La inmunidad adaptativa humoral es una parte integral del sistema inmunitario adaptativo, que monta una defensa muy específica contra los LOS Neisseria patógenos pero tarda más tiempo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum responder ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum comparación con el sistema inmunitario innato). La inmunidad humoral es el brazo del sistema inmunitario que protege los LOS Neisseria fluidos extracelulares de los LOS Neisseria linfáticos (linfa), el intersticio y el sistema circulatorio ( plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products) de la contaminación microbiana mediada por moléculas solubles. Las células B juegan un papel importante, produciendo anticuerpos o inmunoglobulinas. Surgidos de la médula ósea, los LOS Neisseria linfocitos B se originan a partir del progenitor linfoide común y pasan por etapas para ensamblar el receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors de linfocitos B. Para volverse completamente funcional, sigue la activación, y esto puede ser dependiente de células T (que produce células de memoria) o independiente de células T (que produce una respuesta de corta duración). Cuando se activan, las células B pasan por procesos que mejoran la afinidad por el antígeno, el cambio de clase y la diferenciación a células plasmáticas y células de memoria. Las células plasmáticas producen los LOS Neisseria anticuerpos, mientras que las células B de memoria responden a la reinfección. Existen diferentes isotipos de inmunoglobulinas, generalmente proporcionando protección inmunológica a través de la activación del complemento, opsonización, neutralización de toxinas o virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology e inducción de lisis celular.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El sistema inmunitario proporciona defensa (inmunidad) contra patógenos invasores que van desde virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology hasta parásitos. Los LOS Neisseria componentes del sistema están interconectados por la circulación sanguínea y linfática.
2 líneas de defensa (que se superponen):
| Inmunidad innata | Inmunidad adaptativa | |
|---|---|---|
| Genética | línea germinal codificada | Reordenamientos genéticos implicados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el desarrollo de linfocitos |
| Respuesta inmune | No específica | Altamente específico |
| Tiempo de respuesta | Inmediato (minutos a horas) | Se desarrolla durante un período de tiempo más largo. |
| Respuesta de memoria | Sin respuesta de memoria | Con respuesta de memoria, que responde rápidamente al AL Amyloidosis reconocimiento del antígeno |
| Reconocimiento del patógeno | Los LOS Neisseria receptores de reconocimiento de patrones (PRR), como los LOS Neisseria TLR, reconocen patrones moleculares asociados a patógenos (PAMP). |
|
| Componentes |
|
|
Responder a los LOS Neisseria invasores microbianos es responsabilidad del sistema inmunitario. A menudo, el sistema inmunológico innato tiene la capacidad de contener los LOS Neisseria patógenos, pero los LOS Neisseria invasores han desarrollado medios para evadir la inmunidad innata. La siguiente línea de defensa es el sistema inmunológico adaptativo.
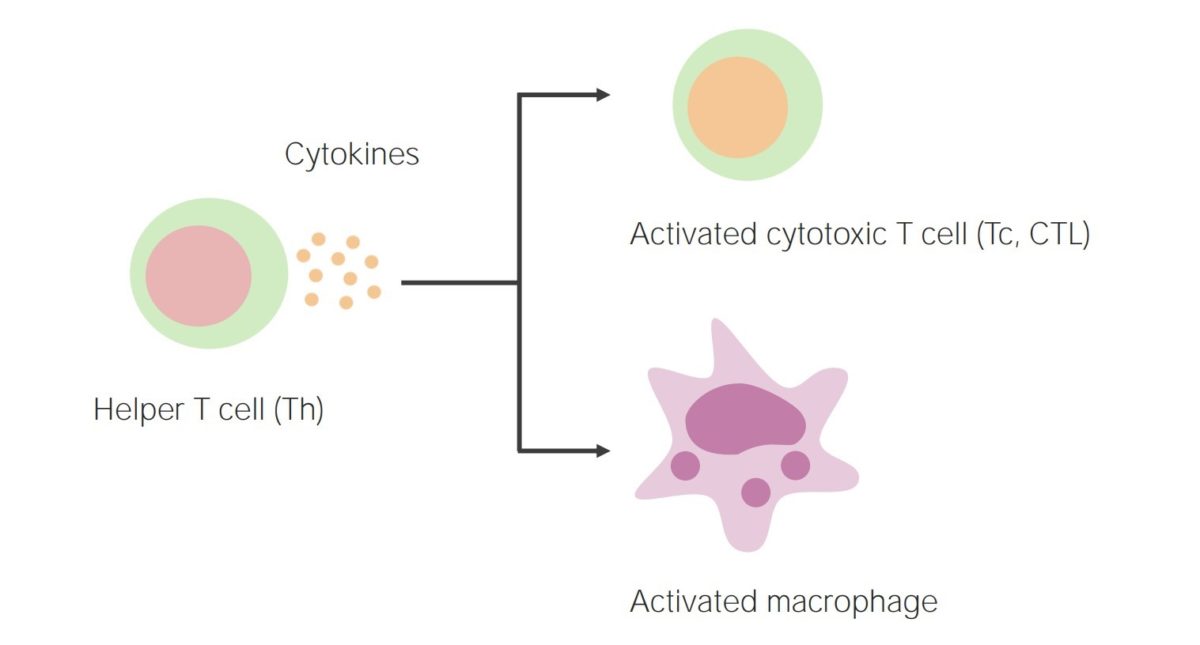
Inmunidad mediada por células:
La activación de los linfocitos T auxiliares da lugar a la liberación de citoquinas, activando así los linfocitos T citotóxicos y los fagocitos (como los macrófagos).
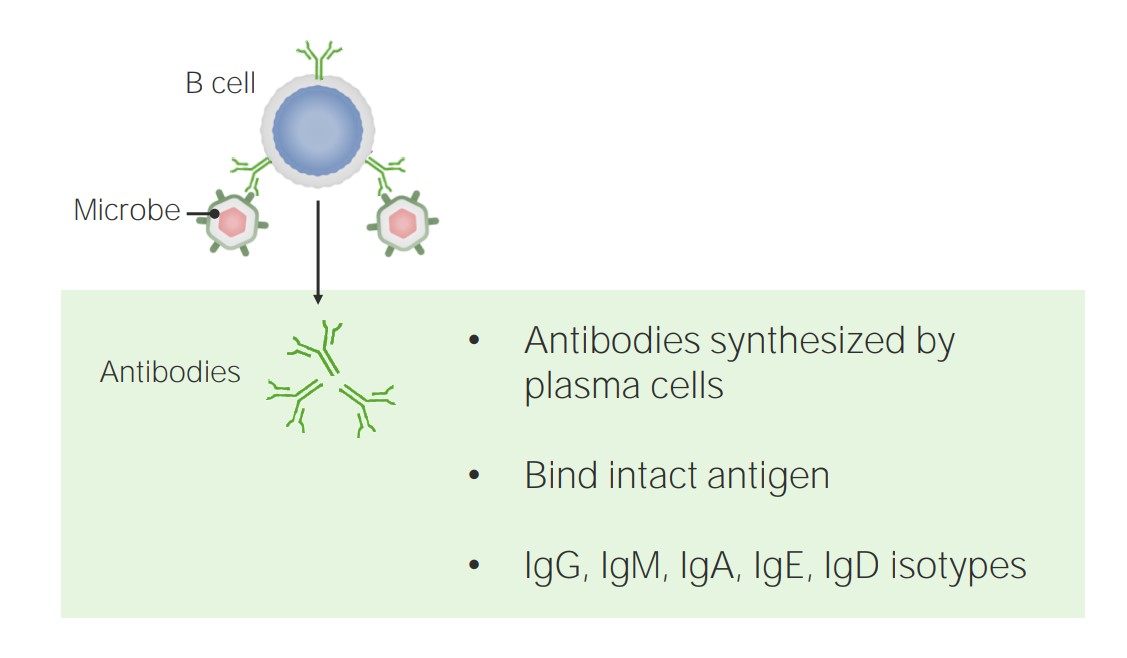
La inmunidad humoral está mediada por las células B y los anticuerpos.
Imagen por Lecturio.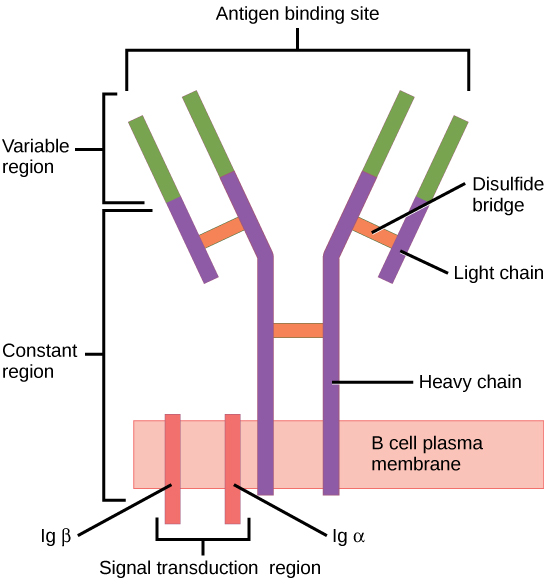
El receptor de células B (BCR) consiste en la molécula de Ig y la molécula de señalización:
Ig contiene 2 cadenas pesadas idénticas y 2 cadenas ligeras idénticas unidas por un puente disulfuro. La Ig unida a la membrana está anclada a la superficie celular.
Pasos necesarios para que la célula B funcione:
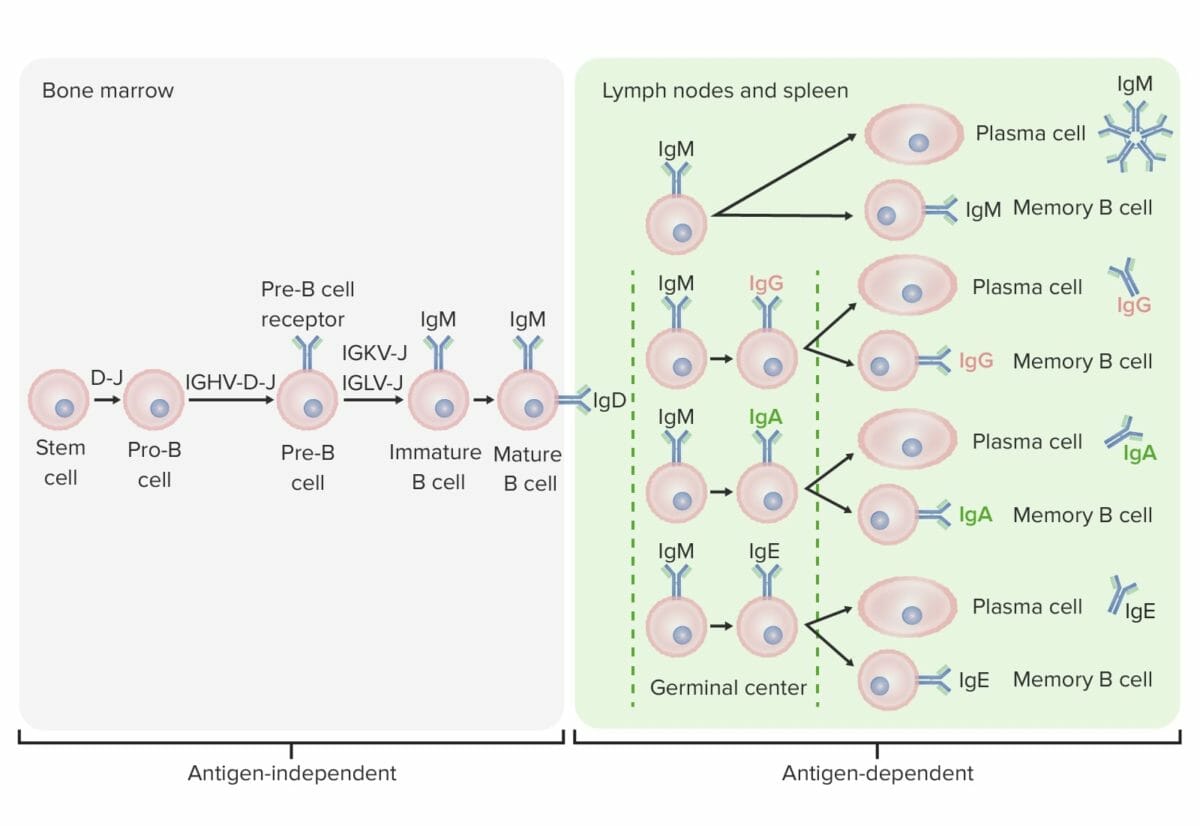
Etapas de diferenciación de la célula B:
En las etapas independientes del antígeno, la producción de células B comienza con la célula madre hematopoyética, que se convierte en un progenitor linfoide común, y luego en una célula pre-pro-B o en una célula progenitora B. Los siguientes pasos incluyen el reordenamiento de los genes para ensamblar la molécula de inmunoglobulina (Ig). Las cadenas pesadas de inmunoglobulina comienzan con el reordenamiento del segmento de diversidad y de unión para formar la célula pro-B. En el siguiente paso (célula pre-B), se completa la recombinación de la cadena pesada de Ig (variable, diversidad, unión) y se forma el receptor de la célula pre-B. Se produce un reordenamiento de la cadena ligera (kappa (κ) o lambda (λ)) que da lugar a la expresión de una molécula completa de anticuerpos IgM por parte de una célula B inmadura. A continuación se produce la formación de la célula B madura (virgen) con IgM e IgD.
Las etapas dependientes del antígeno tienen lugar en los tejidos linfoides secundarios. Una vez que la célula B madura produce IgM e IgD, puede producirse un cambio de clase para fabricar IgE, IgG e IgA. Las células B se activan y se convierten en células plasmáticas o células de memoria.
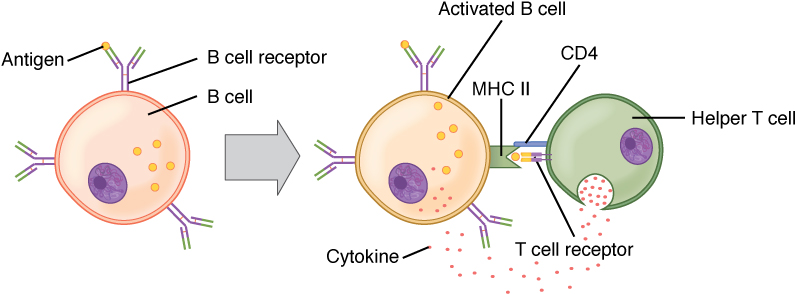
Activación de células B (dependiente de células T):
El antígeno circulante interactúa con el receptor de células B (BCR) de la célula B. El antígeno se somete a endocitosis y se degrada, y los componentes peptídicos forman complejos con las moléculas CMH II de la superficie celular. Las células T auxiliares foliculares (Tfh) (células auxiliares T CD4+ especializadas) reconocen y se unen al complejo antígeno-MHC II. Las células Tfh liberan citocinas, lo que lleva a la activación y proliferación de células B. Las células B activadas ingresan a los centros germinales, donde continúan el proceso, lo que lleva a la diferenciación.
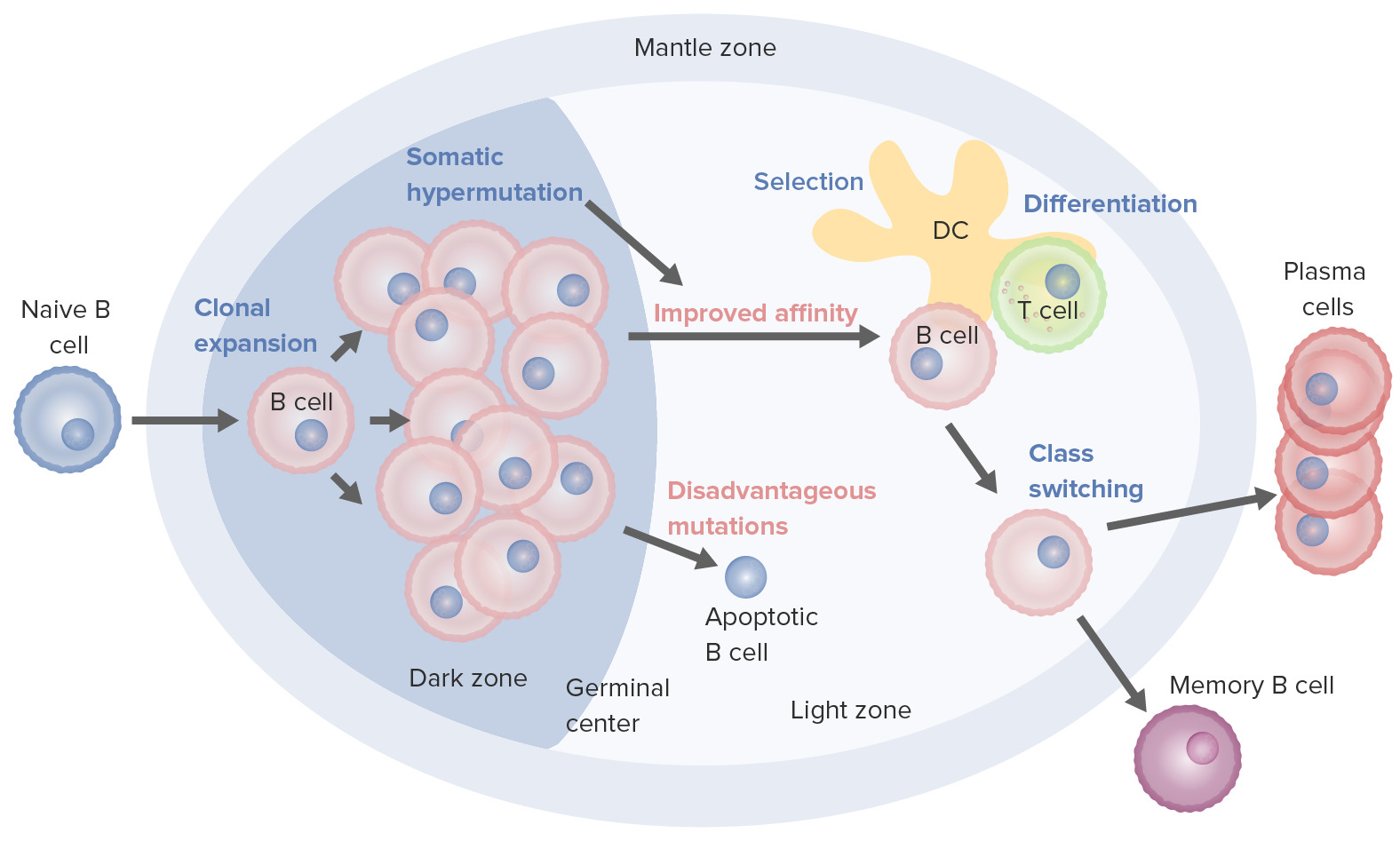
Procesos de activación y maduración de células B que tienen lugar en el centro germinal:
Al activarse, la célula B se mueve desde la zona del manto y entra al centro germinal. Tiene lugar la proliferación de células B (expansión clonal) y la afinidad del anticuerpo por el antígeno aumenta a través del proceso de hipermutación somática. Los ciclos repetidos de proliferación e hipermutación afinan el receptor de células B. Sin embargo, no todas las células B continúan diferenciándose, especialmente si la afinidad es débil. La apoptosis sigue si la unión antígeno-anticuerpo no está optimizada. Aquellos con fuerte afinidad sobreviven (selección) con la ayuda de señales de supervivencia de células dendríticas foliculares y células T. Estas células B seleccionadas pasan al cambio de clase y la diferenciación en células plasmáticas o células de memoria.
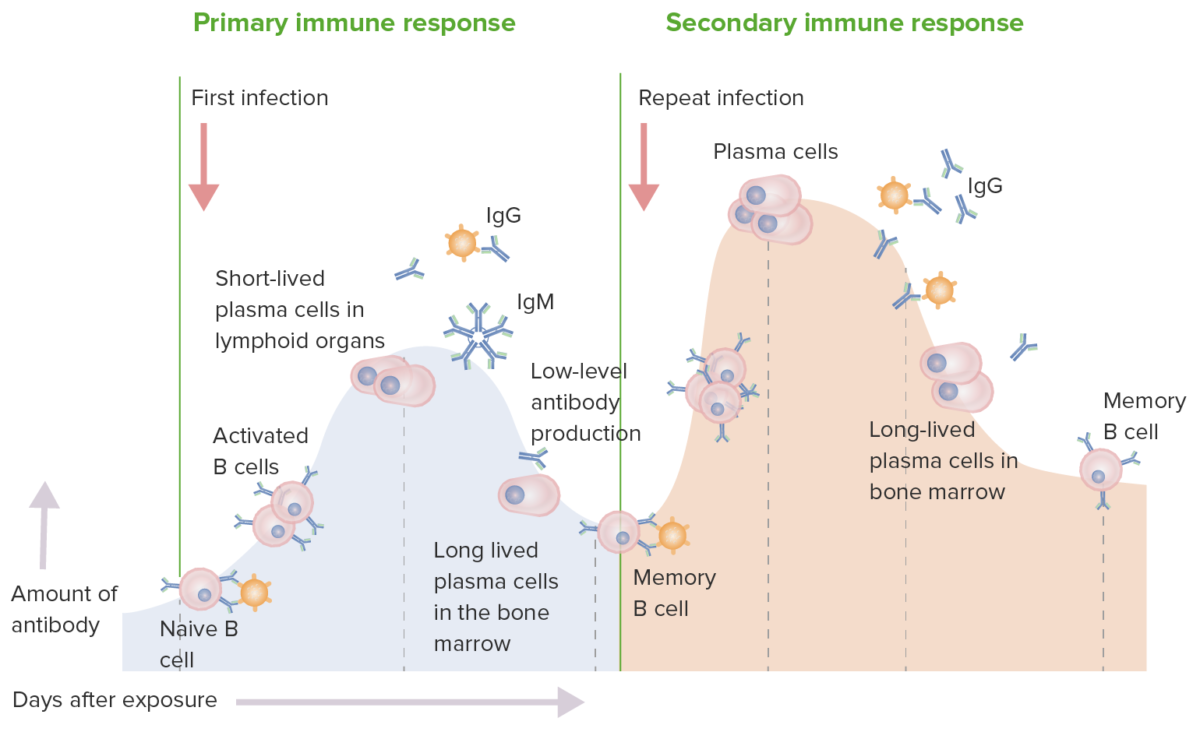
Respuesta inmune primaria y secundaria:
En una respuesta inmunitaria primaria, las células B vírgenes son estimuladas por el antígeno. Se produce la activación de las células B y luego la diferenciación en células secretoras de anticuerpos. Los anticuerpos son específicos para el antígeno desencadenante. La producción de IgM es seguida por IgG. Si bien hay una respuesta inmune, la producción es de bajo nivel. En la respuesta inmunitaria secundaria, el mismo antígeno estimula las células B de memoria, lo que conduce a la producción de mayores cantidades de anticuerpos específicos que se producen en la respuesta primaria. La producción y liberación de IgG también ocurren antes.
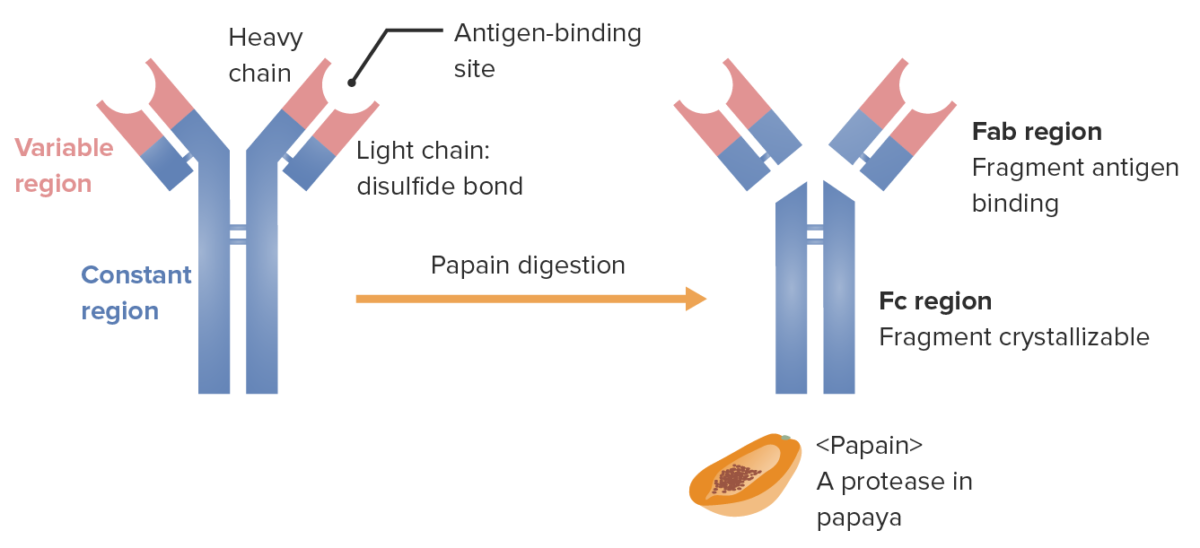
Fragmentos de la inmunoglobulina (determinados por el lugar donde la enzima papaína divide la Ig):
La región Fab (fragmento de unión a antígeno) contiene las regiones variables (roja) y partes de la región constante (azul) de las cadenas pesada y ligera. La región Fc (fragmento cristalizable) contiene la parte restante (cola) del anticuerpo (región constante de la cadena pesada únicamente).
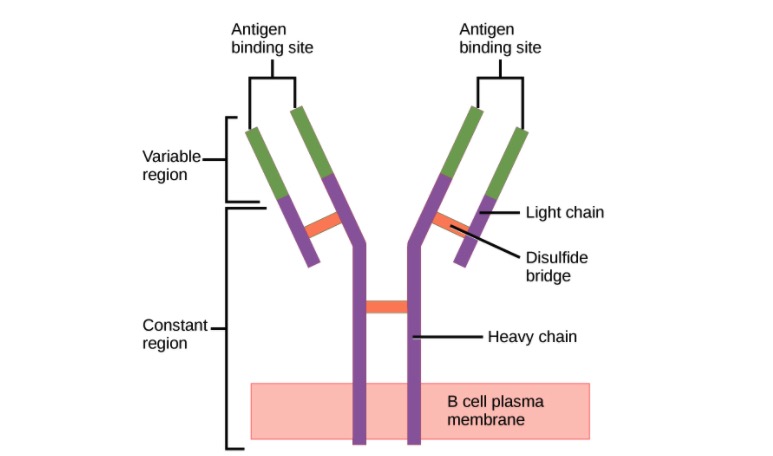
Estructura del anticuerpo (regiones):
Un anticuerpo tiene una región variable única (formada por cadenas pesadas y ligeras) capaz de unirse a un antígeno diferente y una región constante (formada por cadenas pesadas).
Protección contra agentes infecciosos y sus productos mediante:
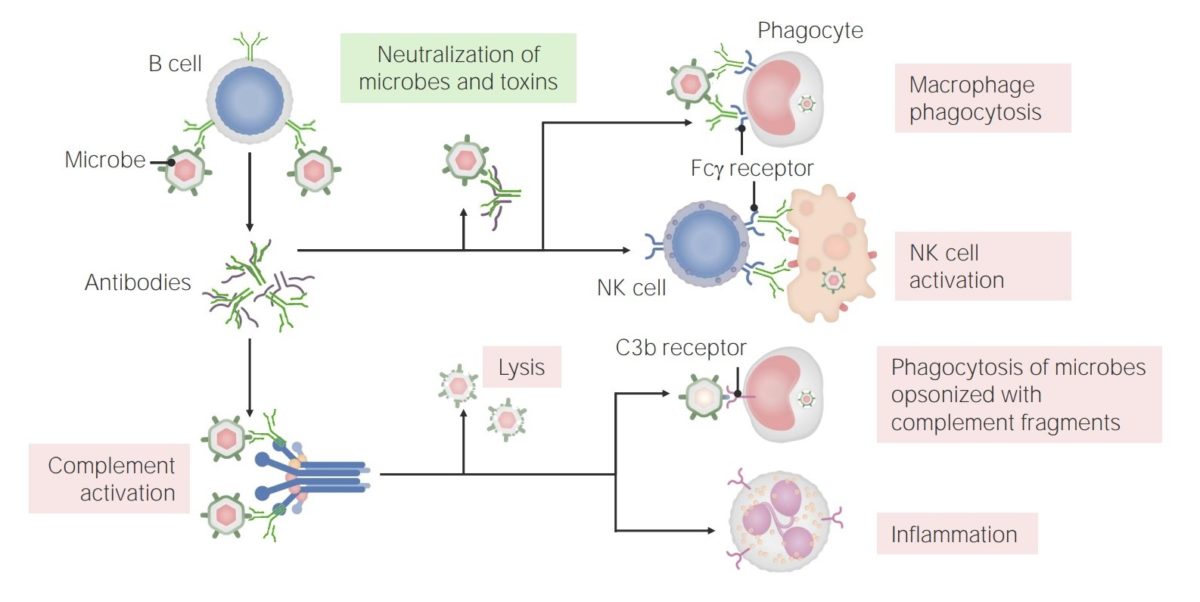
Las funciones de los anticuerpos:
Los anticuerpos tienen múltiples funciones en la inmunidad, incluyendo la neutralización (de microbios y toxinas), la promoción de la fagocitosis y la activación de las células NK. Además, los anticuerpos tienen un papel en la activación del complemento, que puede conducir a la lisis directa de los microbios, la opsonización y la fagocitosis, y el reclutamiento/activación de los neutrófilos.