Una hernia Hernia Protrusion of tissue, structure, or part of an organ through the bone, muscular tissue, or the membrane by which it is normally contained. Hernia may involve tissues such as the abdominal wall or the respiratory diaphragm. Hernias may be internal, external, congenital, or acquired. Abdominal Hernias abdominal es una protrusión anormal del contenido abdominal a través de un defecto o debilidad de la pared abdominal, y puede ser congénita o adquirida. Existen múltiples tipos de hernias en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de la localización anatómica y la fisiopatología subyacente. Las hernias más comunes encontradas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la práctica quirúrgica incluyen las hernias ventrales, inguinales y femorales. Las hernias se diagnostican más comúnmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el examen físico (protuberancia o abultamiento anormal), pero los LOS Neisseria estudios de imagen a veces pueden ser útiles para un diagnóstico definitivo. El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la reparación quirúrgica. La decisión de operar se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria síntomas de los LOS Neisseria pacientes, su deseo de reparación quirúrgica y los LOS Neisseria riesgos de encarcelamiento y estrangulamiento. Las opciones quirúrgicas incluyen enfoques abiertos y laparoscópicos, con o sin la colocación de una malla protésica.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Una hernia Hernia Protrusion of tissue, structure, or part of an organ through the bone, muscular tissue, or the membrane by which it is normally contained. Hernia may involve tissues such as the abdominal wall or the respiratory diaphragm. Hernias may be internal, external, congenital, or acquired. Abdominal Hernias es una protrusión anormal del contenido abdominal a través de un defecto o debilidad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la pared del abdomen. Las hernias pueden ser congénitas o adquiridas.
Se pueden definir varios tipos de hernias de la pared abdominal por su localización anatómica:
Las hernias ventrales se producen por una debilidad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la pared abdominal anterior y pueden ser congénitas o adquiridas.
Las capas de la pared abdominal incluyen:
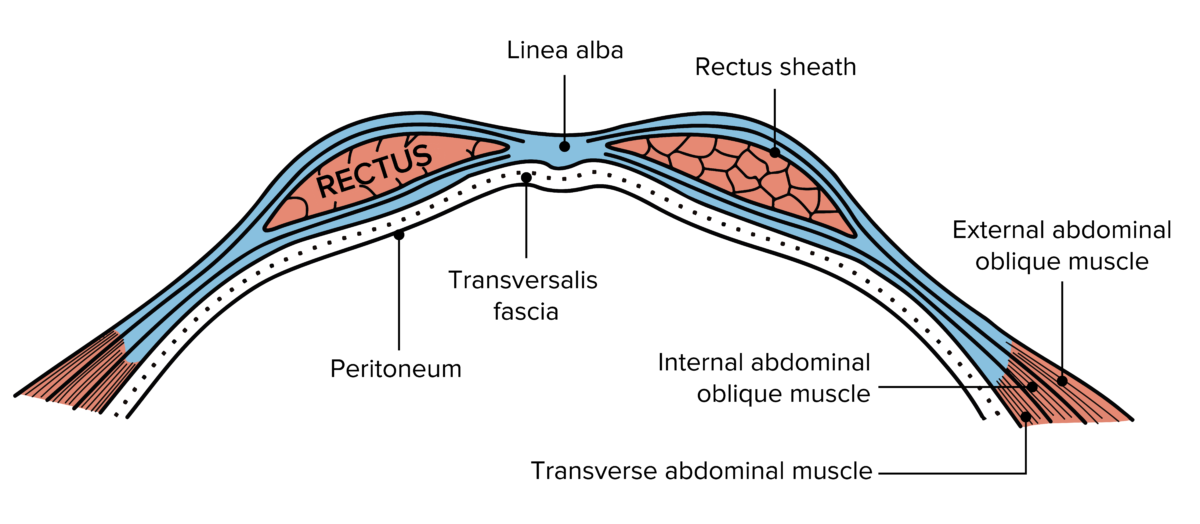
Capas de la pared abdominal
Imagen: “Gray399” por Henry Gray. Licencia: Dominio Público, editado por Lecturio.Hernias epigástricas:
Umbilical:
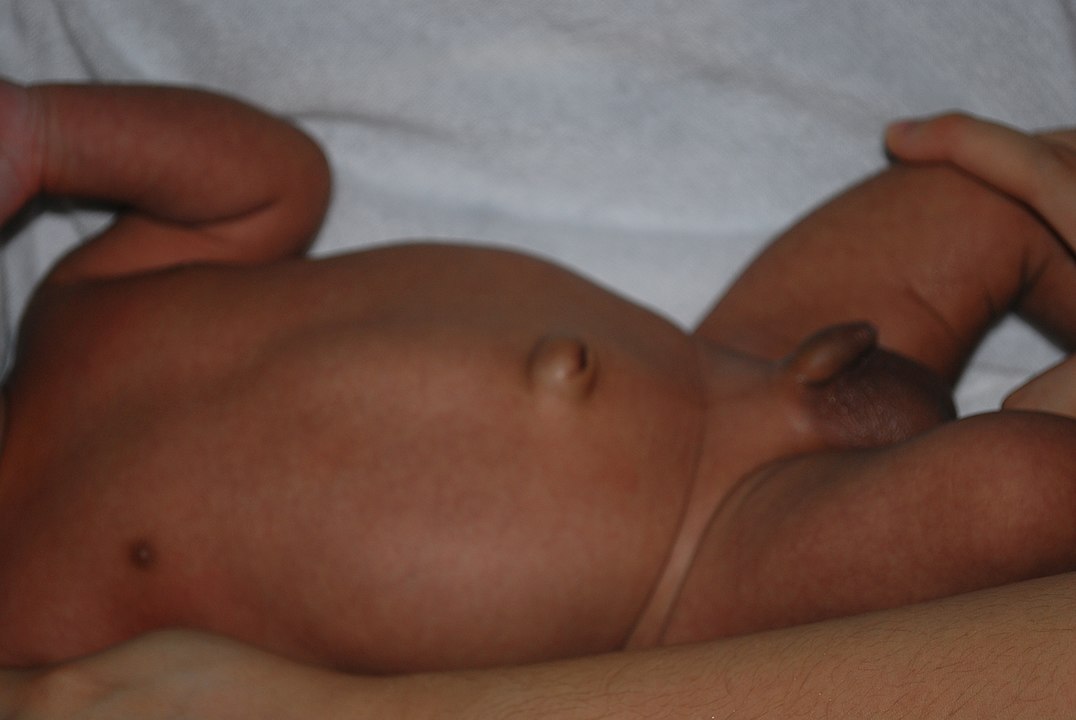
Hernia umbilical en un niño
Imagen: “Umbilical Hernia”, por Jpogi (talk). Licencia: Dominio PúblicoHernias incisionales:
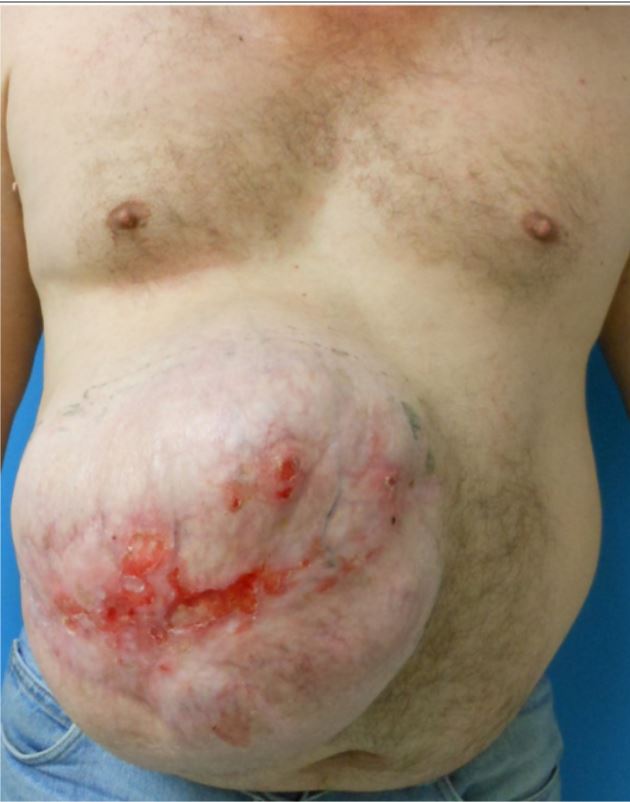
Vista anterior preoperatoria de una gran hernia incisional en el hipocondrio derecho con áreas focales de ulceración cutánea
Imagen: “Repair of giant subcostal hernia using porcine acellular dermal matrix (Strattice™) with boneHernias de Spigel:
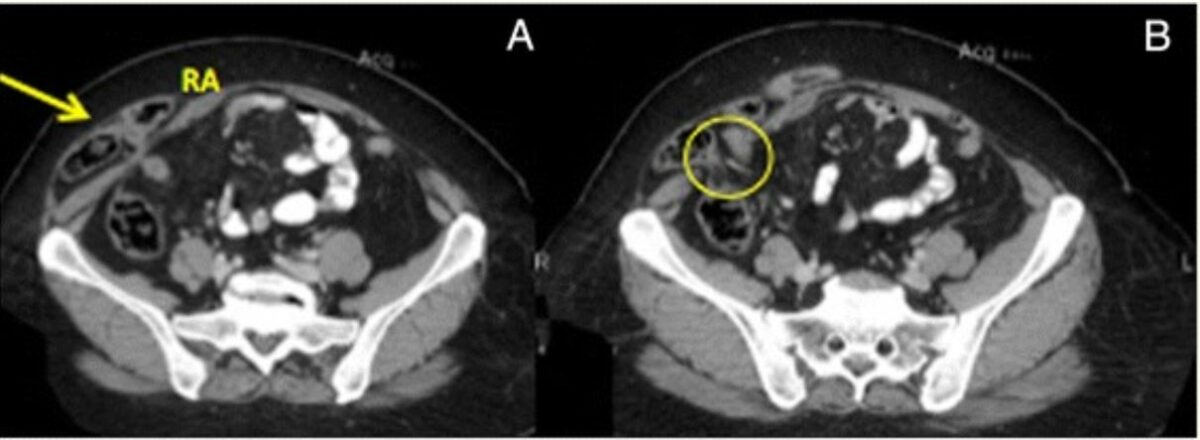
Tomografía computarizada (TC) de hernia espigeliana derecha:
A: Saco herniario (flecha) que contiene el asa del intestino delgado (RA: recto abdominal derecho)
B: Defecto de la pared abdominal (círculo)
Hernias paraestomales:
Indicaciones:
Reparación primaria:
Reparación con malla:
Complicaciones:
Las hernias inguinales se producen a través del suelo o del anillo interno del canal inguinal.

Diagrama esquemático que muestra la diferencia de localización entre las hernias inguinales directas, las inguinales indirectas y las femorales:
Las hernias indirectas se producen a través del anillo inguinal interno. Las hernias directas se producen a través del anillo inguinal externo, medialmente a los vasos epigástricos. Las hernias femorales se producen a través del triángulo femoral, por debajo del ligamento inguinal (de Poupart).
| Límite | Nivel del anillo profundo | Medio | Nivel del anillo superficial |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pared anterior | Oblicuo interno Oblicuo externo | Aponeurosis oblicua externa | Aponeurosis oblicua externa (crura) |
| Pared posterior | Fascia Fascia Layers of connective tissue of variable thickness. The superficial fascia is found immediately below the skin; the deep fascia invests muscles, nerves, and other organs. Cellulitis transversal | Fascia Fascia Layers of connective tissue of variable thickness. The superficial fascia is found immediately below the skin; the deep fascia invests muscles, nerves, and other organs. Cellulitis transversal | Tendón conjunto |
| Techo | Fascia Fascia Layers of connective tissue of variable thickness. The superficial fascia is found immediately below the skin; the deep fascia invests muscles, nerves, and other organs. Cellulitis transversal | Fibras arqueadas del oblicuo interno y transverso del abdomen | Cruz medial del oblicuo externo |
| Piso | Ligamento inguinal | Ligamento inguinal | Ligamento lacunar |
Indicaciones:
Técnica abierta:
Técnica laparoscópica:
Complicaciones:
Las hernias femorales son hernias que se producen a través del triángulo femoral (por debajo del ligamento inguinal).