La enfermedad venosa crónica es un espectro de trastornos caracterizados por la dilatación venosa y/o la función anormal de las venas en las extremidades inferiores como consecuencia de la hipertensión venosa. La "Insuficiencia venosa crónica" se refiere a las formas más graves de la enfermedad venosa crónica. Los LOS Neisseria cambios cutáneos suelen distinguir la insuficiencia venosa crónica de las formas más leves de enfermedad venosa (como las venas varicosas) e incluyen la pigmentación de la piel, la dermatitis Dermatitis Any inflammation of the skin. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) por estasis, la lipodermatoesclerosis y finalmente, el desarrollo de úlceras. El diagnóstico generalmente se basa únicamente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria hallazgos de la exploración física, aunque el ultrasonido doppler Doppler Ultrasonography applying the doppler effect, with frequency-shifted ultrasound reflections produced by moving targets (usually red blood cells) in the bloodstream along the ultrasound axis in direct proportion to the velocity of movement of the targets, to determine both direction and velocity of blood flow. Ultrasound (Sonography) venoso puede proporcionar información adicional sobre la etiología, la localización y la extensión de la enfermedad. El pilar del tratamiento es la terapia de compresión. La base del tratamiento es la terapia de compresión. También existen diversas opciones quirúrgicas para los LOS Neisseria pacientes sintomáticos, como la ablación, la escleroterapia y la reparación valvular.
Last updated: Jan 21, 2023
La enfermedad venosa crónica es un espectro de trastornos caracterizados por la dilatación venosa y/o la función anormal de las venas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las extremidades inferiores como consecuencia de la hipertensión venosa.
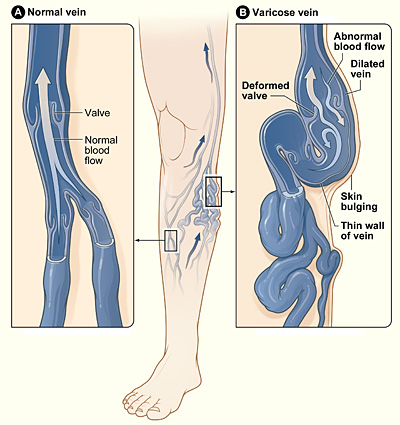
Venas varicosas
Imagen: “Varicose veins” por el National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. Licencia: Dominio Público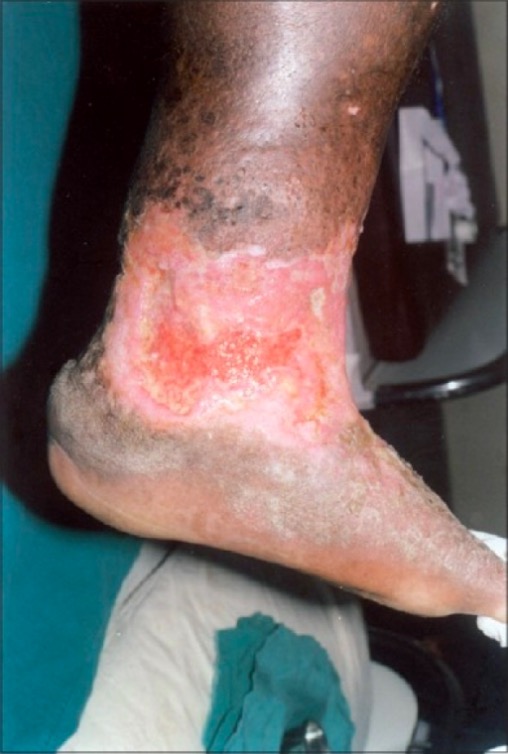
Úlcera por estasis venosa, irregular, en la parte inferior de la pierna y el tobillo, con tejido de granulación poco saludable que no cicatriza:
También hay lipodermatoesclerosis circundante, dermatitis por estasis y pigmentación marrón de la piel, todo ello característico de la insuficiencia venosa crónica.
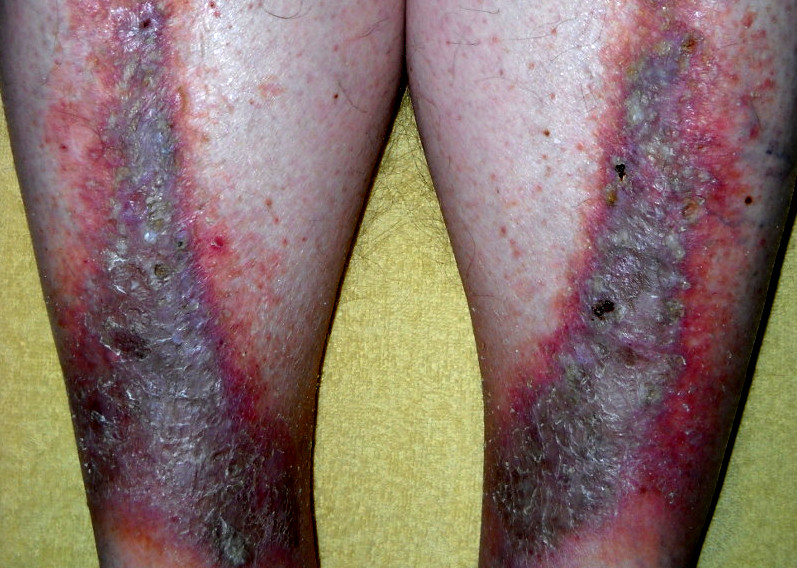
Dermatitis por estasis
Imagen: “Stasis dermatitis” por Cardiologist61. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoAspecto de las extremidades inferiores:
Tiempo de llenado venoso:
Índice tobillo-brazo:
Ultrasonido doppler Doppler Ultrasonography applying the doppler effect, with frequency-shifted ultrasound reflections produced by moving targets (usually red blood cells) in the bloodstream along the ultrasound axis in direct proportion to the velocity of movement of the targets, to determine both direction and velocity of blood flow. Ultrasound (Sonography):
Venografía transversal con TC o RM:
Venografía con catéter (invasiva):
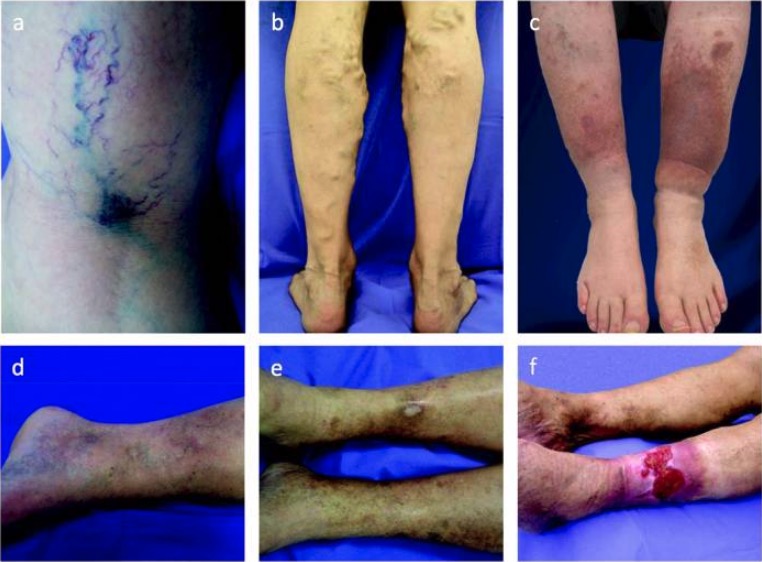
Espectro de enfermedad venosa crónica:
La extensión de la enfermedad puede clasificarse de C1 a C6 basándose en las siguientes manifestaciones:
a: telangiectasias y venas reticulares (C1)
b: venas varicosas (C2)
c: edema y pigmentación de la piel (C4)
d: lipodermatoesclerosis (C4)
e: úlcera cicatrizada (C5)
f: úlcera venosa activa (C6)
Objetivos:
Las alternativas incluyen: