La leucemia mieloide crónica es una proliferación maligna de la línea celular granulocítica caracterizada por una diferenciación bastante normal. La anomalía genética subyacente es el cromosoma Filadelfia, un cromosoma 22 abreviado, que resulta de una translocación recíproca (9;22)(q34;q11). El cromosoma contiene el gen de fusión BCR-ABL1 (de ABL1 en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cromosoma 9 y BCR BCR Lymphocytes: Histology en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cromosoma 22), que induce la activación constitutiva de la tirosina quinasa y, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum consecuencia, la producción descontrolada de granulocitos. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes con leucemia mieloide crónica pueden ser asintomáticos o tener síntomas constitucionales, dolor Dolor Inflammation esternal y esplenomegalia. Los LOS Neisseria estudios de laboratorio muestran leucocitosis y un frotis de sangre periférica muestra un mayor número de células inmaduras. La demostración de la translocación Filadelfia utilizando técnicas citogenéticas se considera el estándar de oro de las pruebas diagnósticas. Sin tratamiento, la leucemia mieloide crónica generalmente tiene un curso trifásico que progresa de una fase crónica a una fase acelerada y conduce a una crisis blástica terminal. El tratamiento incluye terapia con inhibidores de la tirosina quinasa y agentes paliativos, así como trasplante alogénico de células hematopoyéticas.
Last updated: Apr 14, 2022
La leucemia mieloide crónica es una neoplasia mieloproliferativa crónica caracterizada por una proliferación desregulada y descontrolada del linaje granulocítico (células maduras y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum proceso de maduración), con una capacidad mantenida de diferenciación. La leucemia mieloide crónica también se conoce como leucemia mielocítica crónica o leucemia mielógena crónica.
La hematopoyesis comienza con una célula madre hematopoyética, que se incita a dividirse y diferenciarse con estímulos químicos apropiados (factores de crecimiento hematopoyéticos).
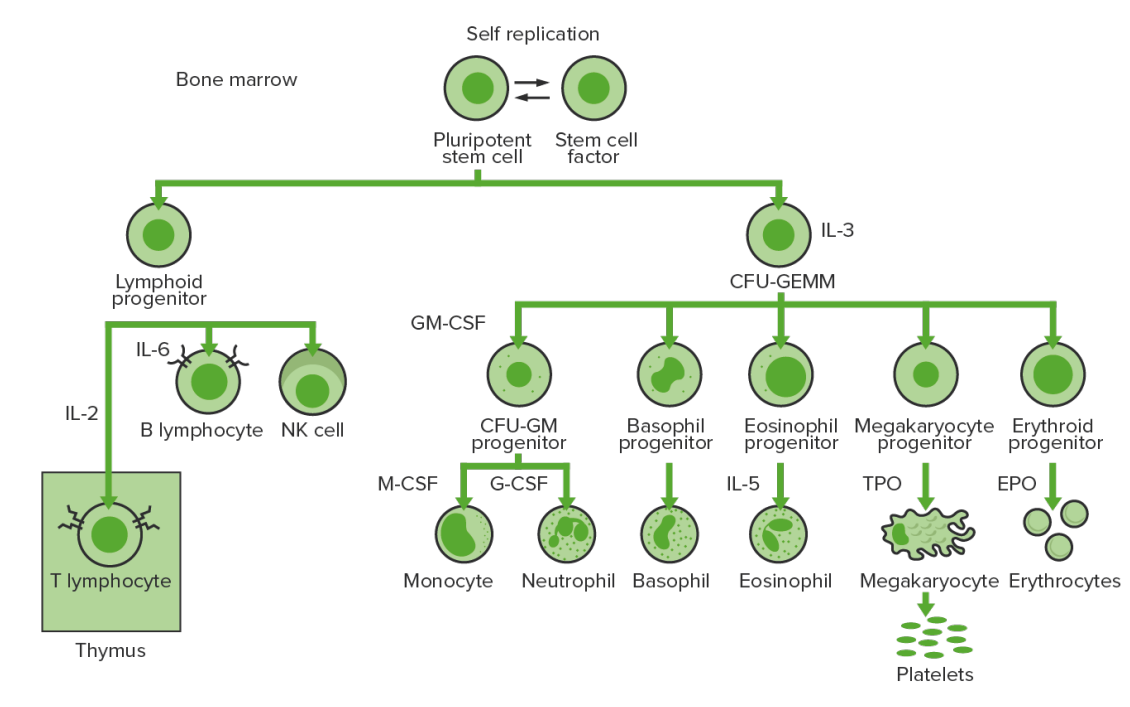
Hematopoyesis de la médula ósea:
Proliferación y diferenciación de los elementos formes de la sangre:
En la leucemia mieloide crónica, existe una proliferación sostenida de células en la línea granulocítica (mieloblastos → neutrófilos, basófilos, eosinófilos). Se observan tanto células maduras como en proceso de maduración; por lo tanto, hay células que son solo parcialmente efectivas.
CFU-GEMM: unidad formadora de colonias: granulocitos, eritrocitos, monocitos, megacariocitos
GM-CSF: factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos y macrófagos
M-CSF: factor estimulante de colonias de macrófagos
G-CSF: factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos
NK: células asesinas naturales
La leucemia mieloide crónica es una anomalía adquirida de las células madre hematopoyéticas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la médula ósea.
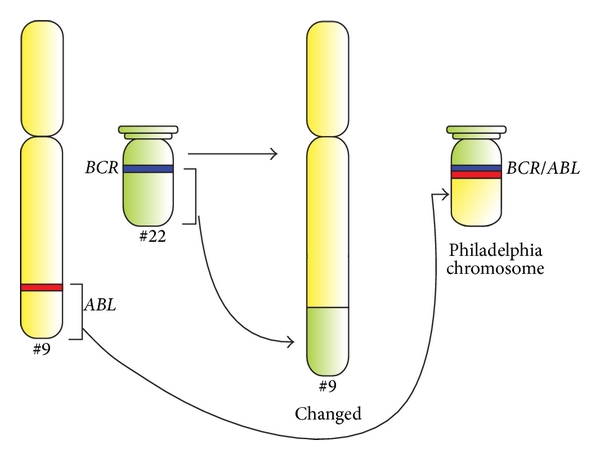
Diagrama esquemático de la translocación que forma el cromosoma Filadelfia y representación esquemática de los genes BCR y ABL.
Los genes ABL1 y BCR residen en los brazos largos de los cromosomas 9 y 22, respectivamente. El gen de fusión BCR-ABL se forma con la translocación del gen ABL1 (del cromosoma 9) al brazo largo del cromosoma 22, creando un cromosoma 22 modificado (el llamado cromosoma Filadelfia).
Los LOS Neisseria síntomas discutidos anteriormente varían en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum severidad dependiendo de las 3 fases de la enfermedad de la leucemia mieloide crónica (basadas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria leucocitos inmaduros o células blásticas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sangre o la médula ósea).
Fase crónica estable:
Fase acelerada:
Crisis blástica (o fase aguda):
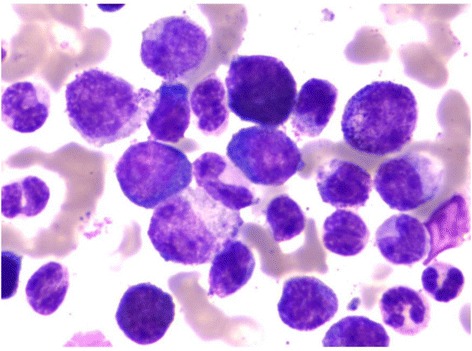
Examen de médula ósea:
Blastos en la médula ósea de un paciente diagnosticado con leucemia mieloide crónica
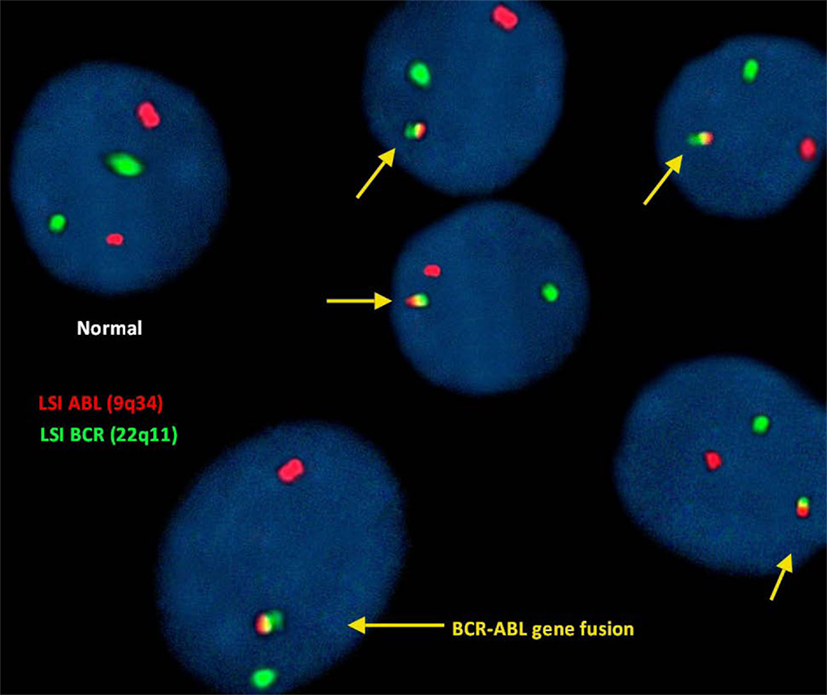
para la detección de (9;22)(q34;q11):
En este estudio, el análisis de hibridación fluorescente in situ del gen ABL (9q34) se identificó como puntos rojos fluorescentes y el gen BCR (22q11) como puntos verdes. Por lo tanto, una celda que presentaba 2 puntos verdes y rojos separados se consideraba una celda normal que no mostraba translocación.
Sin embargo, la translocación irregular en una célula fue identificada por 1 rojo y 1 verde y señales rojas, amarillas y verdes fusionadas (que representan la fusión del gen BCR-ABL).
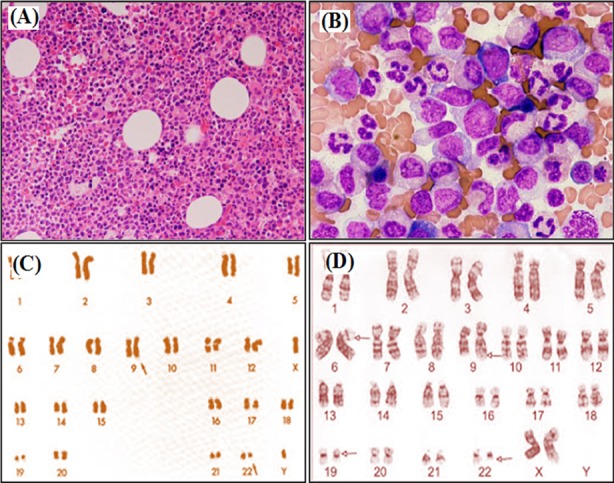
Estudios de médula ósea y cariotipo de leucemia mieloide crónica:
Aspirados de médula ósea que muestran hipercelularidad
A: aumento x100
B: aumento x400
C: análisis de cariotipo del cromosoma Filadelfia estándar (cromosoma 22 alterado)
D: leucemia mieloide crónica con afectación más compleja del cromosoma 6
Las neoplasias mieloproliferativas se pueden comparar con la siguiente clasificación de la World Health Organization (WHO):
| Enfermedad | Mutaciones | Puntos clave |
|---|---|---|
| Leucemia mieloide crónica | BCR-ABL1 (cromosoma Filadelfia) | Proliferación de granulocitos maduros y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum proceso de maduración |
| Trombocitemia esencial | JAK2, CALR o MPL | Producción clonal excesiva de plaquetas |
| Policitemia vera | JAK2 | Elevación de la producción eritrocitaria |
| Mielofibrosis primaria | JAK2, CALR o MPL | Fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans obliterativa de la médula ósea |
Otros tipos:
Fase crónica estable:
Fase acelerada:
Crisis blástica: