La insuficiencia ovárica primaria es una afección resultante del agotamiento o la disfunción de los LOS Neisseria folículos ováricos, que conduce al AL Amyloidosis cese de la ovulación y la menstruación antes de los LOS Neisseria 40 años. La insuficiencia ovárica primaria es principalmente idiopática, pero también puede verse asociada a anomalías cromosómicas y genéticas, como el síndrome de Turner (cariotipo 45,X) y la mutación FMR1. Las pacientes presentan signos y síntomas de menopausia antes de los LOS Neisseria 40 años, incluyendo oligomenorrea o amenorrea, sequedad vaginal (a menudo con dispareunia) e infertilidad. Los LOS Neisseria principales hallazgos de laboratorio son la elevación de la hormona estimulante del folículo ( FSH FSH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates gametogenesis and the supporting cells such as the ovarian granulosa cells, the testicular sertoli cells, and leydig cells. Fsh consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle) y los LOS Neisseria niveles bajos de estrógeno. Una vez realizado el diagnóstico de insuficiencia ovárica primaria, el paciente debe realizarse un tamizaje de anticuerpos suprarrenales autoinmunes, un cariotipo, un tamizaje de mutación de FMR1 y una densitometría ósea basal. El tratamiento incluye la terapia de reemplazo hormonal, el tratamiento de los LOS Neisseria problemas de fertilidad según se desee, y el apoyo psicológico.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La insuficiencia ovárica primaria es el agotamiento o la disfunción de los LOS Neisseria folículos ováricos que provoca el cese de la ovulación y la menstruación. El trastorno se acompaña de niveles elevados de FSH FSH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates gametogenesis and the supporting cells such as the ovarian granulosa cells, the testicular sertoli cells, and leydig cells. Fsh consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle antes de los LOS Neisseria 40 años.
Hipotálamo:
La pituitaria:
Ovario:
Importancia clínica del funcionamiento del eje hipotálamo-hipófisis-ovario en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum mujeres jóvenes:
La insuficiencia ovárica primaria puede estar causada por anomalías cromosómicas y genéticas, por un proceso autoinmune o por toxinas ováricas. Sin embargo, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la gran mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos, nunca se identifica una causa clara.
Las molestias primarias que se presentan suelen ser oligomenorrea o amenorrea (ya sea primaria o secundaria). Siempre hay que excluir primero el embarazo, incluso en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las pacientes que niegan haber tenido relaciones sexuales.
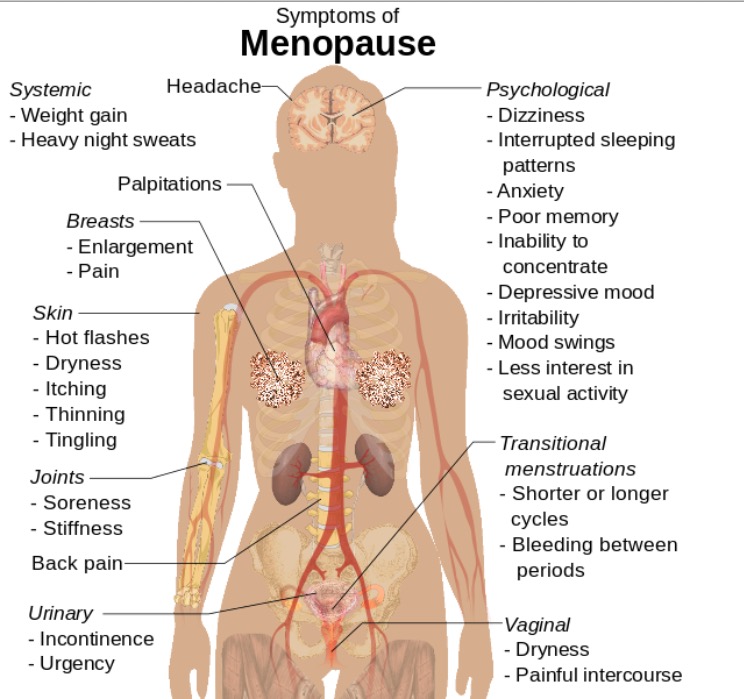
Síntomas de la menopausia que también pueden observarse en la insuficiencia ovárica primaria
Imagen: “Symptoms of menopause” por Mikael Häggström. Licencia: CC0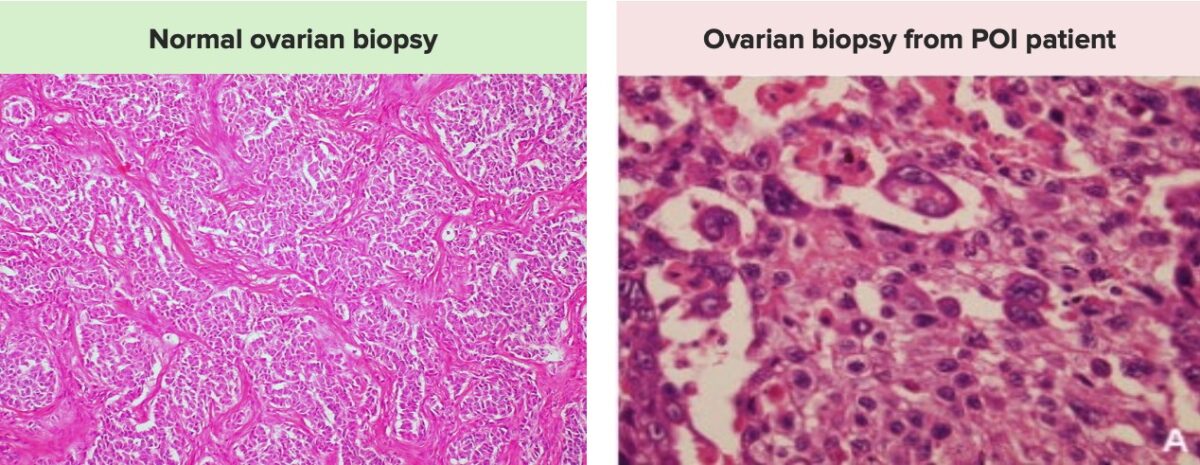
Imágenes que demuestran las diferencias entre una biopsia ovárica normal, a la izquierda, con un número normal de folículos, y una biopsia ovárica de una paciente con insuficiencia ovárica primaria, a la derecha, que muestra un número significativamente reducido de folículos ováricos y ovocitos.
Tenga en cuenta que las biopsias de ovario no suelen obtenerse con fines diagnósticos.
La terapia de reemplazo hormonal es necesaria para prevenir la osteoporosis Osteoporosis Osteoporosis refers to a decrease in bone mass and density leading to an increased number of fractures. There are 2 forms of osteoporosis: primary, which is commonly postmenopausal or senile; and secondary, which is a manifestation of immobilization, underlying medical disorders, or long-term use of certain medications. Osteoporosis y las enfermedades cardiovasculares. Los LOS Neisseria regímenes deben incluir tanto estrógenos como progestágenos.