas es significativamente mayor en el embarazo complicado por polihidramnios en comparación con un embarazo normal.
Imagen por Lecturio.Otras pruebas diagnósticas
| Clasificación de polihidramnios | Índice de líquido amniótico | Bolsillo vertical máximo |
|---|---|---|
| Leve | 24–29,9 cm | 8–11,9 cm |
| Moderado | 30–34,9 cm | 12–15,9 cm |
| Severo | ≥ 35 cm | ≥ 16 cm |
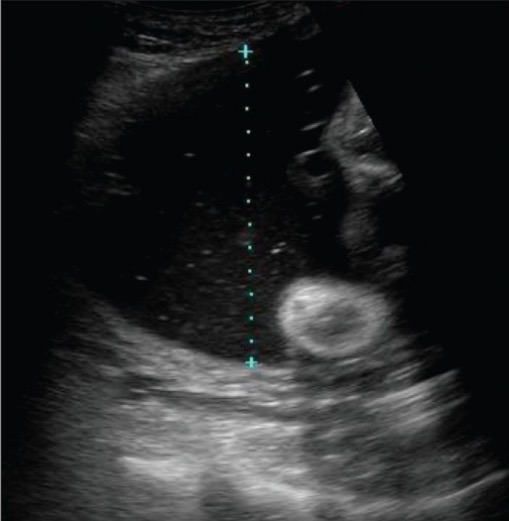
La foto muestra la medición de un bolsillo vertical de líquido amniótico, que se utiliza en la evaluación del volumen de líquido amniótico. Si este fuera el bolsillo de líquido más profundo presente, se conocería como bolsillo vertical máximo; los valores ≥ 8 cm se clasifican como polihidramnios.
Imagen: “Demonstration of the technique to measure a single vertical pocket of liquor” por Kinare A. Licencia: CC BY 2.0