La osteocondritis disecante es un trastorno ortopédico caracterizado por el desprendimiento de un segmento focal de hueso y cartílago subcondral como resultado de una necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage aséptica focal. Esto puede ocurrir a cualquier edad, pero se observa con mayor frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum adolescentes que participan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum deportes competitivos. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes pueden estar asintomáticos o pueden presentar dolor Dolor Inflammation en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las articulaciones, rigidez e inflamación que empeora con la actividad. El diagnóstico se puede hacer con imágenes. El tratamiento depende de la gravedad, pero puede incluir actividad restringida con carga de peso, fisioterapia o cirugía.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La osteocondritis disecante es un trastorno caracterizado por necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage aséptica del hueso subcondral que provoca un desprendimiento focal y el desplazamiento del hueso y el cartílago hacia el espacio articular. El término osteocondritis es un nombre inapropiado, ya que el análisis histológico revela una falta de células inflamatorias.
Se desconoce la etiología exacta. Se han propuesto muchas teorías y es probable que la osteocondritis disecante sea multifactorial.
Patogenia de la osteocondritis disecante:
Etapas de progresión en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la osteocondritis disecante:
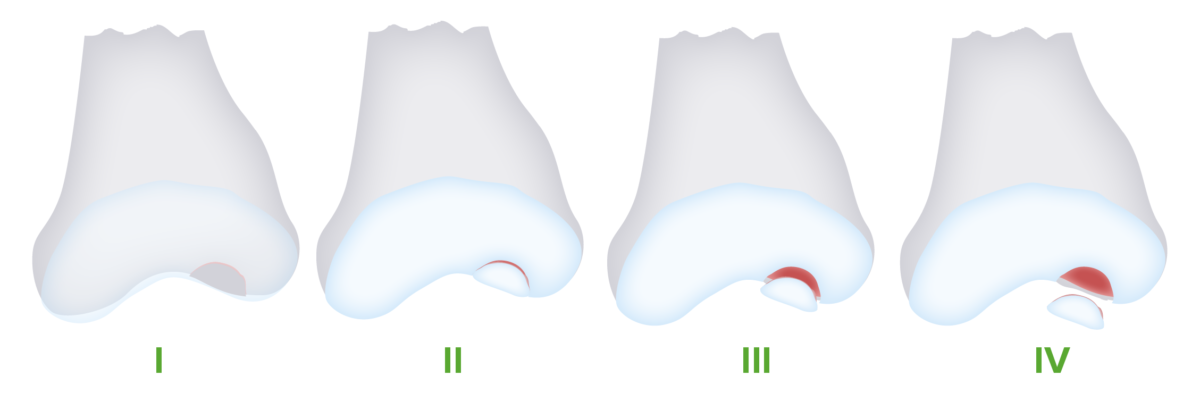
La osteocondritis disecante progresa a través de 4 etapas. Con la lesión continua, la lesión se fragmenta y se separa del hueso subyacente, y eventualmente se desplaza en el espacio articular (cuerpo suelto).
Imagen por Lecturio.Algunos pacientes pueden estar asintomáticos y la osteocondritis disecante se encuentra incidentalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la imagenología. Sin embargo, las personas sintomáticas pueden experimentar:
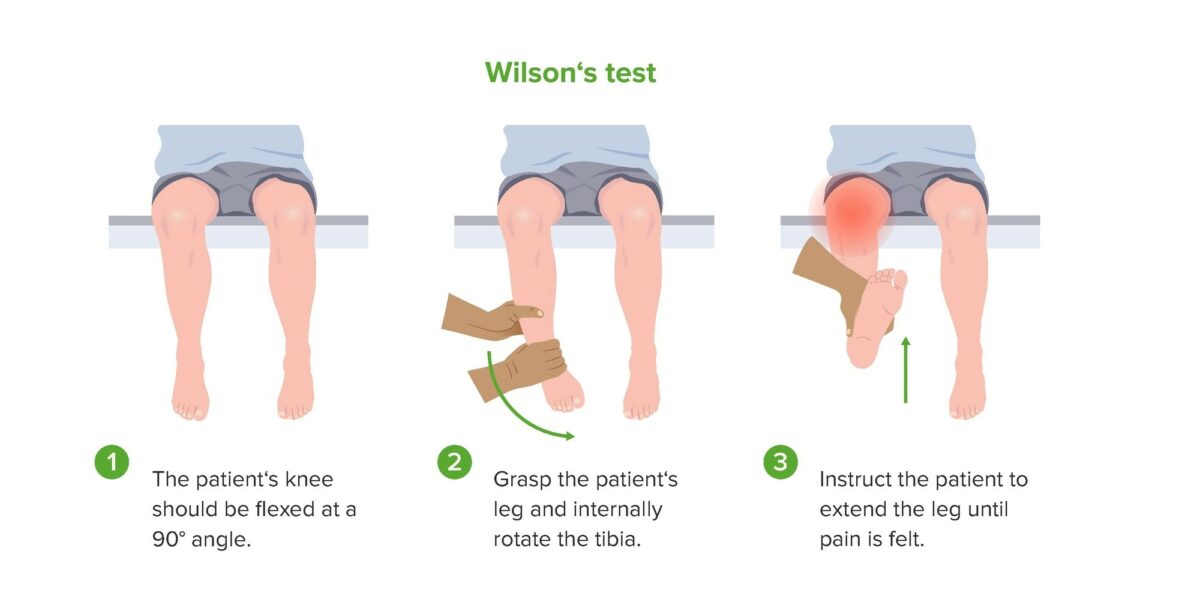
Demostración de la prueba de Wilson, que puede ser positiva en pacientes con osteocondritis disecante de rodilla.
Imagen por Lecturio.Se debe sospechar un diagnóstico de osteocondritis disecante en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum adolescentes con una presentación característica de dolor Dolor Inflammation articular y participación en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum actividades repetitivas y deportivas.
Las radiografías de la articulación afectada suelen ser diagnósticas y son el método de prueba inicial de elección. Sin embargo, estas imágenes pueden ser normales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las primeras etapas de la enfermedad.
Rodilla:
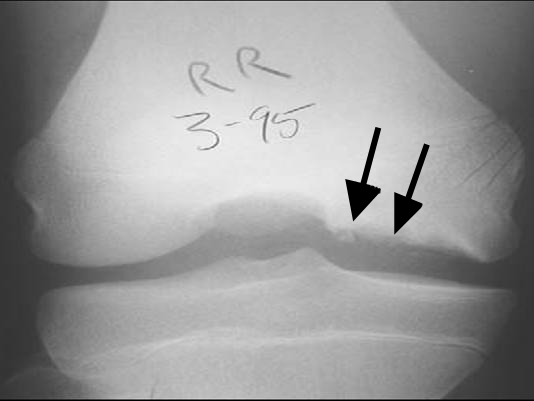
Radiografía de rodilla de un paciente con osteocondritis disecante:
Obsérvese la fragmentación del hueso y la radiotransparencia debajo (flechas).
Codo:
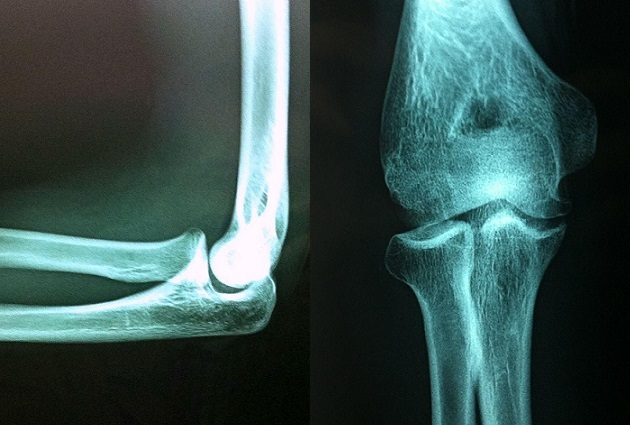
Imágenes de rayos X de un atleta de 16 años con osteocondritis disecante del codo.
Se muestra un foco radiolúcido del capitellum sobre la cabeza radial.
Tobillo:

Imágenes de rayos X de un tobillo que muestran osteocondritis disecante del astrágalo superomedial.
Obsérvese la radiotransparencia y la fragmentación (flechas).
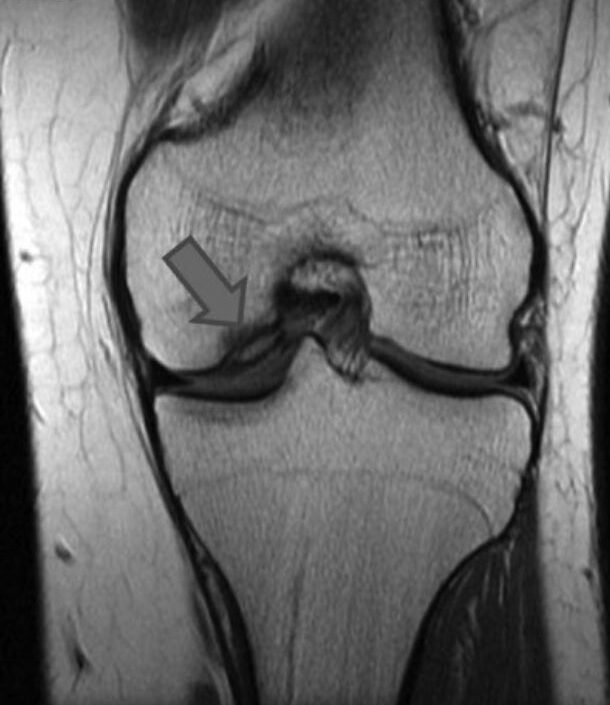
RM de una rodilla que muestra un área de osteocondritis disecante que afecta el cóndilo femoral medial
Imagen: “The present state of treatments for articular cartilage defects in the knee” por Perera JR, Gikas PD, Bentley G. Licencia: CC BY 3.0 , recortada por Lecturio.El objetivo principal del tratamiento es lograr la curación de la lesión osteocondral y devolver la función completa a la articulación afectada. Es posible que se necesiten referir para las especialidades de medicina deportiva o cirugía ortopédica.