El etanol es un compuesto químico que se produce en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pequeñas cantidades en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el intestino delgado y también se ingiere a partir de bebidas alcohólicas. La digestión del etanol implica una vía catabólica compleja que tiene lugar principalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el hígado. El etanol se convierte en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum acetaldehído, luego en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum acetato y finalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum acetil-CoA, que se convierte en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un sustrato para el ciclo del ácido cítrico y finalmente producir energía. El consumo excesivo de etanol puede tener consecuencias metabólicas patológicas, como alcoholismo, enfermedad hepática y cáncer.
Last updated: Apr 17, 2025
Estructura de la molécula de etanol
Imagen por Lecturio.El sitio principal del catabolismo del alcohol es el hígado.
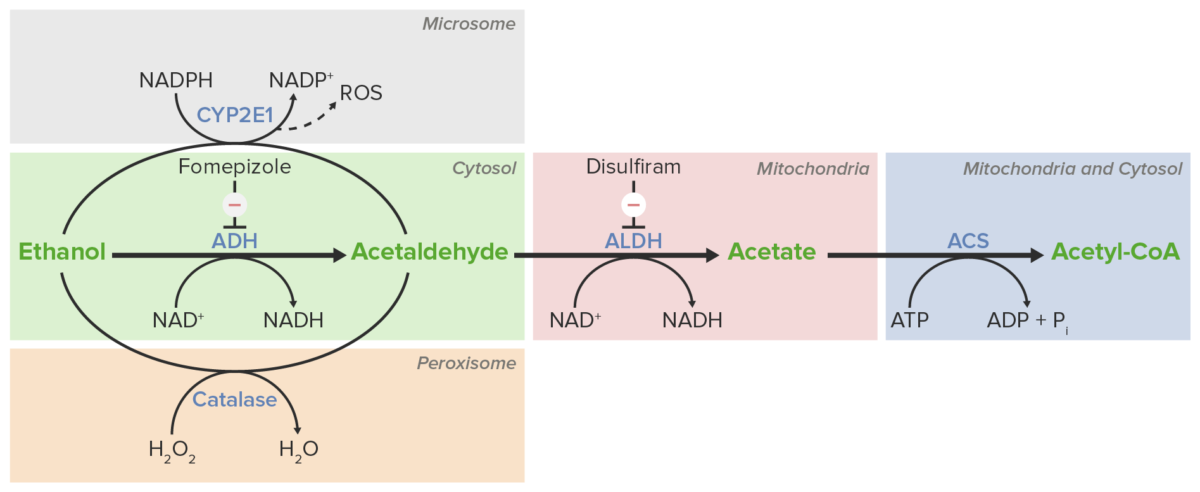
Diagrama esquemático de los pasos del metabolismo del etanol.
Imagen por Lecturio.Muchos medicamentos comunes pueden inhibir las enzimas involucradas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el metabolismo del etanol, lo que lleva a la acumulación de sus productos tóxicos (e.g., acetaldehído):
| Medicamento | Enzima inhibida | Efectos |
|---|---|---|
| Fomepizol | Alcohol deshidrogenasa (ADH) |
|
| Disulfiram | Acetaldehído deshidrogenasa (ALDH) | Causa acumulación de acetaldehído → síntomas de resaca
|
|
|
El consumo excesivo de etanol, como en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el trastorno por consumo de alcohol, conduce a la saturación de la vía metabólica del etanol y la consiguiente acumulación de metabolitos tóxicos, así como a la alteración de otras vías metabólicas.
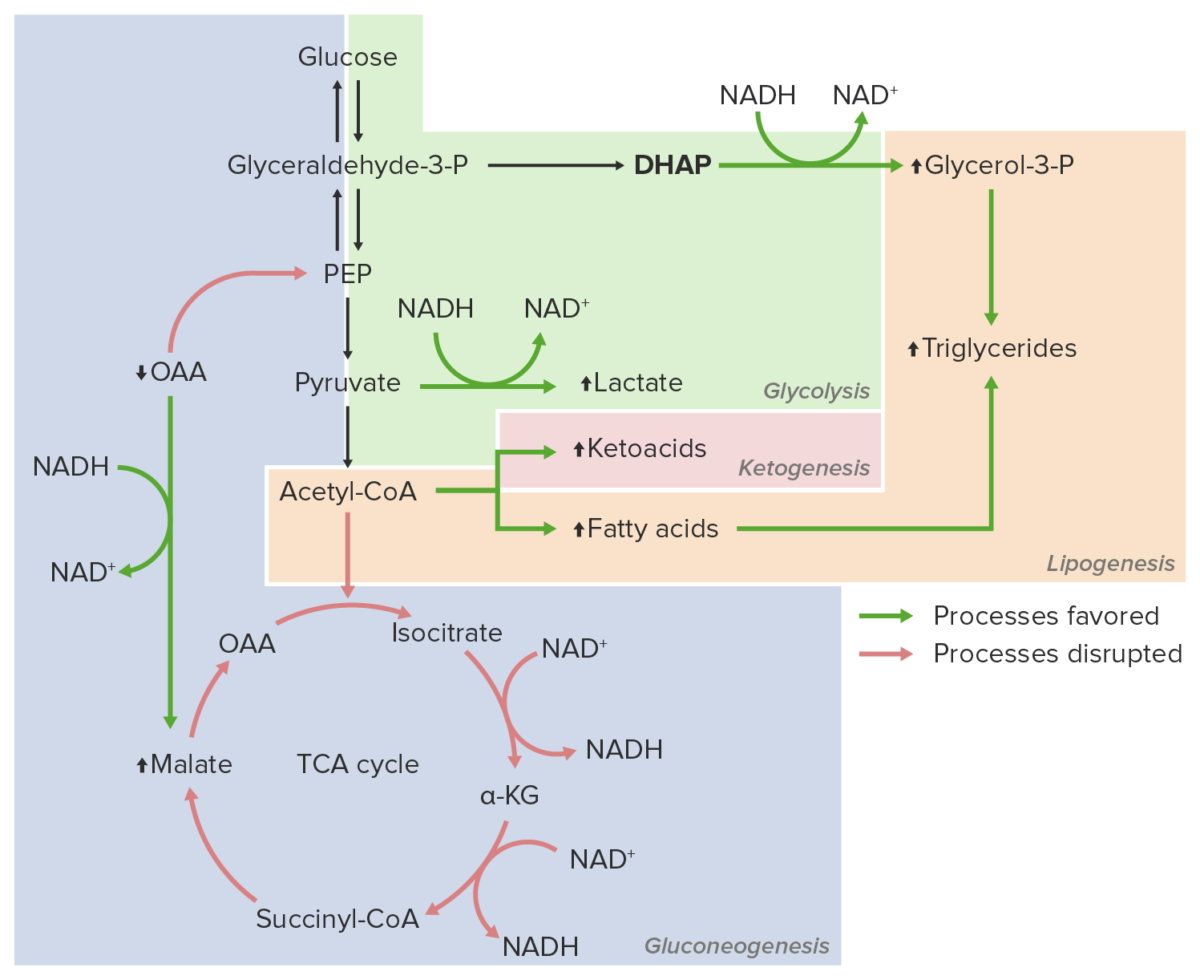
Consumo excesivo de etanol
Imagen por Lecturio.Las siguientes condiciones clínicas están asociadas con el consumo excesivo de etanol: