Mycobacterium Mycobacterium Mycobacterium is a genus of the family Mycobacteriaceae in the phylum Actinobacteria. Mycobacteria comprise more than 150 species of facultative intracellular bacilli that are mostly obligate aerobes. Mycobacteria are responsible for multiple human infections including serious diseases, such as tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis), leprosy (M. leprae), and M. avium complex infections. Mycobacterium es un género de la familia Mycobacteriaceae Mycobacteriaceae A family of gram-positive bacteria found in soil and dairy products and as parasites on animals and man. Several are important pathogens. Mycobacterium en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el filo Actinobacteria Actinobacteria Class of bacteria with diverse morphological properties. Strains of actinobacteria show greater than 80% 16s rDNA/rRNA sequence similarity among each other and also the presence of certain signature nucleotides. Mycobacterium. Las micobacterias comprenden más de 150 especies de bacilos intracelulares facultativos que en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum su mayoría son aerobios obligados. Las micobacterias son responsables de múltiples infecciones humanas, incluidas enfermedades graves, como la tuberculosis Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis), la lepra (M. leprae) y las infecciones por el complejo M. avium. Si bien los LOS Neisseria pulmones son el sitio más común de infección, las micobacterias pueden colonizar e infectar otros sistemas, incluyendo ganglios linfáticos, piel, senos paranasales, ojos, oídos, huesos, SNC y tracto urinario.
Last updated: Jan 20, 2026
Morfología y propiedades:
Propiedades de tinción:
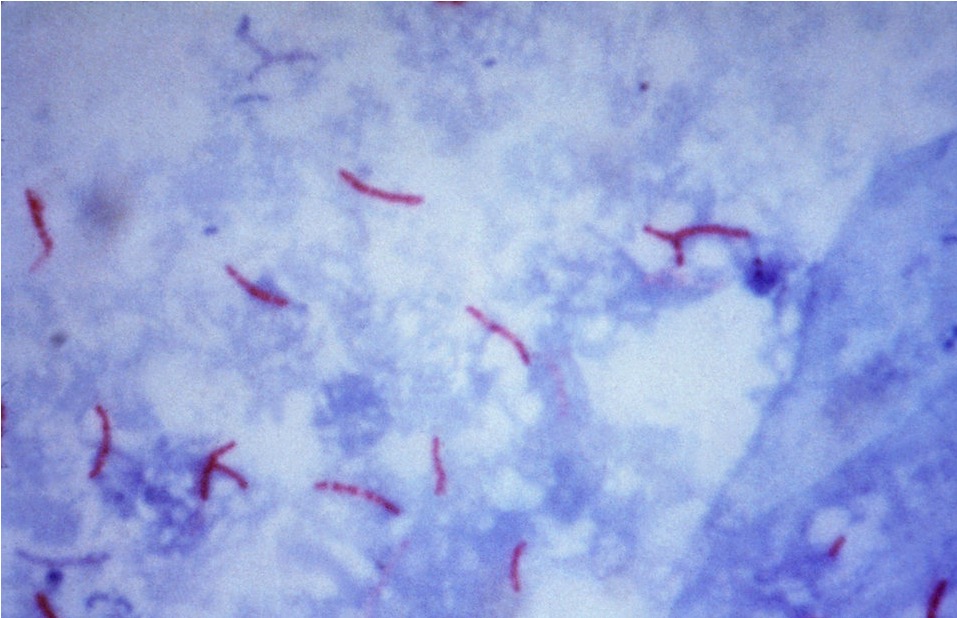
Tinción ácido-alcohol resistente de Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Imagen: “Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria” por CDC/Dr. George P. Kubica. Licencia: Dominio Público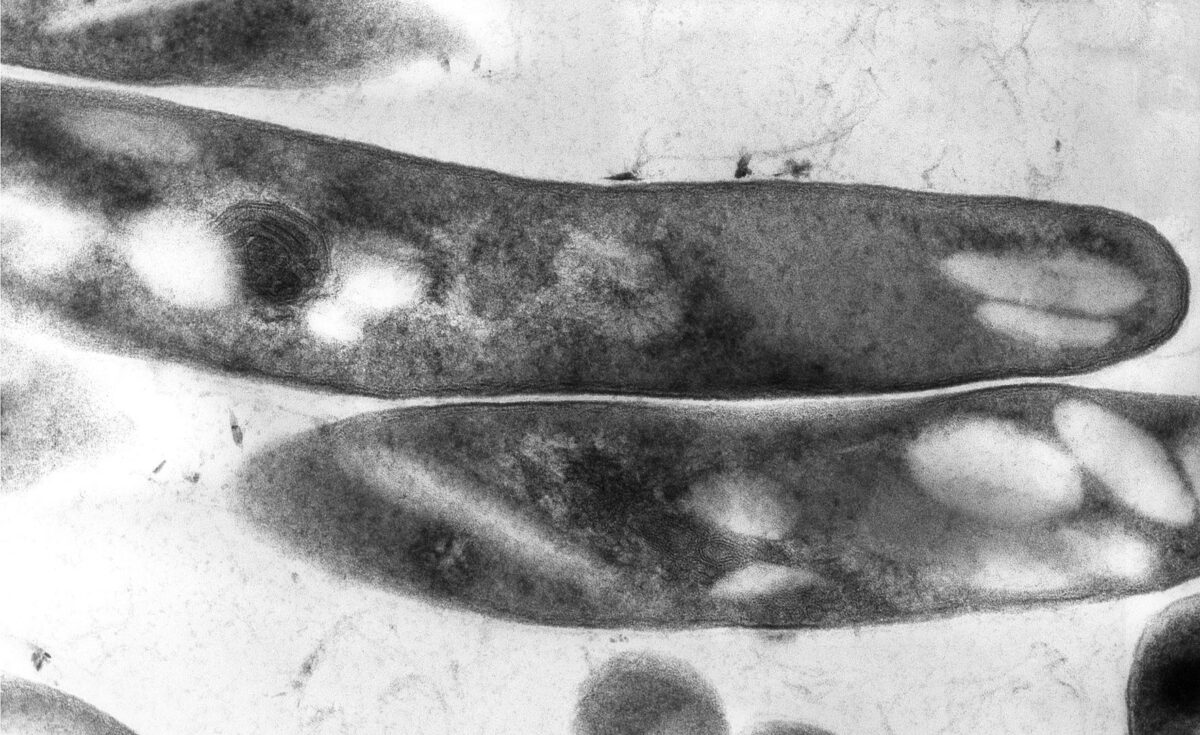
Micrografía electrónica de Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Imagen: “Mycobacterium tuberculosis 01” por Elizabeth White. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoMicobacterias:
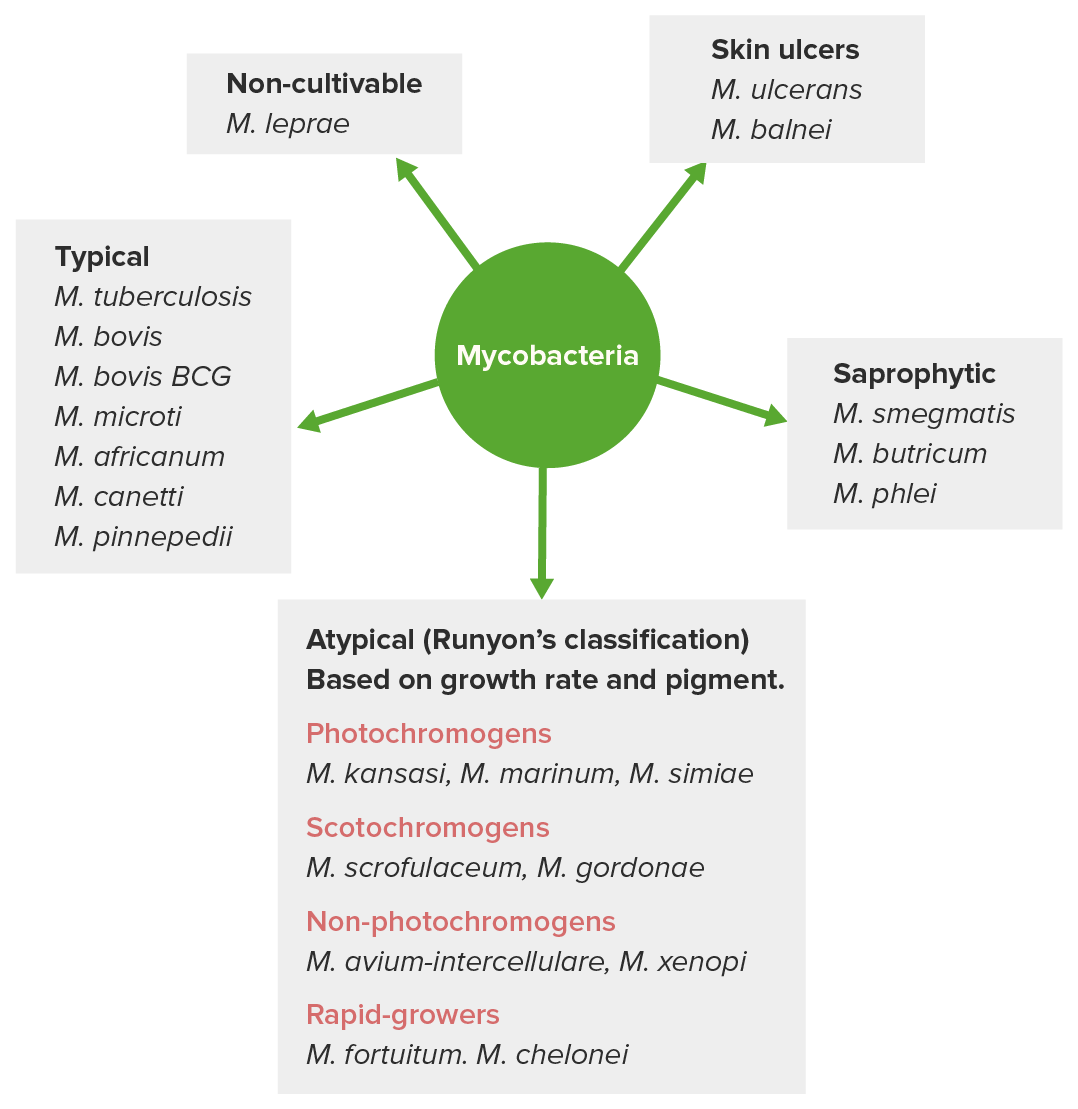
Clasificación de las micobacterias
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Especies patógenas más importantes:
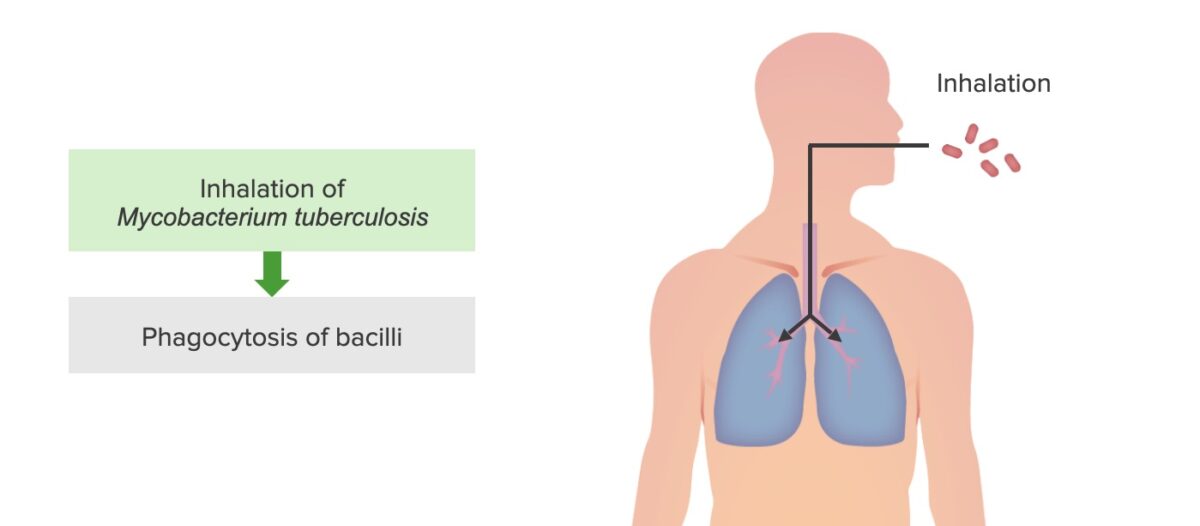
Infección por tuberculosis, paso 1: Inhalación de M. tuberculosis y fagocitosis por macrófagos alveolares
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0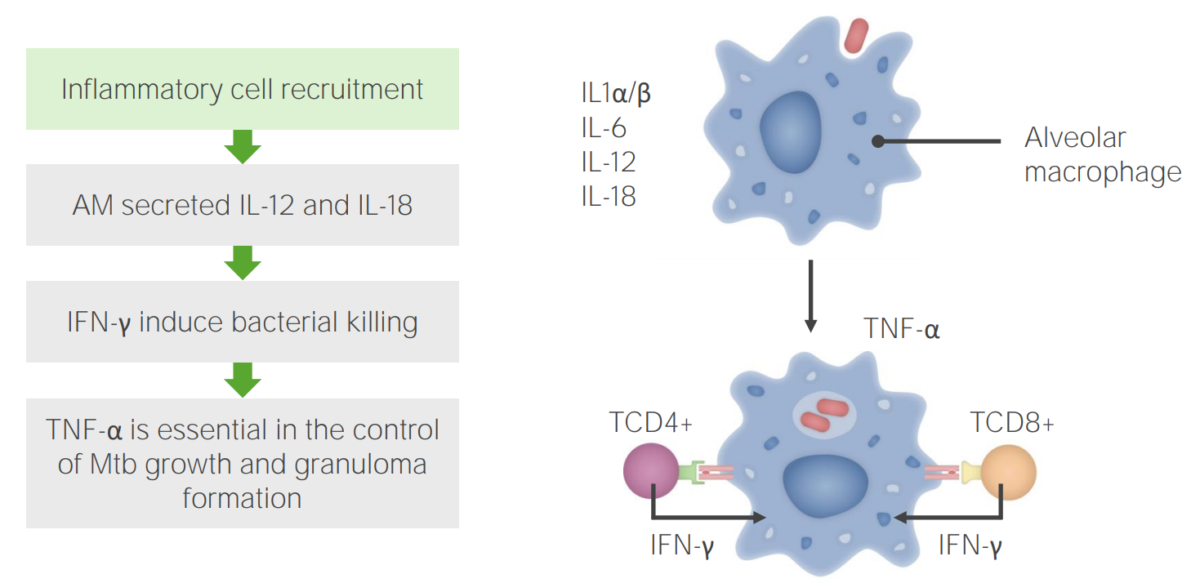
Infección por tuberculosis, paso 2: Reclutamiento de células inflamatorias
AM: macrófagos alveolares (en inglés)
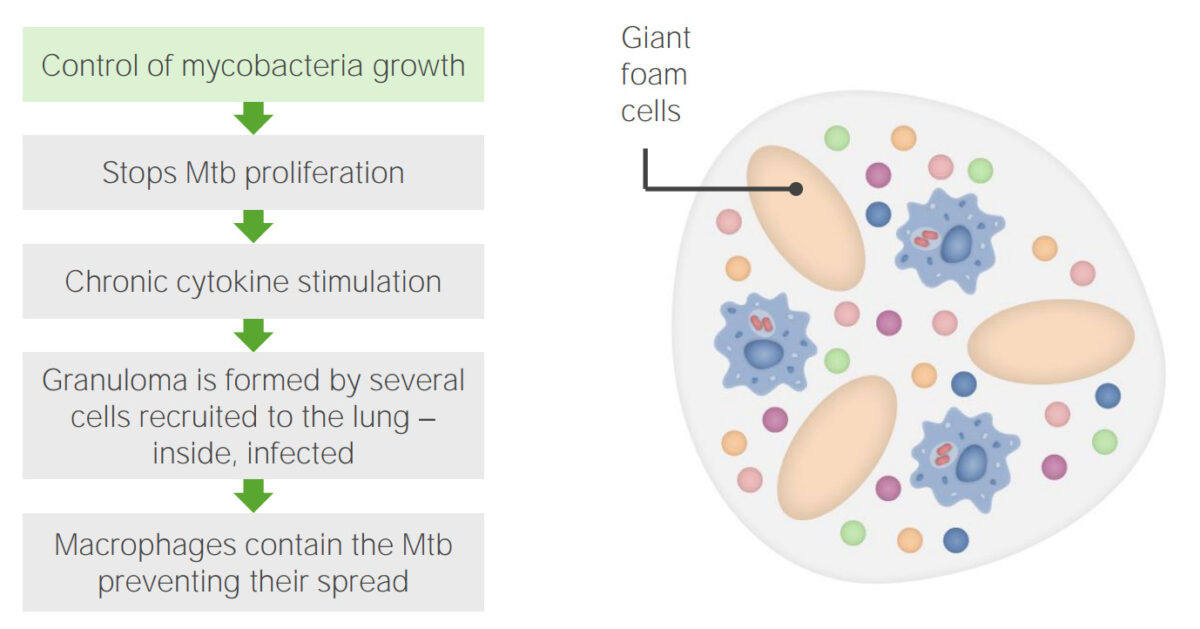
Infección por tuberculosis, paso 3: Formación de granulomas
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0| TB TB Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis primaria | TB TB Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis secundaria | TB TB Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis extrapulmonar (miliar) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Presentación | Dentro de los LOS Neisseria 2 años de la infección, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 5%–10% de los LOS Neisseria casos | Reactivación de la infección en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes inmunocomprometidos | Individuos inmunocomprometidos |
| Localización |
|
|
|
| Síntomas |
|
Recurrencia de síntomas |
|
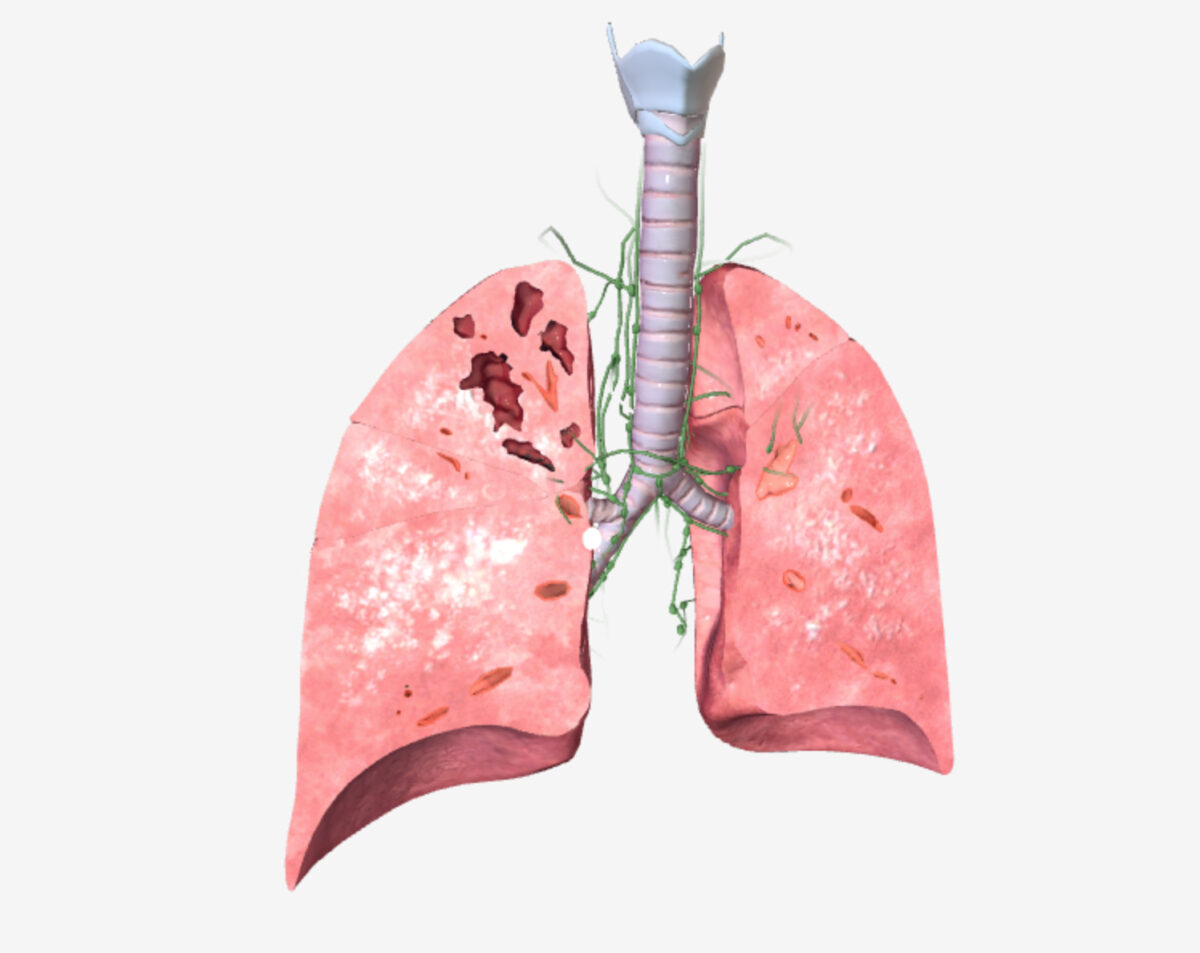
Tuberculosis pulmonar (TB): manifestaciones primarias y secundarias de la enfermedad
Imagen por BioDigital, editada por Lecturio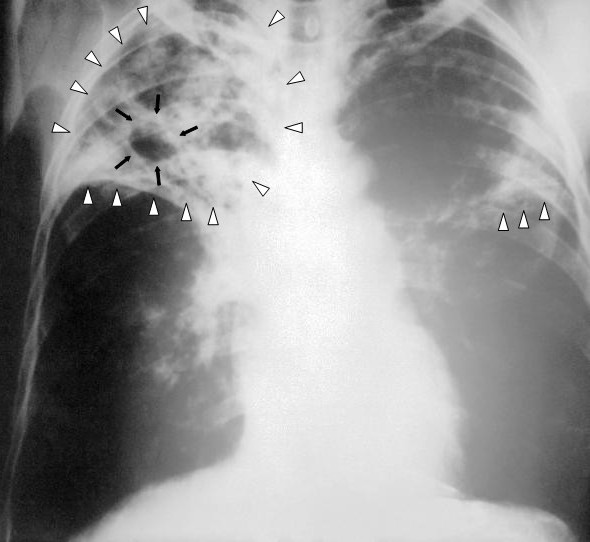
Radiografía de un paciente con tuberculosis:
Radiografía de tórax de infiltrados reticulares bilaterales (triángulos blancos) y lesión cavitaria (flechas negras) en lóbulo superior derecho
Esputo:
Cultivo de micobacterias en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum sangre u orina: en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes con VIH o inmunocomprometidos
Prueba cutánea de la tuberculina (PPD (derivado de proteína purificada) o prueba de Mantoux):
Ensayo de liberación de interferón-γ: sin distinción entre TB TB Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis activa e inactiva

Respuesta inmunitaria a la lepra
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0| Tuberculoide | Lepromatosa | |
|---|---|---|
| Presentación | Individuos inmunocompetentes | Individuos inmunodeprimidos |
| Localización | Piel y nervios | Piel y nervios |
| Síntomas |
|
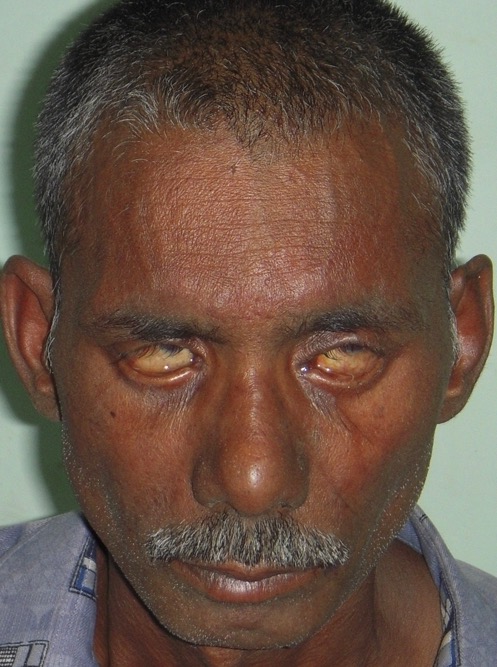
Lagoftalmos en un paciente con lepra lepromatosa:
El paciente intenta cerrar los párpados, pero no puede hacerlo.
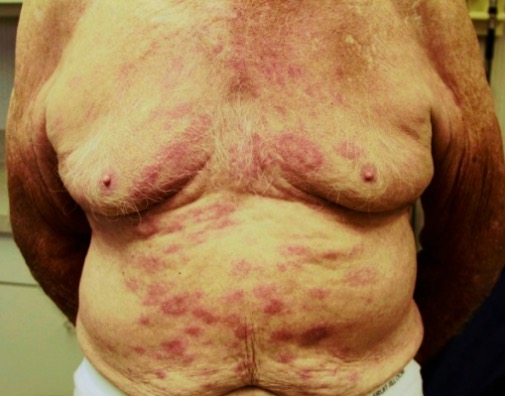
Lepra:
Manchas eritematosas en la piel
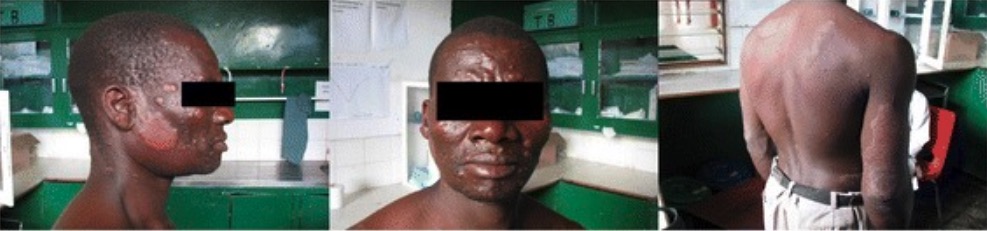
Lesiones cutáneas generalizadas compatibles con lepra lepromatosa:
El paciente comienza a desarrollar facies leonina, con gran cantidad de pápulas y nódulos que afectan la cara, el tórax, la espalda, las piernas y la ingle. Aparecen grandes placas bien delimitadas en la cara del tríceps del brazo derecho y sobre el hombro izquierdo y el flanco derecho.
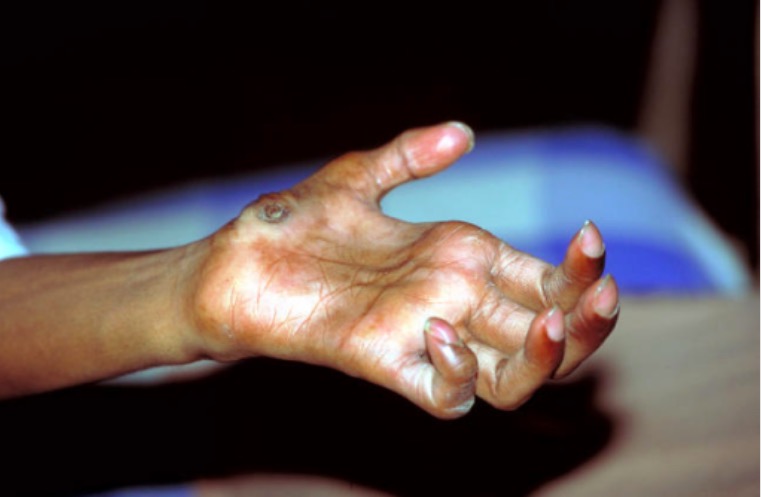
Dedos en garra:
Deformidad típica en un paciente con lepra avanzada
El organismo se identifica mediante biopsia de piel:
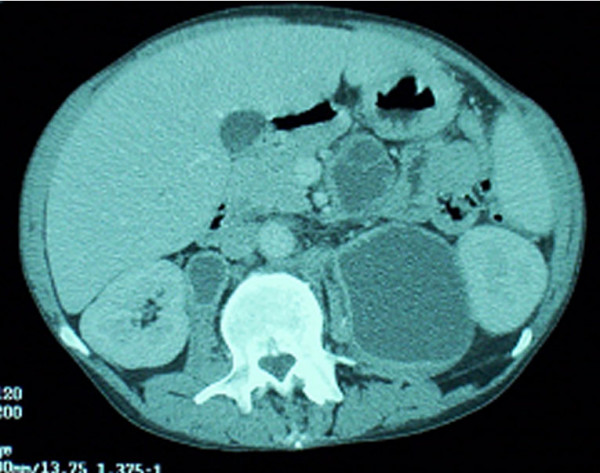
Infección por el complejo M. avium: TC abdominal que muestra múltiples ganglios linfáticos intraabdominales con abscesos
Imagen: “Mycobacterium avium complex immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome: long term outcomes” por Riddell J, Kaul DR, Karakousis PC, Gallant JE, Mitty J, Kazanjian PH. Licencia: CC BY 2.0